Cryptocurrency returns are taxable in India, and a 30% tax (plus applicable surcharge and 4% tax) is required.
Authored by: Ektha Surana
Translated by: TaxDAO
The original English article was published on June 8, 2023.
Is Cryptocurrency Considered "Currency" or "Asset" in India?
Cryptocurrencies and NFTs are classified as "Virtual Digital Assets (VDA)" and the term is defined in Section 2(47A) of the Income Tax Act. The definition is detailed but primarily includes any information, code, number, or token generated through encryption (not Indian or foreign legal tender). In short, "Virtual Digital Assets" refer to all types of crypto assets, including NFTs, tokens, and cryptocurrencies, but excluding gift cards or vouchers.
Is Cryptocurrency Taxed in India?
Yes, cryptocurrency returns are taxable in India. The government's official position on cryptocurrency and other virtual digital assets was clarified in the 2022 budget.
How is Cryptocurrency Taxed in India?
In India, cryptocurrency is classified as a virtual digital asset and is subject to taxation.
- As per Section 115BBH, cryptocurrency trading income is taxed at 30% (plus 4% tax).
- As per Section 194S, from July 1, 2022, a 1% tax is deducted at source (TDS) for the transfer of crypto assets if the transaction amount in the same fiscal year exceeds 50,000 rupees (or in some cases, 10,000 rupees).
- Cryptocurrency tax applies to all investors who transfer digital assets in the current year, whether they are individual or commercial investors.
- The tax rates for short-term and long-term gains are the same and apply to all types of income earned by investors.
Therefore, regardless of whether the income is considered capital gains or business income, the returns from trading, selling, or exchanging cryptocurrencies will be taxed at a rate of 30% (plus 4% surcharge). In addition to this tax, the sale of crypto assets exceeding 50,000 rupees (or in some cases, 10,000 rupees) will also be subject to a 1% TDS.
Key Points on Cryptocurrency Taxation
- Cryptocurrency income is taxed at 30% as per Section 115BBH effective from April 1, 2022.
- A 1% TDS is applicable for the transfer of VDA as per Section 194S effective from July 1, 2022.
- No other expenses can be deducted apart from the cost of acquisition.
- Cryptocurrency returns should be reported in Schedule VDA of the ITR.
Which Cryptocurrency Transactions Require Taxation in India?
You will need to pay a 30% tax if you engage in the following transactions:
- Purchasing goods or services using cryptocurrency.
- Exchanging cryptocurrency for other cryptocurrencies.
- Trading cryptocurrency for fiat currency.
- Receiving cryptocurrency as service remuneration.
- Receiving cryptocurrency as a gift.
- Cryptocurrency mining.
- Earning cryptocurrency wage income.
- Staking cryptocurrency and earning staking rewards.
- Receiving airdrops.
How to Calculate Cryptocurrency Tax
Now that you know you have to pay a 30% tax on cryptocurrency profits, let's see how to calculate the profit. Profit is the selling price minus the cost price.
Understanding the TDS on Cryptocurrency Transactions
The Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is intended to tax cryptocurrency traders and investors at the time of their transactions by deducting a certain percentage at the source. The buyer owing funds to the seller must deduct the TDS amount and remit it to the central government, paying the balance to the seller. In India, the TDS rate for cryptocurrency is set at 1%. From July 1, 2022, the buyer is responsible for deducting TDS at a rate of 1% when paying the cryptocurrency/NFT transfer fee to the seller. If the transaction occurs on an exchange, the exchange may deduct TDS and pay the balance to the seller. Indian exchanges automatically deduct TDS, while individuals in foreign exchanges must manually deduct TDS and submit TDS returns.
- P2P Transactions: In P2P transactions, the buyer is responsible for deducting TDS and submitting Form 26QE or 26Q (whichever is applicable). For example, purchasing cryptocurrency using rupees through a P2P platform or international exchange.
- Cryptocurrency Trading: TDS applies to both the buyer and the seller at a tax rate of 1%. For example, purchasing cryptocurrency with stablecoins.
Airdrop Tax
An airdrop refers to the process of distributing cryptocurrency tokens or coins directly to specific wallet addresses, usually for free. Airdrops are taxed at 30%.
So, how much is the tax amount for an airdrop?
- Receiving Cryptocurrency: Airdrops are taxed based on the value determined by Rule 11UA, i.e., the market value of the tokens received on the date received from an exchange or decentralized exchange. The tax will be levied at 30% of that value.
- Selling, Exchanging, or Spending Later: If you later sell, exchange, or spend these tokens, a 30% tax will be levied on the income earned.
Cryptocurrency Mining Tax
Mining refers to the process of verifying and recording transactions on a blockchain network using powerful computers or specialized mining hardware.
In the blockchain network, transactions are verified by a group of nodes or computers called "miners," who compete to solve complex mathematical problems. The first miner to solve the problem receives a certain amount of cryptocurrency as a reward, which varies by network.
The mining income received will be uniformly taxed at 30%. The cost of cryptocurrency mining will be considered as "0" when calculating the proceeds from the sale. The cost of acquisition cannot include expenses such as electricity costs or infrastructure fees.
So, how much is the tax amount for cryptocurrency mining?
- Receiving Cryptocurrency: The cryptocurrency assets received during mining will be taxed based on the value determined by Rule 11UA, i.e., the market value of the tokens received from an exchange or decentralized exchange on the date received. The tax will be levied at 30% of that value.
- Selling, Exchanging, or Using Later: If you later sell, exchange, or use these assets, a 30% tax will be levied on the income earned.
