Author: Peng SUN, Foresight News
2023, belongs to Ethereum?
Since the completion of the Shanghai upgrade in April, the Ethereum ecosystem has been waiting for the Cancun upgrade (Dencun, Cancun/Deneb) for the past half year, until recently when the Ethereum core developers planned to conduct the Cancun upgrade on the Goerli test network on January 17, 2024.
Despite the grandeur of various conferences such as ETHDenver, ETHParis, and ETHDevconnct, the voice of the entire Ethereum and Layer2 seems pale and powerless in the face of the fair launch of Bitcoin inscriptions and the warming of non-EVM public chain ecosystems.
However, in those light days, has Layer2 made no progress? Not at all. They are not content to sit on the sidelines and insist on decentralizing all aspects of the ecosystem. Foresight News has also noticed that in the past year, mainstream Layer2 solutions such as OP Mainnet, Arbitrum, zkSync Era, Starknet, and Polygon zkEVM have been actively developing their customized Layer2 and Layer3 solutions, attempting to further address transaction costs and scalability issues through modularization. In this field, OP Mainnet has taken more initiative due to its first-mover advantage and institutional ecosystem. Meanwhile, mainnets such as zkSync Era, Scroll, Polygon zkEVM, Base, opBNB, and Linea have successively gone live, leaving users with plenty of imagination regarding their technical advantages, airdrop expectations, and ecosystem applications. In addition, Base, Blast, and ZKFair have adopted aggressive strategies and won many markets in the second half of the year.
As 2023 draws to a close, the hidden currents of the Layer2 battle are surging. Based on this, the author will provide a brief overview of the progress of mainstream Layer2 and some potential Layer2 solutions over the past year, to delight the readers.
Mainstream Layer2
OP Mainnet
Currently, the total value locked (TVL) on the Optimism network is $6.45 billion. Recently, OP broke through $3.8, reaching a historic high.
(1)Network Upgrades and Hard Forks: Regolith, Bedrock, and Canyon
For Optimism, the most important progress in 2023 was the completion of the Bedrock upgrade.
On March 18, according to the Optimism Collective: Bedrock proposal v2, Optimism activated the Regolith hard fork on the Goerli test network, and completed the Bedrock hard fork upgrade in June. The Regolith hard fork is mainly used for the deposit system transactions required by L2. The Bedrock upgrade is the first official version of the OP Stack. This upgrade launched the Bedrock sequencer, with key improvements including further reduction of transaction fees, 70% reduction in deposit time, improved modularization of proofs, and improved node performance.
In November, Optimism also activated the "Canyon" hard fork on the Superchain test network. This upgrade is Optimism's first network upgrade after Bedrock, and was implemented in collaboration with Base.
(2)OP Stack and Superchain
To address the scalability issue of blockchain, Optimism's answer is the modular component OP Stack. OP Stack is similar to Cosmos, which focuses on launching new Layer1, while OP Stack focuses on launching new Layer2. This component allows the assembly to build custom chains "op-chains" to serve any specific blockchain use case. According to Optimism's vision, through shared sorting and messaging layers, the boundaries between future "op-chains" will disappear, integrating L2 into a single operable and composable system superchain, thus solving the fragmentation and interoperability issues of L2.
Currently, Optimism has launched the "Superchain Token List" feature to simplify the cross-chain process of tokens between Ethereum and various OP chains, and to simplify token discovery and management. At the same time, Optimism has also introduced the "Law of Chains" to provide an open and neutral framework for participants in the OP Stack superchain ecosystem, promoting core principles of user protection, decentralization, and economic autonomy. Version 0.1 of Law of Chains has been opened for community feedback, and Optimism plans to formally introduce it into Optimism governance and the initial governance process for new chains joining the superchain ecosystem.
In addition, Optimism is also developing the "fault-proof system" of OP Stack, including components such as Fault-Proof Program (FPP), Fault-Proof Virtual Machine (FPVM), and Dispute Game. The separation of FPP and FPVM allows the same operation program to run in both FPVM and ZKVM, helping OP Stack ZKP to achieve ZK-based validity proofs and provide support for low-latency cross-chain bridges between different networks.
This month, OP Labs further discussed the decentralization roadmap of the Optimism ecosystem, stating that the ultimate goal is to reach the second stage as soon as possible, where no organization can change the status root of the code. At the same time, the Security Council plans to become independent of the Optimism Foundation in 2024.
After the launch of OP Stack, many institutions or projects have launched OP chains in 2023, including Coinbase's Base, Opclave, opBNB, ZORA Network, Public Goods Network, Mode, DeBank Chain, Ancient8 Chain, Redstone of Lattice, and Lyra V2, among others. Cryptocurrency infrastructure startup Conduit, led by Paradigm, public chain Celo, and blockchain infrastructure company Espresso Systems also intend to launch OP Stack chains.
OP Stack clients:
- a16z Crypto launched the Rollup client "Magi" based on OP Stack, replacing the consensus client in OP Stack, and working with execution clients (such as op-geth) for synchronization;
- Test in Prod joined the core development team of Optimism Collective and developed an alternative execution client op-erigon using modular and open-source OP Stack;
- Paradigm, OP Labs, and Base collaborated to develop the high-performance client OP Reth for OP Stack, allowing Ethereum node Reth to be used in OP Stack without modification.
