
Project Introduction
Supra is a "middle layer network" solution dedicated to building a cross-chain interoperable middleware layer called Intralayer, equipped with native oracles, VRF, and automation functions. Its goal is to create a more secure interoperability infrastructure for the future of blockchain. Supra uses "bridgeless" cross-chain technology to connect L1 and L2, Web2 and Web3, achieving vertical integration of these solutions. The vision of Supra is to create a "one-stop" vertically integrated basic network platform that strongly supports the construction of underlying applications in the Web3.0 era.
Author
JUMPENG, a senior research analyst at Shi Lian Investment Research. With a master's degree in finance from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and 7 years of industry experience, he specializes in areas such as Layer1, DeFi, NFT, Layer2, and Gamefi, having researched over 2000 projects and produced over 500 in-depth research reports.
1. Research Highlights
1.1. Core Investment Logic
Supra has enormous market potential as it is at the core of blockchain infrastructure construction, with leading technology, rapidly growing community, and strong ecosystem partners. The core competitive advantages and investment logic of Supra are reflected in:
Excellent research and academic background of the team. Supra was co-founded by several Ph.D. experts in the blockchain and cryptography fields. One of its co-founders, Dr. Aniket Kate, is a well-known expert in cryptography and zero-knowledge proof, having published dozens of high-level papers. This has laid a solid technical foundation for Supra. Additionally, Supra has a research and development team composed of experts in cryptography, blockchain, machine learning, and other fields, most of whom hold Ph.D. degrees from top universities and have experience in blockchain product development and application. The team has published multiple high-quality academic papers in the fields of consensus and oracles, some of which contain original cryptographic and blockchain research results, establishing the technical accumulation of Supra. Furthermore, Supra not only focuses on innovative theory but also applies cutting-edge cryptography to practical products through in-depth cooperation between industry, academia, and research, ensuring the advanced and practical nature of its technical solutions. With its strong academic background, Supra's products have significant improvements in security, performance, and decentralization compared to traditional solutions. Therefore, with its strong academic and research background, Supra has a significant competitive advantage in technology development, which is also an important cornerstone for its rapid development.
Independent innovative data acquisition and cross-chain communication technology solutions. Compared to the centralized design of using third-party oracles, Supra has built a localized decentralized oracle network that can directly obtain data from external sources and process it through its own consensus algorithm, without relying on or trusting external oracles. This technology greatly enhances security and achieves millisecond-level response speed. In addition, Supra has developed the trustless Hypernova cross-chain transmission protocol, which ensures the validity of cross-chain data and events by directly verifying the cryptographic signatures of the source chain, without relying on relay nodes. This "bridgeless" model has higher security and scalability compared to traditional cross-chain bridges that rely on multi-signature verification. These independently developed innovative technologies give Supra leading technical advantages in both key aspects of data acquisition and cross-chain communication. These technological breakthroughs not only promote the development of cryptography and blockchain basic science but also directly translate into the differentiated competitiveness of Supra's products and applications.
In summary, Supra gives the overall impression of being a case of gradual accumulation leading to sudden breakthroughs. It has accumulated 5 years of technical research and development in oracles and cross-chain fields, forming a complete set of network architecture design and technical solutions. This theoretically designed set has significant advantages in key indicators such as security, decentralization, and performance, laying a solid foundation for Supra's technological leadership. Supra's overall functional positioning is IntraLayer, realizing its own oracles and cross-chain services and connecting various blockchains through a central radiation model. This technological architecture and product design are very cutting-edge. With the rapid rise of RWA and cross-chain applications, infrastructure projects like Supra will face incremental market demand. Its product market adaptability is strong, but Supra is still in the stage of product testing and continuous iteration, with a considerable gap from large-scale commercial use, and still needs to be verified through practice. In addition to its strong technical strength, Supra's future development also depends on the results of ecosystem partner network construction, which requires continuous efforts from the team. Overall, Supra has leading technology and product design, is in the high-growth blockchain infrastructure field, and has promising development prospects, but still needs to undergo technological and commercial tests.
1.2. Valuation
According to publicly available information, Supra has completed more than 7 rounds of financing, including a recent private placement round in September 2023, raising over $24 million. Although Supra has not officially disclosed its exact valuation, considering the following points:
A. Supra is a blockchain infrastructure project in a high-growth industry.
B. Supra's leading technical strength in the two important scenarios of oracles and cross-chain.
C. Long-term and continuously upgraded large-scale investment support from investors.
D. Expanding application ecosystem and user base of Supra.
It can be reasonably speculated that Supra's actual valuation is likely to be higher than the publicly announced financing scale. It is likely to have entered the billion-dollar valuation range as an accelerating growth Web3 infrastructure project with enormous value potential. It can be expected that as Supra accumulates core technology and applications, its valuation level will continue to rise.
1.3. Project Risks
The project risks of Supra mainly lie in the fact that the product is still in the testing stage, user and application coverage needs to be expanded, competition from resource advantages of competitors, and the challenges of user inertia and technological commercialization, as detailed in the SWOT analysis section 5.2 of the report.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Project Introduction
Supra is a decentralized middleware layer project that provides oracle, cross-chain communication, VRF, and other services, connecting L1 and L2, Web2 and Web3, to provide a secure interoperability infrastructure for the development of Web3. Supra's vision is to become a self-sufficient system where users do not need to leave the system for most on-chain activities or rely on third-party oracles to obtain real-world application data from off-chain. The core technologies of Supra include the DORA oracle protocol, DVRF random number scheme, HyperNova cross-chain communication protocol, etc., all of which have advantages such as high security, efficiency, randomness, and bridgeless cross-chain, providing reliable solutions for the transmission and verification of on-chain and off-chain data.
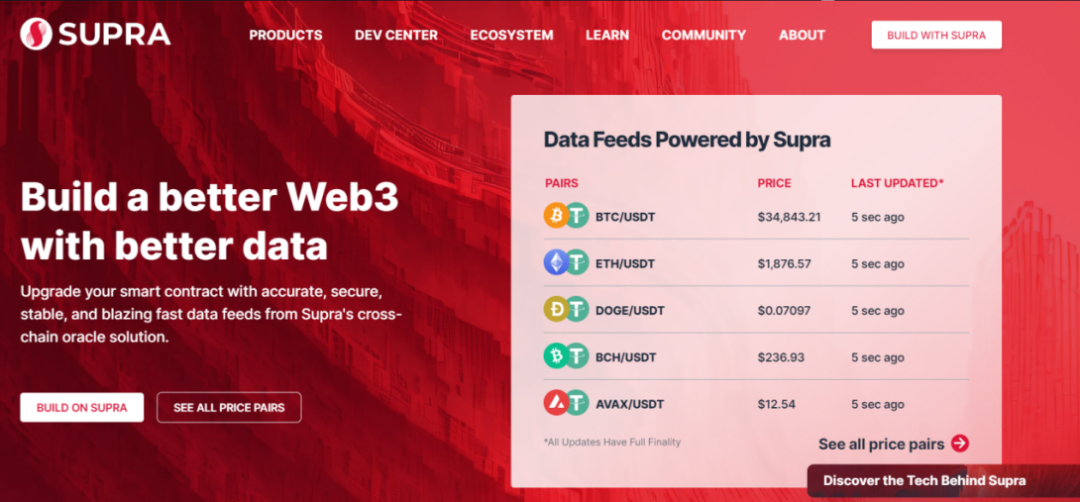
Source: Supra Official Website Homepage
2.2. Team Situation
2.2.1. Overall Situation
In 2017, the team established the Entropy Foundation, headquartered in Switzerland, with the goal of expanding the capabilities of smart contracts and oracles, and Supra Oracles is the flagship project of the Entropy Foundation. The team members consist of professionals with rich experience in cryptography, enterprise integration, IoT solutions, DeFi, innovative consensus modeling, randomness research, and oracle research. It is worth mentioning that Supra is not a new project. Since its inception, it has been around for nearly 5 years, during which the industry has completed a full cycle. However, Supra has not rushed to launch products or tokens, but has chosen to focus on research and development.
2.2.2. Core Members
Dr. Kate: Dr. Kate is the Chief Research Officer of Supra. He is the main author of KZG Commitments (also known as Kate Commitments), a cornerstone of most ZK Proof systems today, and has laid the foundation for Ethereum's L2 scaling strategy. Dr. Aniket Kate brings over 15 years of research experience in applied cryptography, distributed systems, and digital privacy to Supra. For the past decade, he has been actively involved in blockchain work. His high-impact projects include KZG (polynomial) commitments, DKG, Layer-1/2 transaction privacy, and distributed randomness oracles.