Cryptocurrency Staking/Minting Tax
In the cryptocurrency space, minting refers to the process of generating new blocks on a blockchain using a proof-of-stake algorithm in exchange for newly generated cryptocurrency and commission rewards.
Income earned from staking may be subject to taxation. The amount earned from staking depends on the annual interest rate provided by the validator. For example, if you stake 100 coins at a 10% annual interest rate, you will receive 10% interest annually.
The income earned from staking will be taxed at 30%. Additionally, when you sell cryptocurrency assets, you will need to pay a 30% capital gains tax.
Generally, transferring your tokens to a staking pool or wallet usually does not incur taxation. Additionally, transferring assets between wallets is typically considered tax-free.
Cryptocurrency Gifting Tax
In the 2022 budget, virtual digital assets were included in the scope of movable property. Therefore, if the total value of gifts exceeds 50,000 rupees, received cryptocurrency gifts will be taxed as "income from other sources" at the regular fixed tax rate.
Cryptocurrency gifts received from relatives are exempt from tax. However, cryptocurrency gifts from non-relatives valued over 50,000 rupees are taxable. Gifts received on special occasions, through inheritance or wills, marriage, or consideration of death are also exempt from tax.
Losses from Cryptocurrency Transactions
As per Section 115BBH of the tax law, any losses incurred from cryptocurrency cannot be set off against any income (including cryptocurrency gains). Therefore, cryptocurrency investors cannot set off losses from cryptocurrency assets from the previous year when filing their ITR (Income Tax Return) this year.
Additionally, apart from the cost of acquisition or purchase cost, Indian cryptocurrency investors are not allowed to report expenses related to their cryptocurrency activities.
For example, Mr. X purchased Bitcoin worth 60,000 rupees and later sold it for 80,000 rupees. He also purchased Ethereum worth 40,000 rupees and sold it for 30,000 rupees. The exchange charged a transaction fee of 1,000 rupees. The tax for these two transactions should be calculated as follows:
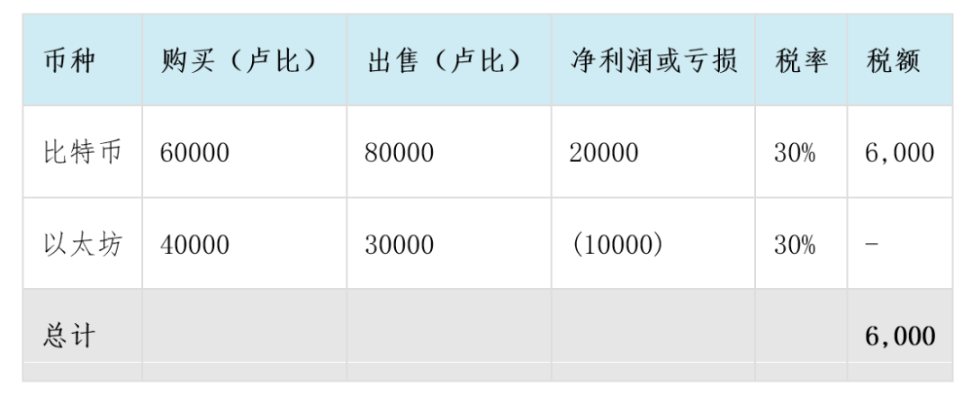
Here, the loss of 10,000 rupees is not allowed to be set off against the gain of 20,000 rupees. The entire income of 20,000 rupees is taxed at a rate of 30%. Additionally, the transaction fee of 1,000 rupees is not allowed to be deducted.
Disclosure of Cryptocurrency Assets in the Balance Sheet
The Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) has mandated the disclosure of gains and losses from cryptocurrency. Additionally, the value of cryptocurrency on the balance sheet date should be reported. Therefore, from April 1, 2021, there have been changes to Schedule III of the Companies Act. This provision can be seen as the first step in government regulation of cryptocurrency.
Please note that this directive applies only to companies, and individual taxpayers are not required to comply with such regulations. However, reporting and taxation of cryptocurrency gains is mandatory for everyone.
Timeline of Indian Cryptocurrency Tax Regulations

Frequently Asked Questions about Cryptocurrency Taxation in India
A. How much tax does India levy on cryptocurrency?
As per Section 115BBH, cryptocurrency gains are taxed at 30% (plus applicable surcharge and 4% tax).
B. How is cryptocurrency tax calculated?
As mentioned above, the taxation of cryptocurrency gains depends on the type of transaction.
C. How is the 30% cryptocurrency tax calculated?
The income you receive from cryptocurrency will be taxed at 30%. Income = Selling Price - Cost Price
D. How to report cryptocurrency on the tax return?
For the financial year 2022-23 and 2023-24, you need to use the ITR-2 form (if reporting as capital gains) or the ITR-3 form (if reporting as business income) to report cryptocurrency tax. The new ITR forms include a specific section "Schedule VDA" for reporting cryptocurrency gains or income. As per standard income tax rules, the gains from cryptocurrency transactions will be taxed as either (i) business income or (ii) capital gains. The classification depends on the investor's intent and the nature of these transactions.
- Business Income: If the transactions are frequent and of substantial volume, the income from cryptocurrency may be classified as "business income." In this case, you can use ITR-3 to report cryptocurrency gains.
- Capital Gains: On the other hand, if the primary reason for owning cryptocurrency is to benefit from long-term value appreciation, the income will be classified as "capital gains." In this case, you can use ITR-2 to report cryptocurrency gains.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