(3)Retroactive Public Goods Funding (RetroPGF)
Retroactive Public Goods Funding (RetroPGF) originally originated in 2021 to provide sustainable funding for public goods. In 2023, Optimism re-launched RetroPGF and completed the second round of Retroactive Public Goods Funding (RetroPGF 2) in March, distributing 10 million OP tokens to 195 individuals and projects including L2BEAT and ETHGlobal.
Voting for the third round of Retroactive Public Goods Funding (RetroPGF 3) ended on December 7, distributing 30 million OP tokens to 643 contributors in the ecosystem (including influential developers, artists, creators, and educators). The results and token distribution will be announced in early January 2024.
Arbitrum
Arbitrum is currently the largest Ethereum Layer2 network in terms of TVL, with a current TVL of $91.3 billion, accounting for 44.97% of the total TVL of the Ethereum Layer2 network, according to Dune data. The total number of transactions on the Arbitrum chain has exceeded 460 million, with over 12 million created accounts and over 4 million on-chain contracts.
(1)ARB Airdrop and Foundation Controversy
In March, the ARB airdrop was one of the major events of 2023, with over 1 billion ARB tokens being claimed by over 580,000 addresses, earning high praise from the community.
However, shortly thereafter, there was controversy in the Arbitrum community regarding "AIP-1: Arbitrum Improvement Proposal Framework." The Arbitrum Foundation's unauthorized sale of 10 million ARB tokens before the community vote raised concerns about the excessive centralization of Arbitrum.
(2)Arbitrum Orbit and Arbitrum Stylus
While Optimism built OP Stack, Arbitrum introduced the Layer3 scalability solution, Arbitrum Orbit, in March 2023.
The difference between OP Stack and Arbitrum Orbit is that OP chains (L2) are independent networks that share security, while Arbitrum Orbit chains (L3) are built on top of Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova, Arbitrum Sepolia, and Arbitrum Goerli, allowing developers to launch their own Layer3 blockchains without permission, sharing Ethereum security.
Arbitrum Orbit uses Rust, C, and C++ to write smart contracts while maintaining full EVM compatibility, saving over 10 times the gas cost in complex cryptography. In the future, Orbit chains can adopt any improvements made to the Arbitrum Nitro technology stack, including permissionless verification, MEV capture, and further cost reduction, without DAO approval. Additionally, Orbit chains are driven by Arbitrum Nitro node software and can communicate with each other.
In October, Arbitrum announced that Arbitrum Orbit is ready for mainnet launch, and development tools and quick start guides for Arbitrum Orbit have been released. Currently, Ethereum scaling project AltLayer's RaaS solution, decentralized derivatives exchange Syndr, cryptocurrency infrastructure startup Conduit, modular blockchain Celestia, Layer2 network Kinto, TreasureDAO, Horizen Labs (Apechain), and NEAR have expressed support for Arbitrum Orbit or plan to launch Orbit chains.
It is worth noting that the Arbitrum Orbit L3 chain will also support Stylus. Stylus is the next-generation programming environment launched by Offchain Labs for Arbitrum One and Arbitrum Nova this year, and it is an upgraded version of Arbitrum Nitro. It aims to solve the problem of developers, as the Ethereum ecosystem language is mainly Solidity, which has many issues and a limited number of developers. Rust, C, and C++ developers are more numerous, so attracting more developers to build DApps in the ecosystem is Arbitrum's choice.
Stylus allows users to deploy DApps on Arbitrum using languages other than Solidity, such as Rust, C, and C++, through WebAssembly smart contract functionality. Stylus is an order of magnitude faster, reduces costs, and is fully interoperable with EVM. Currently, Stylus supports developers using the C language to write smart contracts, but it is still in the alpha stage. Since September, cryptocurrency infrastructure startup Conduit and Rollup as a Service (RaaS) project Caldera have expressed support for Arbitrum Stylus.
(3)Community, Ecosystem, and Governance
- 50 million ARB Short-Term Incentive Plan
In October, the Arbitrum community voted to approve the 50 million ARB short-term incentive plan, with 29 projects including Camelot, Jones, Dopex, GMX, Galxe, LODESTAR, Socket, Timeswap, RADIANT, Pendle, MUX, Frax, Tally, Rysk, Silo, Stella, Good, Gamma, Umami, Abracadabra, KyberSwap, OpenOcean, Angle, Trader, Dolomite, Premia, Vertex, Perennial, and Balancer being selected.
*Foresight News note: The original proposal suggested distributing 75 million ARB to active ecosystem protocols, but the community vote decided to distribute 50 million ARB.
In addition to the 29 selected projects, there are 26 projects that were selected but missed the first round of funding, as they did not receive funding due to the initial 50 million token budget of the short-term incentive plan. As a result, the Arbitrum community voted in December to increase the total budget for the STIP incentive by 21.4 million tokens and increase the number of participating protocols by 26. The 26 projects that received this funding include Gains Network (4.5 million ARB), Stargate Finance (2 million), Synapse (2 million), PancakeSwap (2 million), Wormhole (1.8 million), Magpie (1.25 million), RabbitHole (1 million), dForce (1 million), Vela (1 million), and others.
- Arbitrum Security Council
In September, the Arbitrum team implemented on-chain voting based on the smart contract system for the first time to elect members of the Arbitrum Security Council.