Dr. Raghavendra Ramesh: Dr. Raghavendra Ramesh holds a Ph.D. in computer science from the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, specializing in formal methods. After obtaining his Ph.D. and briefly working as a postdoctoral researcher at IIITB, he joined the Oracle Lab in Brisbane. There, he focused on cross-research in formal methods and network security, developing static analysis tools to detect security vulnerabilities in large Java codebases. Dr. Raghavendra was attracted by the potential of blockchain technology and joined ConsenSys. He made contributions to the Ethereum ecosystem by developing atomic cross-chain technology, formally proving the security of consensus protocols, and participating in Ethereum's stateless approach. Later, he met Joshua Tobkin, the CEO of SupraOracles, and eventually joined the team to help realize Supra's grand vision. Currently, he serves as the Vice President of Research at SupraOracles, leading the research team in distributed protocols, programming languages, and formal methods.

Dr. Pratyay Mukherjee:

Dr. Pratyay Mukherjee has been serving as the Senior Research Director at Supra Research since June 2022. His research covers various aspects of cryptography and computer security. Recently, he has been focusing on the application of cryptography in the payment and blockchain fields, especially threshold cryptography. Prior to this role, he served as a Senior Research Scientist at Swirlds Labs (January 2022 to June 2022) and Visa Research (March 2017 to January 2022). In October 2015, Dr. Pratyay Mukherjee obtained a Ph.D. in computer science from Aarhus University in Denmark, and completed his doctoral studies from August 2012 to August 2015. He spent the final year of his Ph.D. at Northeastern University in Boston. Subsequently, he conducted postdoctoral research at the University of California, Berkeley from the summer of 2015 to the spring of 2017. Prior to that, he obtained a master's degree in computer science from the Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur in 2011, graduating with honors and receiving a silver medal. Even before that, he had already obtained a bachelor's degree in electronics and telecommunications from Jadavpur University in Kolkata (2008).
2.3. Financing Situation
On September 28, 2023, according to Chainwire, Supra, a provider of oracle and VRF services, announced that it has raised over $24 million in funding to date. Investors include Animoca Brands, BCW, Coinbase Ventures, FiveT Fintech (formerly Avaloq Ventures), Galaxy Interactive, Hashed, HashKey, Huobi Ventures, No Limit Holdings, Prosus Ventures, Razer.com, Republic Crypto, Shima Capital, Signum Capital, SMO Capital, Sound Ventures, Sublime Ventures, UOB Venture Management, and Valor Equity Partners.

Source: ROOTDATA
According to data from CrunchBase, Supra has had nearly 10 rounds of funding, with a total funding amount of up to $47.9 million, with the first round of funding starting at the end of 2020. However, the official announcement has only been made for the latest round of funding of $24 million.
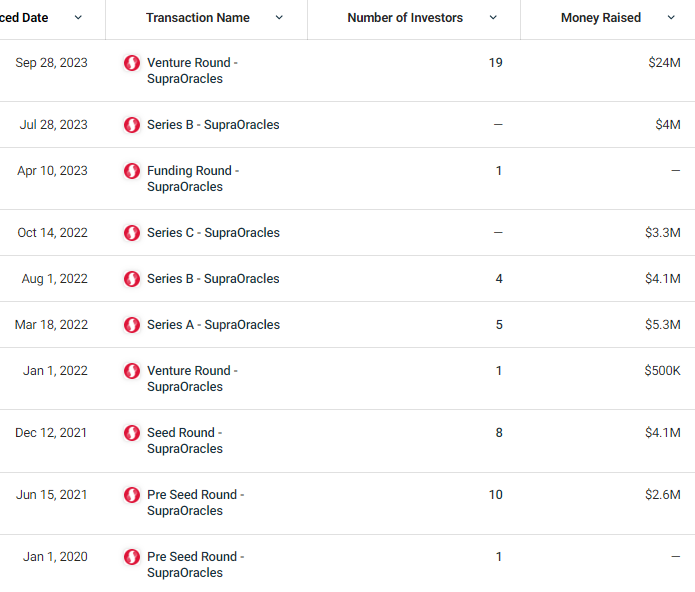
Source: CrunchBase
2.4. Past Development and Roadmap
2.4.1. Past Development

2.4.2. Development Plan and Roadmap
Based on current information, Supra's future development roadmap may include the following aspects:
A. Improve functional modules. Continue to develop new features such as disaster recovery and privacy computing to enhance the overall network capabilities.
B. Expand application scenarios. Deepen involvement in vertical industries such as GameFi and DeFi, and develop more customized application scenarios.
C. Interconnection between chains. Supplement support for more mainstream public chains to achieve true cross-chain interoperability.
D. Ecosystem development. Attract more DApp development and cultivate a rich ecosystem environment.
E. Global deployment. Strengthen international cooperation to help the project gain application and promotion in more regions.
F. Technological iteration and upgrade. Continuously optimize network topology, performance, security, and other indicators to maintain technological leadership.
G. Organizational system construction. Improve governance models, strengthen community participation mechanisms, and design incentive models.
H. Application promotion. Utilize the first-mover advantage to help Supra become an industry standard and continuously expand its influence.
By comprehensively laying out the above business areas, Supra is expected to grow into a top-tier public chain infrastructure service provider in the future.
2.5. Social Media Data
As of November 6, 2023, Supra has shown high visibility on social media platforms. The main channels currently operated by the project include Twitter, Discord, Medium, and Telegram. From the current situation on social media, the project has performed well in terms of product operations. Currently, Supra's Twitter account has attracted over 220,000 followers, with frequent updates and interactions, making it one of the most popular channels for promotion. Additionally, Discord has over 150,000 fans, with intense discussions in some sections. Below are the specific data for each platform:
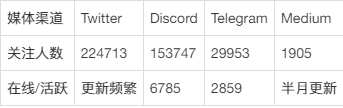
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
The origin of Supra can be traced back to 2017 when it was a project called SupraOracles, a decentralized oracle project. With the development of the entire blockchain trend, Supra has been continuously innovating and expanding. Its business is no longer limited to the oracle sector but also covers more middleware services. According to its current positioning, it is an interoperability infrastructure that provides oracle, cross-chain communication, VRF, and other services, known as IntraLayer. To better understand the project background of Supra, it is necessary to discuss the background and significance of oracles and cross-chain.
3.1.1. Oracles
To better understand the project background of Supra, we first need to understand what an oracle is and why it is needed. With the development of blockchain technology, many scenarios require the blockchain to obtain real-world data from off-chain, such as prices, event results, etc. However, the blockchain itself is a deterministic closed environment and cannot directly obtain dynamic data, which requires a mechanism to securely and reliably introduce data into the blockchain. This is the reason why oracles came into being. Simply put, an oracle is a bridge that connects the blockchain to the real world. It can deterministically import external data into the blockchain through a certain mechanism, allowing smart contracts on the blockchain to rely on this data for execution.
Ideally, the security and decentralization of the oracle network should not be lower than the blockchain it connects to. However, to achieve this, the oracle network needs a large number of nodes to ensure decentralization, which will increase the multi-round consensus time and reduce the performance of the blockchain. With the enrichment of blockchain application scenarios and the increasing demand for real-world information, accurate and secure oracles have become crucial, requiring a balance between security and network performance.
Supra has emerged in this context, aiming to solve the "oracle dilemma" and innovatively design oracle networks to be both secure and efficient. Supra aims to not only be a reliable source of information in the blockchain world but also act as a bridge between blockchains, promoting the broader application of blockchain technology.
3.1.2. Cross-Chain
With the development of DeFi, the circulation of assets and information between blockchains needs to become a reality. However, traditional cross-chain designs have some pain points. Most public chains have their unique design rules and limitations. Additionally, each public chain provides different services, leading to fragmented user experiences. To bridge the connection, multi-signature verification cross-chain bridges were developed early on. Structurally, multiple staking nodes jointly sign events on the source chain and then transmit them to the target chain for corresponding operations. Although it achieves a certain degree of decentralization, its overall weaknesses are still significant. First, the number of verification nodes and staking amounts are far lower than those on the L1 chain, resulting in lower trustlessness than L1. Second, the multi-signature mechanism adds complexity and is difficult to operate efficiently. Third, the verification nodes themselves become targets for attacks, posing security risks. According to statistics, cross-chain security losses amount to as much as $2 billion, making a new type of cross-chain solution with decentralization matching L1 a pressing need.