In October, the Arbitrum Security Council election vote decided that Patrick McCorry (Arbitrum Foundation), 0xhombre (PlutusDAO Tech Lead), John Morrow (Gauntlet Co-founder), Omer (Chaos Labs CEO), Harry Kalodner (Offchain Labs), and Matt Fiebach (Blockworks Research Analyst) would join the council, and the Safe multisig was updated to include the addresses of the 6 elected security council members.
- Restart of Odyssey
In September, Arbitrum collaborated with Galxe to relaunch the 7-week Odyssey event.
(4)Network Upgrades and Hard Forks
Currently, the Arbitrum community is conducting on-chain voting for the "ArbOS 11 version" AIP proposal, which will end on January 8, 2024.
The proposal introduces multiple improvements to Arbitrum, including support for the EVM Shanghai upgrade and the PUSH0 opcode, as well as various bug fixes. These improvements have been audited and are available for adoption by chains such as Arbitrum Orbit, Arbitrum One, and Arbitrum Nova, which are involved in the proposal. The proposal states that the ArbOS upgrade can be considered as a hard fork for Arbitrum.
zkSync Era
As a leader in ZK Rollup, zkSync also made significant progress in 2023.
(1)zkSync Era Mainnet Launch
In February of this year, zkSync announced that zkSync 2.0 was renamed zkSync Era∎, and zkSync 1.0 was renamed zkSync Lite.
In March, zkSync Era mainnet was publicly released. At the same time, zkSync published its decentralized vision, stating that sequencers, ZK provers, zkPorters, community governance, and all other key parts of the zkSync Era network will be decentralized after the core virtual machine and provers are consolidated and stabilized.
It is worth noting that Matter Labs CEO Alex Gluchowski stated that once they want to decentralize the sequencers, tokens will be needed, and the sequencers will be decentralized in about a year. In terms of time, zkSync is expected to launch its token in the first quarter of 2024, as the sequencers are expected to be decentralized around March 2024. In July of this year, zkSync Era also introduced a new STARK-based proof system called Boojum, complementing the zkSync Era sequencers. Boojum provers only require 16GB of RAM and can achieve future decentralization of provers on a large scale.
Recently, the TVL of the zkSync Era network is $597 million. According to OKLink browser data, the number of addresses on the zkSync chain exceeds 6.4 million, and the total transaction volume is 25.07 million ETH.
(2)ZK Stack - Hyperchain
Similar to Optimism's OP Stack and Arbitrum's Arbitrum Orbit, Matter Labs released the ZK Stack for developing "Hyperchain" in June of this year. Developers of Hyperchain can choose to create a Layer2 network running parallel to zkSync Era or a Layer3 network running on top of it, with zkSync Era being considered the first Hyperchain. Cross-chain transactions can be conducted between chains through Hyperbridges.
Currently, Klaytn, Ankr, GRVT, and Cronos Labs have all partnered with Matter Labs and will launch their own Hyperchains.
In terms of mainnet upgrades, zkSync initiated a mainnet upgrade plan on September 7th for block number, timestamp, and hash value. After the upgrade, block.number, block.timestamp, and blockhash will respectively return the block number, timestamp, and hash value of L2 blocks.
(3)Ecosystem and Decentralized Community Progress
In June of this year, Matter Labs allocated $1 million for a16z crypto's "Crypto Startup School" accelerator program, which will be directly used by teams using zkSync Era. In September, zkSync launched a paid online program for 4 to 6 months, aimed at advancing the development of zkSync, ZK Stack, and ZK Credo through individual and team technical contributions. Successful applicants will receive a monthly grant of $3,500 during the Fellowship period for developing their personal products.
In September, the NFT marketplace and creator platform Blockframe joined the core development team of zkSync Era on the NFT market. They are involved in building new primitives that other developers can use, ultimately leading to the permissionless construction and community ownership of the ZK Stack.
In October, zkSync Era officially open-sourced two key components, "Block Explorer" and "Portal (Bridge)," and entrusted them to the core contributor community. The role of Matter Labs in the technical development and ecosystem management of zkSync will gradually decrease. Community users can now run zkSync Portal and seamlessly bridge tokens on their own, while the main interface for exploring transactions, blocks, and contracts, "Block Explorer," is now fully open-source and supports local operation.
Starknet
The TVL of the Starknet network is currently $143 million. According to Nethermind Starknet data, the number of active accounts on Starknet has exceeded 69,000, the block creation time has been reduced from 2000 seconds to 97.09 seconds, and the total funds transferred through StarkGate cross-chain have increased from less than $6,000 to $109 million. As of October 1st of this year, there are 166 full-time developers.
(1)STRK Token
As one of the leading projects for Layer2 scaling using ZK Rollup, the issuance and airdrop of STRK tokens can be considered a major event for Starknet in 2023.
The total supply of STRK is 10 billion tokens, and the initial unlocking date has been postponed from November 29, 2023, to April 15, 2024.
Currently, the eligibility and quantity criteria for the STRK airdrop have been determined, and the Starknet Foundation will allocate over 1.8 billion STRK tokens:
- Approximately 9 billion STRK tokens have been allocated to the Foundation Supply Committee for rewarding users and community members for past and future contributions.
- 9 billion tokens have been specifically allocated for user rebates to refund their transaction fees on the network.
- 50 million STRK tokens have been allocated for DeFi on-chain incentives.