Faced with this pain point, Supra's core goal is to open up seamless cross-chain channels, achieving seamless interconnection between chains through its independently developed "HyperNova" technology. HyperNova uses multi-party distributed signatures and VRF mechanisms to effectively improve cross-chain efficiency and security. At the same time, based on the middleware layer design, Supra completely eliminates single-point trust, truly achieving decentralization. This will provide high-utility infrastructure support for cross-chain businesses, promoting the large-scale operation of cross-chain applications under the Web3 architecture.
3.2. Project Principles
The core principle of Supra is to use its unique consensus algorithm, distributed oracle protocol, distributed verifiable random number scheme, and bridgeless cross-chain protocol to achieve a high-performance, high-security, and highly interoperable network architecture.
3.2.1. DORA Oracle
The main dilemma faced by traditional oracles is how to achieve strong Byzantine fault tolerance and high performance while ensuring decentralization. The DORA oracle is an innovative oracle solution of Supra, which can aggregate multiple off-chain data and events into a single representative value and securely transmit it to the blockchain, providing trusted inputs and outputs for smart contracts. The DORA oracle has a certain degree of Byzantine fault tolerance, meaning that even if some nodes fail or behave maliciously, it will not affect the correctness and consistency of the data.
A. DORA uses a "tribe-clan" (similar to the hierarchical structure of ancient tribal society) structure to divide the oracle network. Each tribe contains multiple clans, and each clan consists of several nodes. This structure achieves high decentralization through random reshuffling.
B. The protocol aggregates the values provided by all nodes and selects a single value to represent the real situation within the maximum and minimum range through a "representative value" mechanism (similar to selecting a median value from the values provided by different nodes, for example, if different nodes report the price of a token as 10, 11, 12, 9, 13, then the "representative value" will be the middle value of 11). It also introduces a "consistency distance" (for example, if the consistency distance is set to 1, and one node reports 10 while other nodes report 9-11, then the node reporting 13 exceeds the consistency distance, and its value will not be accepted), constraining other values from deviating from the honest numerical range.
C. In addition, DORA supports a Byzantine fault tolerance of up to 51%, exceeding the traditional 33% limit. Multi-round asynchronous computation (allowing the oracle network to simultaneously initiate multiple computation tasks, regardless of order, ensuring real-time and fresh data) ensures that new data replaces old data in a timely manner, maintaining a high update rate. In case of instability, there is also a dedicated "backup plan" (similar to a backup measure in case the main plan fails, the backup plan is activated to ensure the task is completed smoothly).
In summary, the DORA oracle adopts a "tribe-clan" distributed structure, efficiently aggregating data from multiple sources through techniques such as hierarchical random shuffling, the "representative value" mechanism, and "consistency distance" constraints. It supports a Byzantine fault tolerance of up to 51%, achieving security, high performance, and a high degree of decentralization.
With this technological advantage, the DORA protocol outperforms industry counterparts in both security and performance. Its "tribe-clan" architecture achieves unprecedented decentralization, while leveraging Supra's unique multiple technical means to ensure oracle quality.

Source: Supra Whitepaper
3.2.2. VRF Randomness
Randomness is an important factor in achieving security in computing systems and is an indispensable part of the design of any public key cryptography scheme. For example, generating truly random numbers is crucial for the successful implementation of encryption methods such as multi-party computation and zero-knowledge proofs. Randomness computation can also be applied to other purposes, such as selecting winners in online lotteries or setting game prizes, providing a random experience in blockchain games, and other types of random selection processes.
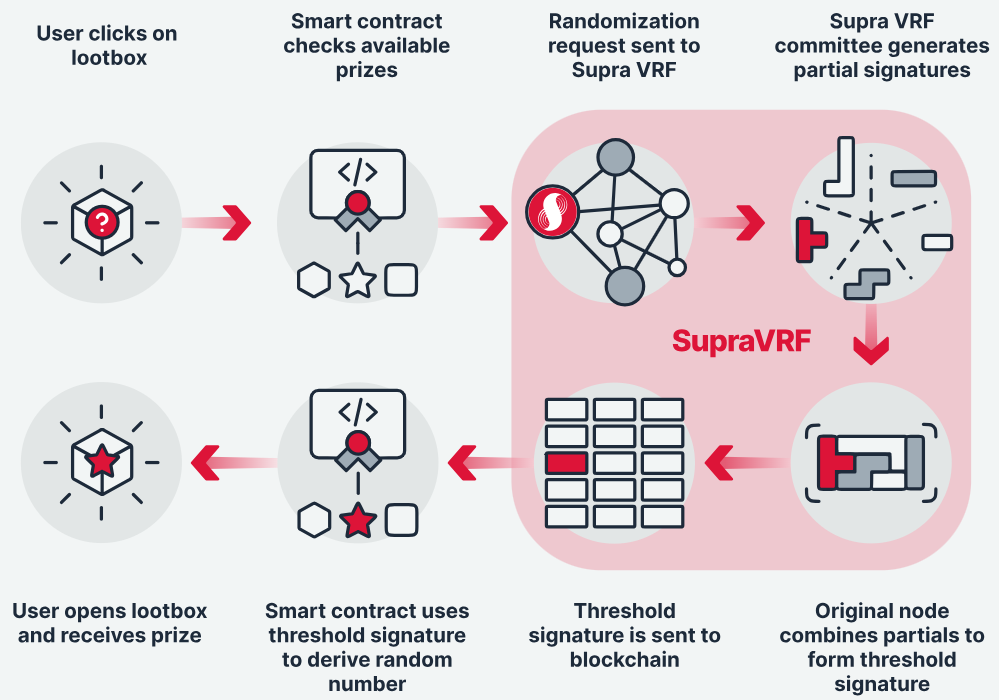
Source: Supra Official Website
But how can reliable and verifiable random numbers be obtained? This requires the intervention of VRF technology. VRF, which stands for Verifiable Random Function, can generate an output that looks completely random based on input and a key, but is actually verifiable. However, relying solely on a single node to store and compute VRF is not decentralized enough. To address this issue, Supra has proposed a Distributed VRF (DVRF) scheme.
A. In the DVRF mode, the key is shared among multiple nodes in a secret sharing manner. Each node will use its own key part to compute partial results, which will be aggregated into the final output.
B. At the same time, Supra uses techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs to make the output result look completely random while being publicly verifiable. This achieves the purpose of VRF generating random numbers while also ensuring decentralization.
Compared to a single-point centralized VRF, Supra's DVRF has significant advantages in security and decentralization. It can better provide verified true random data for blockchain applications and serves as an important infrastructure component.
Source: Supra Whitepaper
3.2.3. HyperNova Cross-Chain Communication Protocol
In the previous section on project background, the pain points of current cross-chain communication were detailed, i.e., native communication with multiple chains. Native cross-chain communication means using the cryptographic signature algorithms of two chains to communicate, allowing smart contracts to verify the data provided to them. However, many chains use different encryption technologies. Through its unique HyperNova cross-chain communication protocol, Supra achieves "bridgeless" interoperability between blockchains. Through this protocol, Supra can directly verify the consensus information of other chains, such as Ethereum, without the need for intermediate relay nodes.
A. Supra continuously monitors and tracks the validator set of other chains. For example, in Ethereum, Supra can obtain the current active validator node list and their public keys. When these validator nodes reach consensus and package new blocks, Supra can directly verify the block's cryptographic signature using the public key.
B. To transmit information from the Ethereum chain, HyperNova uses a "relay" approach. Relay nodes are only responsible for forwarding data from the source chain and do not participate in data verification. Supra cryptographically verifies this information using its own algorithms and core technologies. As long as there is at least one honest relay node forwarding the information on the source chain, Supra can fully verify the authenticity of the information.
Compared to the "multi-signature" traditional cross-chain bridge, HyperNova reduces the trust requirement for intermediate nodes. It achieves efficient and "bridgeless" native interoperability between the source and target chains, ensuring the security and decentralization of cross-chain transactions. This allows Supra to conveniently and efficiently connect to other mainstream public chains, establishing a comprehensive cross-chain service system.