- Through the "Devonomics" program, a portion of network fees will be allocated to developers. The initial allocation covers all transaction fees accumulated from project inception to November 30, 2023, and is distributed in ETH, totaling approximately 1,600 ETH (over $3.5 million). In the future, the allocation will switch to using the Starknet token STRK after the upgrade to version 0.13. The Devonomics allocation will be automatically executed based on the level of fees generated by each dApp through an algorithm.
(2)Cairo 1.0 and Mainnet Upgrade
As early as the beginning of January this year, StarkWare launched the first public version of Cairo 1.0. Cairo is a Turing-complete programming language that was first introduced in 2020 for efficiently writing STARK-provable programs. One of the most important changes in Cairo 1.0 is the syntax, which allows for writing more secure code. Cairo 1.0 also introduces Sierra, a new intermediate representation that ensures proof generation for every Cairo run.
In March, when Starknet Alpha v0.11.0 went live on the mainnet, Cairo 1.0 was first launched, with significant improvements including a 5x reduction in computational costs. In June, Starknet was upgraded to v0.11.2, officially activating Cairo 1, allowing developers to deploy Cairo 1 smart contracts on the mainnet.
Later in April, Starknet's 2023 goals and roadmap will focus on improving network performance and UX, including improving network efficiency, reducing transaction costs, and implementing a fee market.
According to this plan, the Starknet mainnet v0.12 Quantum Leap was launched on the testnet and mainnet in July, with Quantum Leap focusing on addressing throughput and latency issues. In August, Starknet launched the second part of Quantum Leap, version v0.12.1, which includes changes such as memory pool validation, including failed transactions, and built-in Keccak. This upgrade focuses on optimizing transaction efficiency. On September 5th, Starknet completed the upgrade to Starknet v0.12.2, further increasing maximum throughput and TPS.
At the same time, the entire core stack of Starknet, including Full Node, Execution Engine, Sequencer, and Prover, including StoneProver, has been open-sourced. The open-source core stack is an important step towards the decentralization of Starknet.
In the October decentralized roadmap for Starknet, the goal is to transition the operations of sequencers and provers to a decentralized proof-of-stake protocol, including two paths: implementing various components required to run a decentralized protocol and gradually transitioning operational power to Starknet stakers. The transition of operational power to Starknet stakers includes four paths: transitioning to a decentralized network architecture while keeping sequencer operations centralized, ensuring the availability of a fully open-source software stack, developing increasingly widespread testing and integration networks, and attracting stakers to join before the sequencers ultimately transition to proof of stake.
Based on this, Starknet completed the mainnet upgrade to v0.12.3 on December 21st. The Starknet Feeder centralized gateway has stopped serving various types of queries and will only retain endpoints related to synchronization for full nodes, serving as a gateway for querying the centralized sequencer status of Starknet. Previously, in August, full nodes supporting the JSON RPC protocol for Starknet had matured, and Starknet had recommended developers to switch to three full nodes: Pathfinder, Juno, and Papyrus, with the current Feeder gateway being a temporary solution.
In addition, recent reports indicate that the Starknet mainnet v0.13 update will take place on January 10, 2024, at which time Starknet will support STRK token payments for Gas, which is already available on the testnet. Starknet also plans to improve the fee market in the first quarter of 2024 and deploy a hybrid on-chain and off-chain data solution called Volition in the second quarter of 2024.
Starknet Appchains
While Optimism, Arbitrum, and zkSync Era are all working on customizing Layer2 and Layer3 blockchains, Starknet is also making progress.
In July 2023, Starknet announced at the EthCC conference in Paris that it will launch its own Layer3 - Starknet Appchains. Starknet Appchains can be launched by applications using the Starknet stack and can configure network block sizes, latency, data availability modes, transaction fees, consensus mechanisms, etc., based on specific app configurations. They have the characteristics of customizability, decentralization, rapid iteration, independent governance, cost efficiency, congestion avoidance, and enhanced privacy.
Developers can also build Layer3 on Starknet and even build Layer4 and other layers on top of Layer3, as shown in the diagram below.
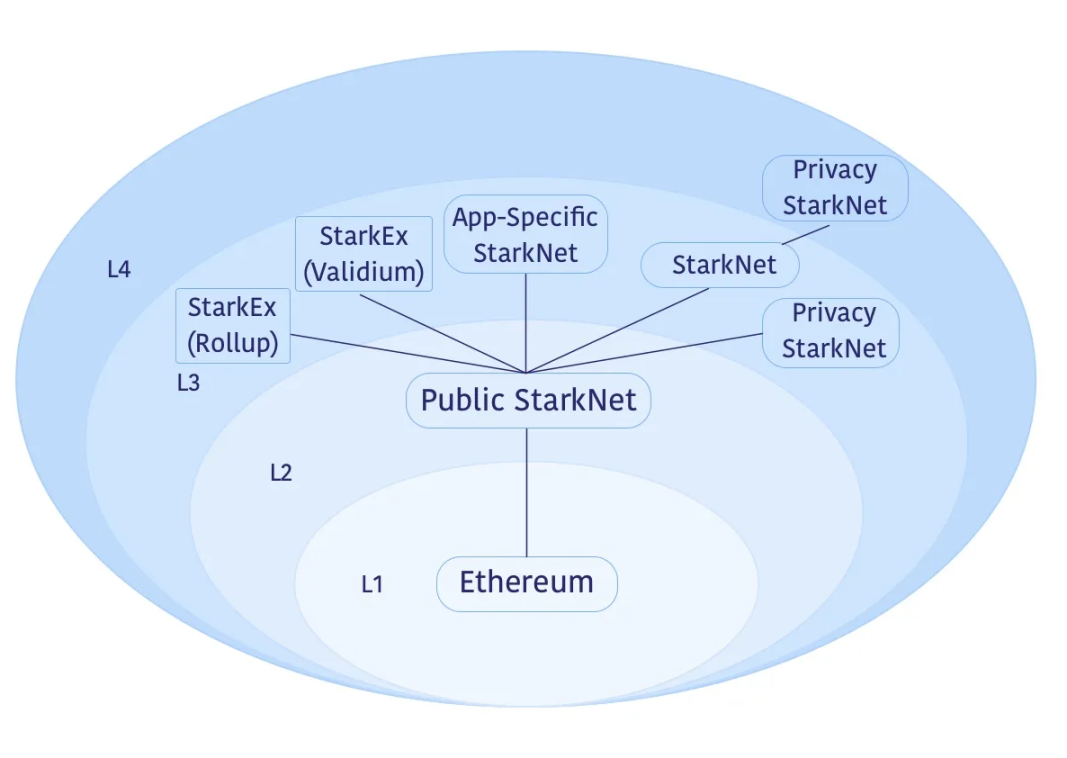
Currently, the cryptocurrency institutional liquidity platform Paradigm has incubated an application chain called "Paradex" on Starknet. Paradex is a hybrid derivatives exchange that combines Paradigm's liquidity with DeFi transparency and self-custody. It will operate its own chain based on the Starknet developer stack and is the result of a six-month collaboration between StarkWare and Paradigm.
In addition, the dedicated sequencer on Starknet Layer3 is Madara, which can execute transactions and package them, and can also enhance Starknet's interoperability and on-chain privacy level.
Scroll
Scroll has been a darling of the Ethereum ecosystem since its mainnet launch, and the Scroll network TVL is currently $53.89 million.
(1)$50 Million Fundraising
In March of this year, Scroll completed a $50 million fundraising round, with investors including Polychain Capital, Sequoia China, Bain Capital Crypto, Moore Capital Management, Variant Fund, Newman Capital, IOSG Ventures, Matrix Partners, and OKX Ventures, among others. This round of fundraising valued the company at $1.8 billion.
(2)Mainnet Launch
In August, Scroll announced the launch of the Scroll Beta testnet on the Sepolia testnet for developers and users. New features or improvements include zkEVM upgrades, bridge upgrades, and infrastructure upgrades.
On October 10th at 14:00, the Genesis Block of the Scroll mainnet was created. A week later, on October 17th, Scroll officially announced the launch of the mainnet. The Scroll mainnet will first be populated by infrastructure providers, followed by support for deploying various projects and development tools. The next milestone on the Scroll roadmap is to build a decentralized proof network and decentralized sequencers.
(3)Scroll Origins NFT and Airdrop Expectations
In mid-2023, after launching three successful testnets and going live on the mainnet, Scroll began encouraging developers to deploy contracts on its mainnet. From October 10th to December 9th, within 60 days of the Genesis Block, deploying any contract to the Scroll mainnet had the opportunity to receive three different stages of NFT (Quintic, Quartic, Cubic). This NFT serves as a pass for future participation in airdrops.
Scroll Origins NFT was open for minting on December 15th.
(4)Future Development
During the "Foresee 2024: Web3 Pioneer 'New Year's Speech'" hosted by Foresight News on December 27th, Scroll co-founder Sandy Peng shared that the tools needed by developers such as Chainlink, The Graph, and RPC are now all online. Next, familiar Ethereum ecosystem projects will gradually be deployed on Scroll, and the focus of development in 2024 will also lean towards native projects on Scroll. Next year, there will also be encouragement for ecosystem projects to have more Fair Launches and support community participation.
Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM is an EVM-equivalent ZK-Rollup solution that first went live on the mainnet in late March. The working principle of Polygon zkEVM is to integrate ZKP into the EVM environment on Polygon, using ZKP and zk-rollups together to allow for off-chain processing of a large number of transactions, which are then batched and verified on-chain. This approach greatly increases network throughput.
Currently, the TVL of the Polygon zkEVM network is $135 million. The total number of wallets is over 480,000, the total number of contract deployments exceeds 22,000, and the number of active wallets is approximately 7,334.
1. Mainnet Beta Launch and Network Upgrades
In October 2022, the Polygon zkEVM testnet went live. After multiple audits, the Polygon zkEVM mainnet Beta was officially launched in March, featuring characteristics such as permissionless, EVM equivalence, and open-source. In the first phase of the mainnet Beta, a dedicated security council will be established to facilitate rapid upgrades of Polygon zkEVM. In the second phase, Polygon will take a series of measures to ensure user protection in case of any issues, with a higher level of decentralization and no security council with special access privileges.
The Polygon zkEVM cross-chain bridge, Polygon Bridge, went live in April. Currently, about 40 projects have been deployed on Polygon zkEVM, including QuickSwap, Balancer V2, Gamma, Beefy, PancakeSwap, and others. The Polygon team has open-sourced all the code of zkEVM under the AGPL v3 license to share its code and encourage collaboration with the developer community.