3.2.4. IntraLayer
With the flourishing development of blockchain, the disconnection of services between different chains has led to the lack of a unified ecosystem for Web3, causing users to jump between different chains and applications, resulting in fragmented experiences. The IntraLayer proposed by Supra aims to create an "intermediate layer" that seamlessly integrates multiple blockchains into a unified whole through its powerful decentralized network framework. It achieves seamless connectivity across L1, L2, Web2, and Web3. IntraLayer incorporates Supra's unique middleware services such as oracles, VRF, native cross-chain, etc., as infrastructure, building an "all-inclusive" network where all services share the same security foundation and provide ultra-high performance through vertical integration. Developers only need to integrate once to easily access multiple chains connected by IntraLayer, and applications can enjoy extremely low development and operating costs.
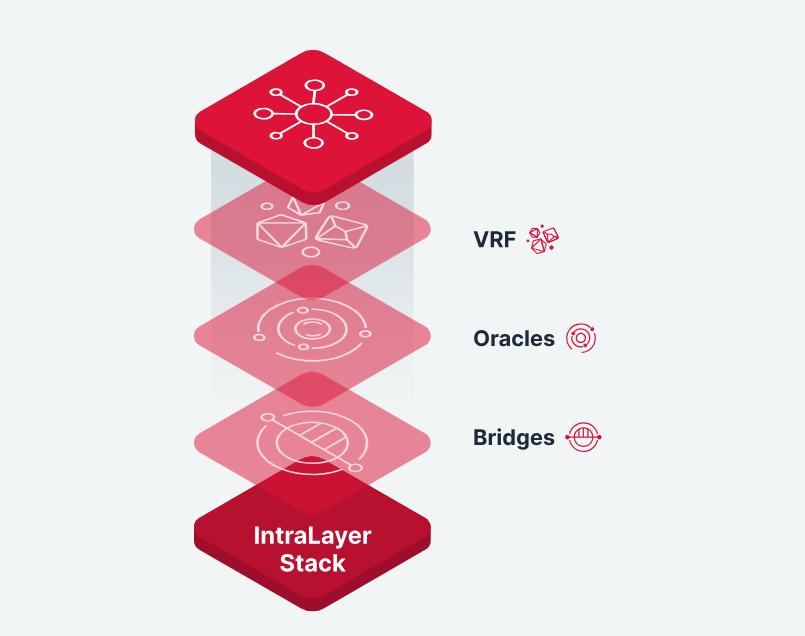
Source: Supra Official Website
IntraLayer simplifies and enhances interoperability. Specifically, IntraLayer has the following main features:
1) Solves the problem of communication barriers between blockchains by connecting more chains through a universal cross-chain gateway
In the traditional model, each blockchain operates like isolated islands, unable to directly communicate with each other, similar to people speaking different languages encountering barriers. This problem will become increasingly prominent for the vast and diverse Web3 ecosystem. In the face of this problem, IntraLayer, introduced by Supra, acts as a "universal translator," connecting independently operating chains through secure bridges into a unified whole, technically achieving communication translation between different chains. Specifically, IntraLayer abstracts and hides the inherent differences in blockchain networks, providing a unified development and access interface for dApps. Developers only need to obtain resources from various chains through IntraLayer, without needing to focus on the details of the underlying chains. At the same time, any user can access dApps deployed across multiple chains connected to IntraLayer without additional steps, just like being in the same language environment, making it convenient and efficient. This effectively addresses the pain points of fragmentation in the Web3 ecosystem. Based on IntraLayer, Supra has used technical means to build bridges connecting various chains, opening up new possibilities for comprehensive interconnection between chains in Web3.
2) Provides a one-stop seamless cross-chain service for dApps using a hub-and-spoke model
IntraLayer adopts a hub-and-spoke model, with Supra as the core hub, enabling efficient interconnection between smart contracts and all connected chains. Developers only need to deploy their dApps built on Supra to this network through a simple one-time integration. Afterward, whether developers want to expand it to any chain currently connected to IntraLayer or to new chains connected in the future, they can achieve one-time deployment with zero learning costs. At the same time, the IntraLayer team will continue to expand the number of chain ecosystems available for dApp connections, providing developers with unlimited potential opportunities. In summary, the IntraLayer architecture cleverly achieves the infinite effect of developers being able to develop once and interact with the entire network. Developers can easily expand the application scope like upgrading in a game, while focusing on core business to reduce costs, greatly improving development efficiency.
3) Brings about synergistic effects through deep integration
IntraLayer deeply integrates Supra's built-in oracles, VRF, and native cross-chain functions, all of which have their own advantages. However, IntraLayer's unique design lies in its vertical integration of these three solutions within the same decentralized secure network. Through this "deep integration," each function can fully leverage synergistic effects. For example, oracles and VRF can share the security infrastructure, significantly reducing costs. At the same time, cross-chain verification can be directly based on oracle results, improving verification speed. This means that IntraLayer, while maintaining the expertise of each solution, achieves nonlinear growth in overall performance. For developers, this vertical architecture also reduces development complexity. They can focus on business module development on a single platform, rather than dealing with complex interaction details. In short, IntraLayer's strength lies in its full utilization of the synergistic effects of each function through deep system integration, creating significant value for both users and developers.
4) Achieves cross-chain interconnection for smart contracts through a hub-and-spoke architecture
IntraLayer adopts a hub-and-spoke network architecture pattern with Supra at the center, a design named the "hub-and-spoke model." As the core of the network, Supra serves as the connecting link between various blockchains. Developers can deploy smart contracts to the Supra platform through a simple one-time integration. Subsequently, whether developers wish to spread the contract to any chain currently connected to IntraLayer, such as Ethereum, Aptos, or future connected new chains, they can be deployed in a one-time manner. This "hub-and-spoke" model greatly simplifies the difficulty of cross-chain application development. Developers no longer need to write ported contracts for each target chain to achieve interconnection. Meanwhile, by continuously increasing the number of connected chains, Supra also provides unlimited expansion space for developers, accelerating the formation of the value chain in the Web3 ecosystem. In summary, through its "hub-and-spoke" architecture, Supra efficiently achieves the interoperability and interconnection capability of smart contracts across multiple chains, with developers requiring only one integration, contributing to the interconnection of Web3.

Source: Supra Official Website
In summary, IntraLayer eliminates the gap between blockchain networks, organizing them into a unified business collaboration network. It is a key middleware for achieving blockchain interoperability and serves as the infrastructure driving the large-scale implementation of Web3.
3.3. Project Process
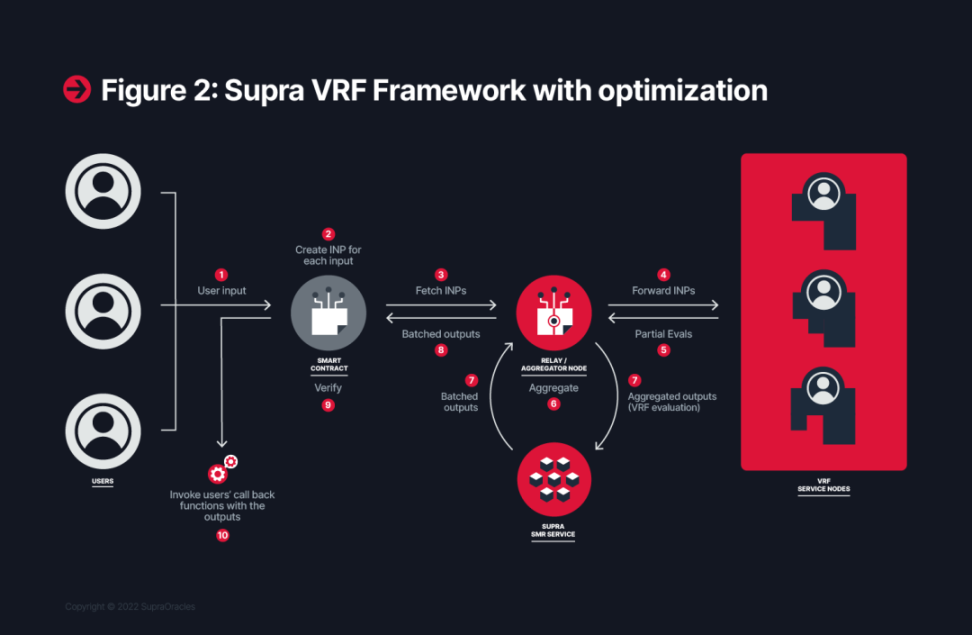
After understanding the principles of the Supra project, let's briefly summarize the operation process of Supra to deepen the understanding of the project. The operation process can be divided into the following steps:
1) Data Acquisition Phase
- Supra's decentralized oracle network is composed of multiple nodes responsible for obtaining data from the external world.