The Polygon zkEVM mainnet will not have a separate token, and network gas fees will be paid in ETH. It is expected that staking and governance in Polygon zkEVM will use the POL token in the future. Additionally, Polygon zkEVM supports account abstraction through ERC-4337, allowing users to pay fees with any token.
After the launch of the mainnet Beta, Polygon zkEVM underwent significant upgrades in September and November, namely the Dragonfruit (ForkID5) and Inca Berry (ForkID6) upgrades. The Dragonfruit upgrade will keep the Polygon zkEVM mainnet Beta in sync with the latest version of Solidity, maintaining equivalence between Rollup and EVM by incorporating support for the latest EVM opcode PUSH0. The Inca Berry upgrade includes encryption optimizations, bug fixes, and updates to nodes and provers, including adding data flow to the sequencer and improving WebSocket subscriptions.
2. Launch of Polygon 2.0
For scalability and interoperability, Polygon's solution is to launch a new L2 product suite to unify Polygon zkEVM, Polygon PoS, and Supernets.
In June of this year, Polygon launched Polygon 2.0, a unified network of L2 chains supported by ZK technology, aimed at achieving interoperability between Polygon zkEVM, Polygon PoS, and Supernets through cross-chain coordination protocols to provide unlimited scalability and unified liquidity. The Polygon 2.0 architecture consists of four protocol layers: staking layer, interoperability layer, execution layer, and proof layer.
Additionally, the launch of Polygon 2.0 will also involve updating MATIC to POL, with the upgrade expected to be completed in 2024.
Base
The TVL of the Base network is currently $674 million. According to Dune data, the total number of transactions on the Base network is 65.95 million, the total number of users exceeds 2.66 million, and the total number of contract deployments exceeds 55.2 million.
1. Mainnet Launch
Base is an Ethereum Layer2 network built by Coinbase based on the OP Stack, with the testnet going live in February and the mainnet in August.
Previously, Coinbase had repeatedly stated that Base had no plans to issue tokens. However, at the Mainnet 2023 event hosted by Messari in September, Coinbase's Chief Legal Officer, Paul Grewal, indicated that Base had not completely ruled out the possibility of token issuance, but was currently not focused on the protocol's economics and tokenization, emphasizing the importance of regulatory clarity.
Currently, Base has open-sourced monitoring systems Pessimism, smart contracts, and GitHub repositories.
2. Collaboration with Optimism
Upon the launch of the Base testnet, it was stated that in the short term, it would establish a shared bridging and sequencing initial superchain structure with the Optimism mainnet and other L2 upgrades.
After the launch of the Base mainnet, collaboration with Optimism includes protocol management, economics, and governance. In terms of protocol management, if the Law of Chains is approved, a decentralized security council will be responsible for upgrades to Base, OP Mainnet, and other OP chain upgrades. Before adopting this blockchain law, Base and OP Mainnet will also share upgrades.
Regarding economics and governance, a portion of the trading revenue from Base will be returned to the Optimism Collective. Specifically, the larger of 2.5% of the total sequencer revenue or 15% of the net sequencer revenue on the Base chain (L2 transaction revenue minus L1 data submission costs) will belong to the Collective. Optimism envisions this structure to become a "blueprint" for all Superchain members, strengthening the sustainability of shared infrastructure.
The Optimism Foundation also provides Base with the opportunity to earn up to approximately 118 million OP tokens over the next six years, as a retrospective reward for Base's contributions to expanding Ethereum and the OP Stack.
3. Tokenized Assets Alliance
On September 7th, Coinbase, Circle, Aave, and others jointly launched the Tokenized Assets Alliance (TAC), with other members including Base, Centrifuge, Credix, Goldfinch, and RWA.xyz. The alliance believes that RWA tokenization is the future of the crypto industry, aiming to help educate the industry, advocate for standardization and innovation, and collectively build the necessary infrastructure for RWA adoption.
4. Ecosystem and Community
- Base Ecosystem Fund
As of the time of writing, there are over 276 DApps and service providers in the Base ecosystem, including Chainlink, Blockdaemon, Infura, QuikNode, Blockscout, Etherscan, Dune analytics, Hop Protocol, Nansen, 0x, Ondo, Panoptic, Aave, Gelato Network, Pyth Network, Rainbow Wallet, Ribbon Finance, Balancer, PoolTogether, Euler Labs, The Graph, Wormhole, SushiSwap, Covalent, and others. Coca-Cola also launched NFTs on Base in August.
Coinbase and Coinbase Ventures have launched the Base Ecosystem Fund to make significant investments in Base-based companies and organizations in the seed stage. The ecosystem fund supports four main directions: 1. stablecoins that track inflation rates (flatcoins); 2. on-chain reputation platforms; 3. on-chain limit order book (LOB) trading platforms; 4. more secure DeFi, including tools to prevent smart contract code vulnerabilities or protocol logic errors, as well as on-chain insurance and insurance protocols, or any other products that can provide critical support to users in the event of smart contract failures.
- Community Incentive Activities
Shortly after the mainnet went live, Base launched activities such as Onchain Summer, Build on Base, Based Accounts, and Builder Grants to incentivize developers to build digital art, music, games, social, new protocols, new tools, new infrastructure, account abstraction infrastructure, etc., on Base.
It is worth mentioning that the social app friend.tech gained popularity on Base in August.
opBNB
1. Mainnet Launch
opBNB is a Layer 2 network based on the OP Stack launched by BNB Chain, with the testnet going live in June and the mainnet officially launching on September 13th. opBNB is EVM-compatible and can maintain a similar level of security as L1.
2. Technological Progress and Future Plans
According to the opBNB website and documentation, opBNB aims to support games, social, metaverse, high-frequency trading, etc. Therefore, reducing transaction costs and increasing TPS are important technological goals for opBNB.
In December, the average transaction cost on opBNB has been reduced from around $0.005 to around $0.001. BNB Chain developers stated that they will further reduce the average transaction cost to $0.0005 within the next 6 months, and increase TPS from 4761 to 10,000.
Additionally, opBNB will focus on enhancing the network's resilience and decentralization through Proof Enhancement, account abstraction, data availability with BNB Greenfield (DA), interoperability with BNB Greenfield, and decentralized sequencers. Specifically, BNB Greenfield will provide infrastructure from multi-chain platforms for full on-chain or DApp use, enabling cross-chain programmability with opBNB. Greenfield will also be positioned as the basic data availability layer for opBNB. Greenfield will enable smart contracts as resource owners from Q4 2023 to Q1 2024 to better control the permissions of BSC/opBNB.
Furthermore, the BNB Chain community proposed the opBNB roadmap on November 22nd, suggesting that opBNB may also build an AppChain using the OP Stack's Superchain to achieve interoperability with multiple Layer2 networks.
Currently, projects such as Hooked Protocol, Orbiter Finance, Muverse, PancakeSwap, LayerZero, Thena, Polyhedra Network, zkPass, and MyShell have gone live or integrated with opBNB.
3. Ecosystem Incentives
On December 6th, BNB Chain announced the TVL incentive plan to encourage projects to deploy applications on opBNB. The application period has ended, and the competition phase is currently ongoing, with the competition ending on January 14th. The total prize pool is up to $160,000, and participating projects will receive a corresponding share based on their competition ranking.
Linea
Linea is a zkEVM Rollup developed by ConsenSys, with the current network TVL at $184 million.
1. Mainnet Launch
In March of this year, ConsenSys rebranded its Layer2 network ConsenSys zkEVM as Linea and opened testing to all developers, users, or protocols.
In July, Linea officially launched the mainnet Alpha version, open to the Linea community for access to Linea Mainnet Alpha. Three days after its launch, Linea's TVL exceeded $12 million. On August 17th, Linea completed the Alpha mainnet launch and deployed an ERC-20 token bridge.
However, on July 11th, Linea also stated that it would use ETH as its native currency and currently has no plans to launch the Linea token.
On November 15th, Linea announced preparations for the next major version, Alpha v2, with lower transaction costs, faster transactions, 100% EVM coverage, and the open-sourcing of Linea Stack. Specifically, Alpha v2 will use blob to store call data on L1 to reduce Rollup costs. Additionally, the team is working to reduce fixed transaction costs by compressing data sent to L1 and aggregating proofs. Linea will reduce block time to 4 seconds and increase speed by 3 times, and introduce a mechanism to further reduce block time in the future. To achieve client diversity, both Besu and geth are supported, and the new Linea sequencer will use Linea-Besu instead of Linea-geth.
2. Linea Ecosystem Investment Alliance
On August 17th, Linea launched the Linea Ecosystem Investment Alliance (EIA), a consortium of over 30 venture capital firms, including Amber Group, Animoca Brands, BlockTower Capital, Fenbushi Capital, Huobi Ventures, IOSG Ventures, etc., to support the builders of the Linea ecosystem.
3. Linea Voyage
Linea Voyage is a loyalty program launched by Linea, which has already been initiated twice this year.
The first was the 7-week loyalty program Linea Voyage launched on the public testnet from May to June, aimed at rewarding NFT users for performing tasks related to the testnet to put pressure on the network and conduct large-scale testing activities before the mainnet launch.
The second was the 6-week The Linea Voyage: DeFi event launched by Linea on the mainnet in November, featuring 10 events and 10 core tasks with participation from over 40 DApps.
In addition, Linea launched the Voyage XP token on September 28th, aiming to unify the measurement and recognition of contributions to the development of the Linea ecosystem. Voyage XP represents the contribution of each community member to the ecosystem, covering users, startups, DApps, and Linea team members.
Blast
At the end of November to early December, the most exciting development in the Layer2 space was Blast, a Layer2 network launched by Pacman, the founder of Blur, which completed a $20 million financing round led by Paradigm and Standard Crypto.
Blast is specifically built for NFTs, allowing the Blur ecosystem to avoid asset depreciation, reduce NFT transaction costs, and introduce perpetual NFT trading. Blast can provide native returns for ETH and stablecoins, with user balances automatically compounding and earning additional Blast rewards. When users cross-chain ETH or stablecoins such as USDC, USDT, and DAI to Blast, it will be deposited into on-chain treasury protocols like MakerDAO, and the returns will be passed back to Blast users through Blast's automatic base stablecoin USDB.
The community has been debating Blast's "Pinduoduo-style" viral marketing and the centralization risk of its contract address. In terms of marketing, Blast allows users to invite friends to earn airdrop points, promoting the growth of the Blast network through user referrals. Data shows that this method, which has been overused in Web2, is still effective in Web3 due to Blur, Pacman, and the expected airdrops. As of December 28th, Blast's network TVL has exceeded $1.1 billion.