- Each oracle node retrieves the same type of data from multiple external sources, such as obtaining BTC prices from multiple exchanges. The purpose of obtaining data from multiple sources is to avoid the risk of a single point of failure.
- Supra uses the Verifiable Random Function (VRF) algorithm to generate random numbers and allocate data sources to each node using these random numbers. This ensures that all data sources are captured by the nodes without missing any.
- After receiving the allocated external data sources, each node initiates data retrieval to obtain the latest data at millisecond intervals.
2) Data Verification Phase
After obtaining external data, the nodes perform verification, including: a. Checking the correctness of the data format; b. Detecting and filtering out invalid and abnormal data; c. Comparing with the node's local historical data and removing data with significant deviations.
Cross-validation is performed between different nodes. Each node compares the data it has obtained with the data obtained by other nodes and makes corrections if significant errors are found.
3) Data Aggregation Phase
- After data verification is completed, each node enters the data aggregation phase.
- Nodes collect the results of data from all external sources and calculate a representative data value. Calculation methods include taking the median, arithmetic mean, etc.
- Supra uses consistency distance and representative value algorithms to further optimize the results of data aggregation, ensuring their convergence within the normal value range.
4) Data On-Chain Phase
- Nodes package the calculated aggregated data into transactions and broadcast and verify them through the Supra blockchain network.
- Supra's SMR service (Supra does not participate in the validation work of other chains, but it accurately and continuously tracks the validation status of each block being processed on other chains) assigns a global sequence to the data and writes it on the chain, ensuring the integrity and determinacy of the data written on the chain.
- Once the data is written on the chain, it is available for external dApps to query and use.
5) Data Application Phase
Smart contracts can read the on-chain data and process it according to predefined logic. For example, triggering decentralized lending and trade settlement.
Supra's VRF service can generate secure random numbers, supporting on-chain gambling, NFT lotteries, and other applications.
Through the Hypernova bridgeless cross-chain transmission protocol, data and assets can be securely transferred to other blockchains.
In conclusion, through technological breakthroughs, Supra achieves efficient and secure external data acquisition and application in blockchain networks, serving as a key infrastructure for driving the implementation of the Web3 world.
3.4. Project Ecosystem
As a new generation oracle and blockchain middleware infrastructure, Supra's product line covers various aspects such as oracles, random numbers, cross-chain, and automation services, supporting multiple scenarios for blockchain applications, mainly with the following uses:
1) Oracle Use Cases
In decentralized finance scenarios, Supra's oracles can securely obtain real-time external price data, such as cryptocurrency and fiat currency exchange rates, stock market prices, commodity prices, etc. These data are crucial for DeFi projects such as algorithmic stablecoins, prediction markets, options trading, lending protocols, etc. Compared to traditional oracles, Supra has higher performance and security, contributing to an improved user experience for DeFi applications.
A. CBDC and Public Chain Interoperability: Supra can help central bank digital currencies achieve secure interoperability with public chains, providing essential support for cross-chain DeFi and asset pricing.
B. NFT Financial Realization: By collecting and analyzing NFT-related data, Supra can help NFT unlock its financial potential, benefiting content and creator earnings.
C. Serving Private Chains: Supra can effectively connect public and private chain ecosystems, serving government and enterprise-level private chains.
D. Reducing Data Provider Costs: Data providers can achieve more efficient cross-chain ecosystem connections through Supra, bringing more commercial value.
In summary, Supra is not only a high-performance and secure oracle product, but more importantly, as a decentralized infrastructure, it addresses practical issues in Web3.0 through various advantages, better serving CBDC, DeFi, GameFi, NFT, and other broad fields, which is of significant market significance for Supra.
2) Random Number Functions (VRFs)
As an important infrastructure, Supra's developed Verifiable Random Function technology can generate secure random number sequences for games, which is crucial for blockchain games requiring fair randomization, improving user participation experiences in lottery activities, and creating unique NFTs.
A. Specifically, Supra's VRF allows game developers to easily implement various random mechanisms. For example, fair random player matching in games, random drop game rewards, designing random NFT attributes, etc., all effectively enhance user participation experiences.
B. Furthermore, compared to relying solely on a central server, Supra's decentralized VRF design can effectively ensure fair game rules, avoiding unfairness caused by third-party server issues.
C. It is worth noting that Supra has deep cooperation with multiple well-known game projects, utilizing its VRF service. This fully validates the reliability and advantages of Supra's technology in this application area.

Source: Supra Official Website
Overall, as an important GameFi infrastructure, Supra's exploration of VRF random number technology and industrial applications will continue to promote the quality improvement of blockchain game services.
3) Cross-Chain Support
HyperNova is Supra's original "bridgeless" cross-chain communication protocol. It enables native seamless interconnection of cross-chain assets through cryptographic information from the source chain to the target chain.
A. Based on HyperNova, developers can build dApps compatible with multiple public chains using a consistent programming interface. There is no need to focus on the details of data transmission between relay nodes, only on the business logic. For example, HyperNova can support cross-chain game player cross-server functionality, or the integration and release of NFTs from different chains, expanding user groups.
B. Furthermore, HyperNova can also empower the development of various complex applications, such as automatic execution of cross-chain lending protocol liquidation logic, CBDC and public chain open interfaces, DID identity recognition based on blockchain and off-chain open interfaces, etc.
C. It can even integrate traditional financial APIs, such as cross-border remittances or supply chain finance, etc.
In conclusion, HyperNova naturally integrates multiple chain and intermediary function modules. This greatly reduces the difficulty of cross-chain development, empowering developers to innovate applications and promote the global development of Web3.

Source: Supra Official Website
4) Decentralized Automation Services (IFTTT)
Supra supports event-driven If This Then That (IFTTT) workflow automation mechanisms, enabling a wide range of automation application scenarios.
A. In terms of liquidity management, IFTTT can easily accomplish complex position rebalancing logic, including setting stop-loss and take-profit orders based on price fluctuations, achieving liquidity synchronization between multiple exchanges, etc. This helps institutions manage risks more scientifically and efficiently.
B. Additionally, Supra supports the development of automated trading strategies, such as automatically placing trading orders based on trend analysis, or adjusting fund allocation based on asset prices and trading pairs recommendations, quantifying and high-frequencyizing DeFi strategy.
C. Furthermore, IFTTT can also empower the automation of cross-chain asset management and lending business. For example, when the value of custodied assets reaches a certain standard, it automatically completes loan or profit distribution and other complex business processes, comprehensively reducing the cost of human involvement.
D. Finally, Supra's cross-chain bridge also supports the integration of enterprise applications with on-chain IFTTT rules, enabling traditional enterprise workflows to link to the blockchain, achieving initial automation transformation.
Overall, Supra's IFTTT functionality can deeply promote the full automation of DeFi operations and management, bringing great convenience to finance and enterprises.
5) Conclusion
Supra not only provides single technical capabilities such as oracles and random numbers but also supports flexible combinations of two or more capabilities to better meet different business needs. In addition, Supra's technology covers multiple verticals such as finance, gaming, and enterprise automation. It not only provides essential infrastructure for the development of DeFi but also promotes GameFi and digital business. Overall, as an all-in-one infrastructure platform, Supra's mature technical system, rich application scenarios, and strong integration capabilities provide first-class technical service guarantees for various industries. The proactive development of the Supra ecosystem also indicates its long-term commitment to basic research and development, driving the sustainable development of Web3.0. The future holds promise for Supra to explore new application scenarios with more partners.

Source: Supra Official Website
3.5. Project Data
According to the official information released, the Supra project is currently in the mainnet Alpha phase, and its core products, the oracle DORA and the Verifiable Random Function DVRF, have been deployed on multiple public chains. The specific data is as follows:
1) Oracle DORA
- Supported on over 40 testnets
- Successfully launched on 13 mainnets
- Supports connection to 120 external data sources
- Provides over 1.6 million data updates to the chain daily
- Data latency is 5-6 seconds, with the optimization target being 2-4 seconds
Each data update contains approximately 50 data units. In other words, Supra obtains and verifies over 65 million data units for the blockchain daily, making it the oracle with the highest data volume in the industry.