As for contract risk, Blast's contract is an upgradable contract controlled by a 3/5 multisig, with all 5 addresses being anonymous new addresses. Blast could potentially execute code upgrades and immediately steal funds through multisig. This 3/5 multisig is highly likely to act maliciously, and may even be controlled by the same person. It can be said that, except for contracts deployed on Ethereum, all others are centralized, but with endorsements from well-known institutions.
Potential Layer2
Lumoz (formerly Opside)
Lumoz is a decentralized ZK-RaaS platform that uses a hybrid consensus of PoS and PoW, allowing developers to quickly generate zkEVM application chains. Lumoz's co-founder and CEO is Liu Sheng, a graduate of Tsinghua University who previously worked at ByteDance and is also the founder of Trustless Labs. In April of this year, Lumoz completed a $4 million seed round of financing, led by Web3.com Ventures.
In May, Lumoz launched a 3-month incentive Pre-Alpha testnet and initiated a whitelist pre-application for validator nodes. At the same time, Lumoz publicly released its token economics, with 33% allocated to PoS and PoW rewards.
In August, Lumoz launched the ZK-Rollup LaunchBase on the testnet, supporting developers to build dedicated application rollups, including various components such as Layer1, zkEVM, Gas, Data Availability, and Sequencer. LaunchBase now allows developers to choose specific rollups to build their applications from EVM-compatible Layer1s such as Lumoz, Goerli, Mumbai, and BNB testnets, supporting Polygon zkEVM, zkSync, Scroll, and Starknet's four zkEVMs.
In the third and fourth quarters of this year, Lumoz completed the expansion of the ETH, BNB Chain, and Polygon base chains, expanded networks such as zkSync, Scroll, Linea, and achieved native cross-rollup communication, and a GPU version of PoW.
Recently, Lumoz will launch Fair-L2 LaunchBase to support more fair launches of high-quality ZK-L2 projects. Currently, more than 20 projects have submitted applications for Fair-L2 listing, including BTC L2, game platform chains, DePIN chains, social application chains, and more.
In addition, Liu Sheng stated at the "2023 Hong Kong Web3 Carnival" forum on "Web3 Technical Infrastructure: Layer 2 Networks" that the mainnet will be launched next year.
Ola
Ola is a second-layer programmable privacy and scaling solution based on ZKVM, developed by the Sin7y Labs team. In July of this year, Ola completed a $3 million seed round of financing, jointly led by Web3.com Ventures and Foresight Ventures, with participation from Token Metrics Ventures, J17 Capital, Skyland Ventures, LD Capital, CatcherVC, and others.
In February of this year, Ola completed a proof of concept, launched the custom smart contract language Ola-lang, and integrated Ola-lang into the developer-friendly platform IDE: VScode.
In April, Ola released the second version of its technical whitepaper, emphasizing the design and construction of the most important foundational modules in Ola, the high-performance ZKVM, OlaVM; ZK-friendly smart contract language, Ola-lang; and the privacy design architecture.
In August, Ola supported the Poseidon2 hash in its proof system, with a 40% improvement in Prover performance.
During the Istanbul DevConnect in November, Ola announced the opening of the Ola Dev Testnet whitelist application, and the code for its smart contract language Ola-lang and virtual machine OlaVM was officially open-sourced. The Ola public testnet and mainnet will be launched successively next year.
Recently, Ola reached a strategic partnership with Lumoz, a ZK-RaaS (ZK-Rollup as a Service) platform, and Ola will be integrated into Lumoz's ZK-Rollup LaunchBase, allowing developers to generate ZK-Rollups with privacy attributes without code.
ZKFair
ZKFair was the star of December, quickly gaining market attention through various airdrop methods. This is a ZK-L2 network, with the testnet launched on December 7th and the mainnet launched on December 20th, with a 100% fair launch. In just one week, ZKFair's network TVL reached $1.23 billion.
The surge in ZKFair TVL is due to the Gas Fee Airdrop. The total supply of ZKF tokens is 10 billion, all of which are distributed to the community through airdrops. 25 billion are airdropped to community users, including Polygon zkEVM, zkSync, Linea, Scroll, ZKSpace interaction addresses, Lumoz point holders, and Ordinals community, while the remaining 75 billion are produced in 4 rounds through Gas Fee Airdrop starting from 11:00 on December 24th. By the end of December 26th, over 200,000 people participated in the airdrop activity, with a total Gas consumption of 108 million USDC.
The ZKF obtained by users will be officially available for claiming on January 1, 2024, at 11:00. At that time, all 10 billion ZKF tokens will be uniformly released and circulated. ZKFair will not issue any additional ZKF tokens in the future.
2023 Foresight News Year-end Series Recommended Readings:
- "2023 Top Ten Annual Events: Hong Kong, Binance, BlackRock…"
- "Year-end Review | Overview of the 2023 Cryptocurrency Industry Search Rankings"
- "Ten Must-read Cryptocurrency Articles of 2023"
- "Web3 + AI Track Panorama: Over 130 Projects, What Other Undiscovered Treasures Are There?"
- "2023 Moments of Anxiety Collection: Everywhere Hundredfold Thousandfold, Are You Definitely Free?"
- "The Eve of the Web3 Gaming Explosion? Taking Stock of the Major Players Entering the Tens of Millions Financing Threshold"
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