Source: Supra Official Website
2) Verifiable Random Function DVRF
- Deployed on over 25 testnets
- Successfully launched on mainstream public chains such as Arbitrum, Base, Optimism, DFK Chain, Doge Chain, Klaytn, etc.
- Technical collaborations with multiple GameFi applications
- Supports fair random game and other application scenarios

Source: Supra Official Website
3) Key Services to be Launched
- HyperNova cross-chain communication protocol
- Decentralized automation service IFTTT (IFTTT is a decentralized automation service that allows users to create and execute cross-chain automated tasks based on their needs and conditions)
From the above data, it can be seen that Supra's products have entered the implementation phase and are not just at the conceptual stage outlined in the whitepaper. Its oracle product's data volume also reaches the highest level in the industry, demonstrating outstanding performance. These factors reflect the project's technical strength and product sincerity. If it continues to innovate its products, expand its ecosystem, and enhance user experience, Supra is poised to become an excellent middleware service provider in the blockchain world, driving the integration of Web3 into the real economy.
4. Track Space and Potential
4.1. Track Overview
4.1.1. Track Positioning
Supra belongs to the middleware project in the field of blockchain infrastructure and has dual functions of oracles and cross-chain, which determines that it targets two specific tracks: oracles and cross-chain.
4.1.2. Track Scale
1) Oracles
According to CoinGecko's data as of November 10, 2023, the total market value of the oracle track is $93.73 billion, accounting for 0.64% of the entire cryptocurrency market. As a crucial channel for connecting on-chain and off-chain data, oracle technology is increasingly mature and widely used in fields such as DeFi and GameFi. With the deepening of Web3.0 applications across various industries, it is expected that the demand for off-chain data will become more diverse, and the value of oracle services will be further demonstrated, leading to a continuous expansion of the market size.
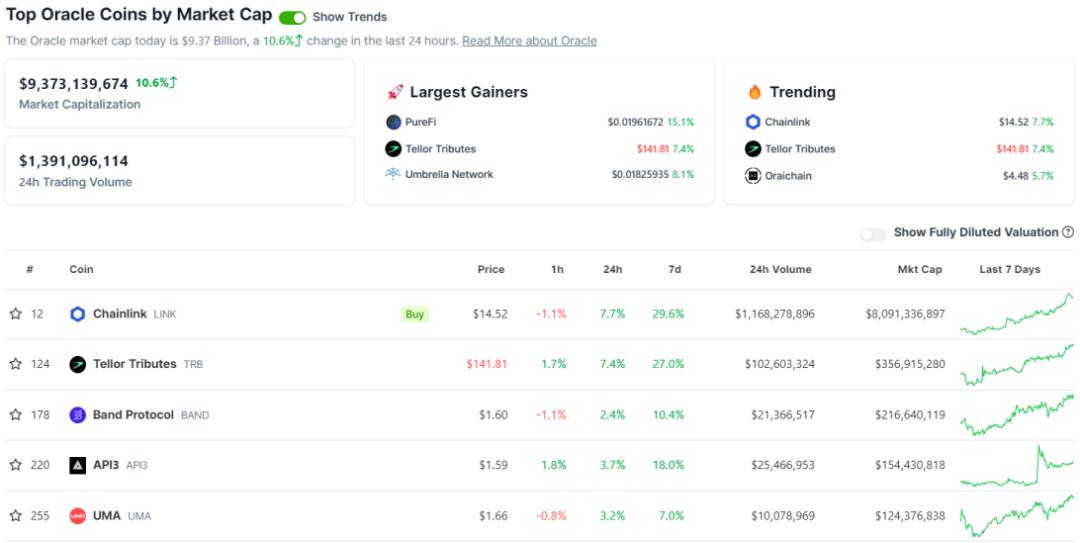
Source: Coingecko
2) Cross-Chain
According to CoinGecko's data as of November 10, 2023, the total market value of the cross-chain track is $16.67 billion, accounting for 0.11% of the entire cryptocurrency market. Cross-chain technology facilitates interoperability between different chains, promoting the development of commercial applications in the cross-chain field, especially in DeFi. As the scale of cross-chain ecosystem alliances expands, the corresponding infrastructure demand will continue to grow, leading to a continuous expansion of the cross-chain market size.
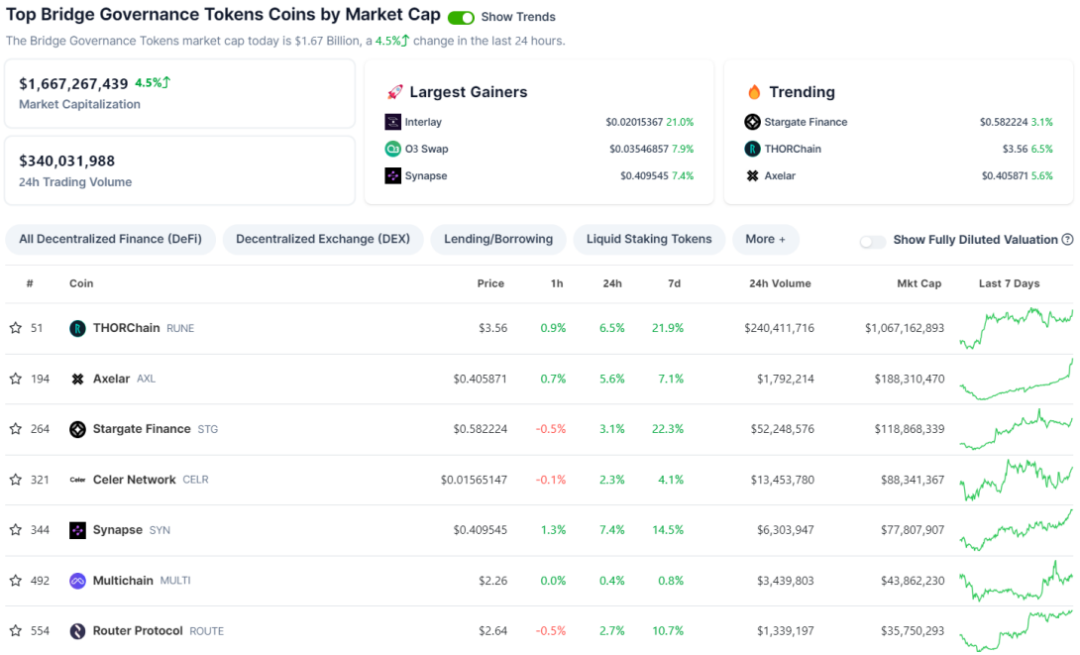
Source: Coingecko
4.1.3. Track Landscape
1) Oracle Track
Oracles are essential bridges for blockchain interaction with the external world. The main competitors in the oracle track currently include:
① Chainlink: Chainlink is the world's largest oracle network, with a vast node computing resource and extensive collaborative projects. It is widely used in the DeFi field and is one of the data sources for mainstream algorithmic stablecoin price benchmarks. Chainlink supports various data formats, but its network nodes are relatively centralized.
② Band Protocol: Band Protocol incentivizes high-quality data provision through token economic design and supports various types of data sources. Nodes need to stake BAND tokens to provide data services. Band Protocol's data can be tracked and verified on the blockchain, ensuring data transparency.
③ API3: API3 has built a fully decentralized oracle network, connecting chains and external APIs through Airnode oracle nodes. API3's advantage lies in the high decentralization of its oracle nodes, with no centralization risk, but its network scale is relatively small.
④ DIA: DIA achieves decentralized financial data acquisition by building an open financial data index and oracle network. DIA uses token incentives to mobilize community forces, but currently, its data sources are relatively limited.
⑤ Tellor: Tellor uses a PoW consensus mechanism to verify data, avoiding trust issues associated with centralized oracles. However, PoW can lead to certain performance and efficiency issues, and Tellor's application scenarios are relatively limited.
Overall, Chainlink remains the leader in this track, occupying a dominant position. Other competitors are also striving to open up the situation through technological or application innovations, but there is still a certain gap to truly challenge Chainlink's position.
2) Landscape Evaluation
The reasons for Chainlink's dominant position in the oracle field include its first-mover advantage in entering the field, strong network effects from its numerous project integrations, especially in occupying important DeFi application scenarios, and becoming a supporter of mainstream algorithmic stablecoins. This greatly enhances its influence. In addition, Chainlink's node threshold is relatively high, and Validators are more concentrated, coupled with support from multiple institutions, including SWIFT, and a strong community influence, laying the foundation for its leading position. However, relying solely on the first-mover advantage is difficult to maintain a monopoly in the long term. On-chain security is always the most critical consideration, which is also the entry point for latecomers like Supra. As the security risks of monopolistic positions become increasingly prominent and the industry's demand for interoperability and scalability increases, whether Chainlink can continue to maintain its dominant position in the future will also depend on how it responds to these challenges. Emerging competitors like Supra have the opportunity to challenge the status quo through technological and scenario innovations, which will also mutually influence the direction of industry development and demand trends.
3) Cross-Chain Track
Cross-chain technology is still relatively early. According to CoinGecko's classification statistics, the projects with a large market value in the cross-chain field currently include:
① Polkadot: Polkadot is a heterogeneous multi-chain architecture that connects various specialized chains through a relay chain to facilitate asset circulation between chains. It has strong scalability but can only perform cross-chain operations within its own ecosystem.
② Cosmos: Cosmos supports the interaction of independent blockchains through the IBC protocol, enabling communication and asset transfer between different chains. Currently, the Cosmos ecosystem is in rapid development.
③ Ren: Ren enables permissionless exchange of encrypted assets between different chains through Darknodes. It is currently mainly used for BTC cross-chain, but there is a centralization risk.
④ Celer: Celer Network focuses on building a cross-chain technology stack for payments and applications. Its cross-chain solution emphasizes fast asset conversion.
⑤ Multichain: Multichain supports the cross-chain transfer of over 20 mainstream blockchain assets, with simple operations suitable for asset transfers, but it only focuses on the asset level.
⑥ Connext: Connext provides cross-chain communication and asset transfer solutions for Layer 2, but it is still in the early stages, and its ecosystem needs to be enriched.
4) Cross-Chain Landscape Evaluation
Currently, Cosmos and Polkadot, as pioneers in cross-chain infrastructure, have certain advantages in ecosystem development. However, major public chains are developing their own cross-chain capabilities, leading to a competitive landscape. Compared to asset cross-chain, data and state cross-chain are more challenging, posing industry pain points. Security and performance are considered key indicators of cross-chain project quality. In addition, the lack of unified cross-chain standards and coordination mechanisms also increases industry uncertainty. Overall, cross-chain technology, as a new and innovative field, is still in its early stages and faces numerous challenges. As application scenarios continue to expand, the demand for interoperability will also increase. There is still significant room for optimization in cross-chain technology and standards, which also brings enormous potential for rapid development and new growth points in the industry.
4.2. Competitive Analysis
4.2.1. Core Competitive Factors
As two important tracks in Web3, the core competitive factors for oracles and cross-chain include performance, security, decentralization, scalability, and cost.
- Performance: Refers to the throughput and response latency of oracle and cross-chain systems, directly impacting their ability to support large transaction volumes and complex application scenarios.
- Security: Relates to the system's ability to withstand various attacks, serving as the foundation of user trust.
- Decentralization: Reflects the fairness of system management.
- Scalability: Determines whether the system can adapt to the expanding ecosystem.
- Cost: Affects the ability to reduce usage costs and improve efficiency.
The superiority or inferiority of these indicators determines the competitiveness of oracle and cross-chain projects in the market and applications. Only by comprehensively and excellently addressing these issues can products rooted in reality and recognized be cultivated. It is also the direction that each project needs to focus on for continuous optimization and innovation. Only by continuously optimizing products according to demand can a strong position be consolidated in these two important tracks.
4.2.2. Competitive Advantages
Based on the previous analysis and considering Supra's network characteristics, the competitive advantage analysis of Supra can be conducted from the perspective of the core competitive factors mentioned above.
1) Higher TPS and Millisecond-level Response Time
Supra adopts an optimized network topology structure, capable of processing tens of thousands of requests per second, leading the industry. Through the use of the BFT state machine replication protocol and algorithm optimization, Supra's oracle response latency can reach the millisecond level, significantly outperforming similar products. This provides extremely fast data access services for smart contracts. In comparison, other oracle projects such as Chainlink require multiple request responses, leading to increased latency and costs. Orion Protocol also requires multiple matching executions, facing similar latency cost issues. Overall, Supra focuses on improving oracle throughput and response efficiency, achieving outstanding performance through technical optimization, which is an important advantage in its technological development.
2) Higher Security, Use of Threshold Signatures and Cryptographic Mechanisms
Supra adopts a "tribe-clan" structure, tolerating up to 51% Byzantine faults. It utilizes threshold signatures and multiple aggregator mechanisms, significantly enhancing its resistance to attacks. Through random shuffling and verifiable random numbers, Supra effectively prevents node collusion and economic incentive attacks. Its distributed aggregation and verification mechanism also ensures the security and credibility of data. In comparison, other oracle projects such as Chainlink rely on data source nodes, potentially facing issues of unreliable data. Band Protocol and API3 also rely on third parties, posing risks in data transmission and verification. Overall, Supra's design principles, which emphasize both distribution and cryptography, have provided a clear advantage in ensuring oracle security, which is also a significant feature of Supra's technological development.
3) Verifiable Random Numbers, Support for On-Chain Games and Applications
Supra utilizes distributed verifiable random function technology to generate high-quality random numbers, providing reliable support for random shuffling, games, NFTs, and other processes. Through decentralized verifiable random algorithms, Supra can generate provably reliable random numbers as needed, benefiting the fairness of on-chain games. In comparison, other oracle projects such as Chainlink lack dedicated random services, or the quality of random numbers is questionable. Overall, Supra places importance on the application of random numbers and optimizes their security and reliability through technical means such as DVRF. This sets it apart in ensuring the fairness of smart contracts in the industry.
4) Localized Design for Better Support of Asset Cross-Chain
Supra adopts a local oracle network, decoupled from external services, significantly reducing cross-chain transaction costs and latency, better supporting asset circulation. Supra uses the "bridgeless" protocol HyperNova to achieve native chain identification and verification between source and target chains, without relying on intermediary nodes for cross-chain communication, increasing security and reliability. In comparison, other projects such as Chainlink often rely on bridge nodes, facing risks of cross-chain instability. Overall, Supra demonstrates a clear advantage in supporting efficient cross-chain capabilities through network topology and protocol optimization.
5) Economically Efficient, Significantly Reducing Computational Costs
Supra utilizes technologies such as batch verification and zero-knowledge proofs to greatly reduce on-chain computational loads. According to tests, its gas costs are approximately 30% of the industry average, significantly reducing usage costs.
Overall, Supra has comprehensively addressed the three major challenges of performance, security, and cost through technological innovation, demonstrating core competitive advantages in the competitive arena.
4.3. Token Economic Model Analysis
4.3.1. Token Total Supply and Distribution
Supra's native token is $SUPRA, with a total supply of 10 billion, of which 3% is allocated for public sale. Calculated at an issuance price of $0.01, the public sale amount is $3 million, resulting in a market value of $100 million.
4.3.2. Token Value Capture
The $SUPRA token is mainly used for network governance, payment of network service fees, and has the following values:
A. Governance Rights: Holding tokens for network governance and participation in decision-making. B. Service Usage Rights: Payment of network service fees to obtain service usage rights. C. Discount Benefits: Token locking to obtain network service discounts. D. Data Access Rights: Payment of data access fees to obtain data usage rights. E. Proof of Work Rights: Serving as proof of work in the network to receive profit sharing.
4.3.3. Core Demanders of Tokens
A. Node Operators: Need to stake tokens to provide network services. B. Developers: Need to pay tokens for using network services. C. Data Consumers: Need to pay tokens to access data services. D. Investors: Obtain network income and decision-making power. E. On-chain Users: Pay tokens for using on-chain services.
5. Preliminary Value Assessment
To conduct a preliminary assessment of Supra's value, the following questions can be analyzed:
5.1. Core Questions
In which stage of operation is the project? Is it in the mature stage or in the early to middle stage of development?
From the current situation, the Supra project is still in the middle stage of development:
A. Product and technology development is continuously being optimized. For example, while DVRF has been demonstrated on multiple mainnets, features such as the HyperNova cross-chain protocol and the IFTTT automation service have not been fully rolled out.
B. In terms of user coverage, Supra has not truly entered the stage of widespread application. Currently, user experience and product maturity still need to be strengthened.
C. In terms of market recognition, Supra's popularity is not as high as that of pioneers like Chainlink, and there is still a need to strengthen product and marketing efforts.
D. In terms of funding, although strategic financing has been secured, the scale is relatively small compared to the support of large single funds entering the mature stage.
E. In terms of personnel recruitment, Supra still needs to recruit more talents in project management and marketing operations.
Overall, Supra is currently in an important development period of technological and application innovation, and it needs to strengthen product optimization, ecosystem consolidation, user cultivation, and funding support to truly enter the mature stage and achieve widespread application.
What are the main variable factors in the project's operation? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
A. User Volume: The number of active users, contract calls, etc., directly impact the scale of Supra's operation. These factors can be easily quantified through Dapps, on-chain data, etc.
B. Development Activity: Code commit volume, issue resolution efficiency, etc., reflect development capabilities. These indicators can be tracked through platforms such as Github.
C. Number of Applications: The number of supported Dapps directly determines the usage scenarios of Supra. Counting can be done through official channels.
D. Quality of Ecosystem Development: The strength of partners, investment in the ecosystem fund, etc., indirectly impact development. It is difficult to measure accurately and requires qualitative description.
E. Market Share: The proportion of application scenarios and technological advantages relative to competitors. Estimation requires comprehensive data from multiple sources.
Most of these important variable factors can be quantitatively analyzed through publicly available channels, with a few supplemented by qualitative analysis, contributing to a comprehensive assessment of Supra's project operation.
What is the project's management and governance approach?
Currently, Supra's management and governance approach follows a relatively traditional centralized development decision-making model. In the future, it may consider moving towards a decentralized direction, but this would need to be based on the maturity of technology and the ecosystem. The daily operation and product iteration of the project are managed and decided by the core development team. Additionally, product roadmaps and technical directions are periodically announced after being deliberated by the development team. In the future, a DAO may be established for token holders to participate in some governance decisions.
5.2. SWOT Analysis
5.2.1. Project Strengths
The project's strengths are detailed in the Core Investment Logic section.
- Backed by an excellent research and academic background team
- Independently developed innovative data acquisition and cross-chain communication technology solutions
5.2.2. Project Weaknesses
- The product is still in the testing phase: As an emerging blockchain infrastructure provider, Supra's biggest risk lies in the fact that its core products such as oracles and cross-chain solutions are still in the testing and continuous optimization phase, and have not yet formed mature commercial products. Specifically, these products need to be fully checked and iteratively upgraded in different practical scenarios in terms of performance, security, usability, and other indicators, and there are limited user cases at present. Whether they can truly meet user requirements is still to be verified. In addition, from technical products to commercial operations, a complete business system needs to be established, including market promotion, sales channels, customer service, etc. All of these test the team's commercial operation capabilities. In summary, due to the core products of Supra being in the testing and continuous iteration phase, compared to mature commercial solutions, its success faces a certain degree of uncertainty. Product maturity and commercialization capabilities are the main risk points for Supra at present.
Limited User and Application Coverage Needs Expansion: As an emerging oracle and cross-chain infrastructure provider, another core risk that Supra currently faces is the low user coverage and the need to expand application scenarios. So far, Supra has achieved initial applications on some test networks, but compared to its leading competitors, its user base and application scenarios are still relatively limited. How to quickly gain a user base and application support will directly impact its business prospects. Specifically, Supra needs to continue to increase integration efforts in major ecosystems, strive for support from more leading applications, and expand its user base. At the same time, it needs to identify more differentiated application scenarios, such as enterprise-level solutions, to expand the scope of solutions. In terms of user groups, in addition to the developer community, it also needs to actively cultivate end users, establish brand awareness, and reputation. In summary, the limited user base and single application scenario are currently one of Supra's weaknesses. Expanding user coverage and application scope is a risk point that the Supra team needs to address, requiring continuous technological innovation and business development capabilities.
5.2.3. Project Opportunities
Urgent Need for High-Quality Oracles and Cross-Chain Solutions by Many Public Chains: Oracles and cross-chain functionality are becoming increasingly important for public chains, which is an inevitable trend for the development of each chain. However, most mainstream chains currently have limited capabilities in this regard, with low-quality oracles and single reliance on third-party cross-chain channels, causing many inconveniences for business applications. As a project that independently develops cross-chain infrastructure, Supra not only leads the industry in oracle performance and security but, more importantly, provides a secure and efficient communication bridge across multiple chains. This means that Supra can help major public chains further improve themselves, open up new possibilities for applications, and meet the urgent pain points in the chain industry. Supra has gained significant business opportunities by satisfying the urgent needs of the chain industry, which will also be an important driving force for its sustainable development in the future.
Strong Demand for Blockchain Infrastructure: The current stage of blockchain technology is accelerating towards the application phase, and there is an urgent demand for blockchain infrastructure such as oracles and cross-chain solutions. This provides an important development opportunity for Supra. With the rise of large-scale applications such as DeFi, GameFi, Metaverse, the demand for external data is rapidly increasing, requiring faster and more secure oracle services. At the same time, assets and data need to circulate between different chains, leading to an increasing reliance on cross-chain solutions. It is foreseeable that as blockchain application scenarios flourish, the demand for middleware layer services will continue to grow rapidly. This provides broad development space for infrastructure providers like Supra. With its technological advantages, Supra is expected to seize opportunities and gain a larger market share in the oracle and cross-chain fields. As the product gradually improves and matures, Supra will also be able to quickly acquire a user base through integration with major leading applications. Once it forms large-scale use cases, it will generate strong attraction, accelerating its commercialization process. Blockchain infrastructure construction is in a rapid development stage, and Supra has a unique first-mover advantage.
5.2.4. Project Threats
Competitive Advantage of Competitors and User Inertia: As an emerging force in the oracle and cross-chain fields, Supra's biggest competitive threat lies in facing resource-rich first-mover advantage competitors and user inertia towards existing solutions. Specifically, the leading company in the oracle industry, Chainlink, has accumulated a large number of users and partners across major ecosystems. This not only brings significant network effects to Chainlink but also enhances user dependency and stickiness to its services. Disrupting its established market position will be a long-term effort. Additionally, blockchain users and developers tend to have certain habits and prefer to use validated solutions, leading to new entrants like Supra needing to spend more effort on education and customer acquisition. In summary, the external challenges faced by Supra mainly focus on the resource and channel advantages of competitors and the need to change user inertia towards existing solutions. Overcoming these barriers through technological innovation and quality service is the direction that Supra needs to strive for currently and in the future.
Long Road Ahead for Technological Commercialization Experience: Despite having an advantage in technological development, there is still a long way to go from product maturity to true commercial operation, which is a challenge that Supra currently and in the future needs to address. Specifically, Supra's core technologies such as oracles and cross-chain solutions are still in the testing and continuous optimization phase, with a considerable gap from large-scale commercial use. They need to undergo thorough checks and iterative upgrades in terms of product performance, security, and usability. In addition, from technical products to commercial operation, a complete business system needs to be established, including market promotion, sales channels, customer service, financial management, etc. This requires the company to have strong business operation and management capabilities, as well as significant human and material resources. It can be foreseen that after undergoing a sufficiently long process of technological and commercial iteration, Supra can become a mature commercial solution and company. In this process, the challenges faced by the Supra team are continuous technological improvement and the accumulation of commercialization capabilities. Only by addressing both aspects can it ensure its competitiveness in the market.
5.3. Airdrop Project
Supra is conducting a token airdrop plan through the "Countdown to Blast Off" event, with a total of 400 million $SUPRA tokens. The plan adopts a "learn to earn" socialized gaming model, where players can learn about the latest developments from Supra and have the opportunity to receive $SUPRA for free by completing tasks. So far, nearly 240,000 community members have participated, showing high interactivity. The reason Supra is using this learning-to-earn model for the airdrop is to drive community learning interaction in a fun gaming way, reduce the natural barriers for newcomers through learning, and provide a playable experience for users. At the same time, the airdrop is also a way for Supra to reward and engage the community, effectively promoting the community's increasing activity and growth. Currently, the Supra airdrop plan has been well-received by the community, providing not only an opportunity to learn about the product but also a chance to directly obtain $SUPRA, creating a win-win interactive plan for both new and old users.

Source: Supra Official Website
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




