Layer2 can greatly improve throughput and reduce gas fees through various technical means on top of Layer1, allowing ordinary users to easily use dApps and DeFi services, and enjoy a truly high-speed and affordable blockchain transaction experience. This allows blockchain technology to move towards the commercial application field with millions of users.
What is Layer2?
Layer2 refers to the second-layer protocol built on top of the public blockchain (Layer1), with the aim of expanding the transaction capabilities and application scenarios of the blockchain. Currently, most common Layer2 solutions are built on top of the Ethereum network.
Layer2 achieves this by constructing a second-layer protocol network outside the main chain, where most transactions and executions are completed, and then periodically batched and submitted to Layer1 for verification through various mechanisms.
This can greatly increase the transaction speed of the blockchain and reduce transaction costs. At the same time, Layer2 also inherits the advantages of public chains such as decentralization, security, and privacy.
Why is Layer2 important?
Public chains like Ethereum, as Layer1, provide the infrastructure for decentralization and censorship resistance, but they have limitations in transaction speed and cost. Especially during the bull market when DeFi, GameFi, and NFTs are popular, the network can become congested, and gas fees can skyrocket, making it difficult for many users to use dApps.
We all know that blockchain should be a cheaper and faster way to transact, which is its core value and appeal. But if each transaction costs hundreds of dollars in gas fees, how is it different from traditional payment tools like Visa, PayPal, or wire transfers? Users cannot be attracted to use Web2 if they have to bear higher blockchain transaction costs to avoid 1-3% fees.
This is where Layer2 comes in!
Layer2 can greatly increase throughput and reduce gas fees on top of Layer1. This solves the scalability issues of Layer1, allowing ordinary users to easily use dApps and DeFi services, and enjoy a truly high-speed and affordable blockchain transaction experience. This allows cryptocurrencies to move towards commercial applications with millions of users, rather than just staying in niche areas.
For public chain networks, Layer2 can bring the following advantages:
Expand the transaction capabilities of the blockchain: Layer1, due to the limitation of transaction speed by block time, is difficult to support large-scale commercial applications. Layer2 can greatly increase transactions per second (TPS) to achieve high throughput.
Reduce transaction costs: Operating on Layer2 can avoid the high gas fees of Layer1, making blockchain applications more affordable for more users.
Expand functionality and application scenarios: Layer2 can introduce more features, such as privacy protection, cross-chain operations, and expand the applications of the blockchain.
Improve user experience: The transaction experience of Layer2 can be closer to traditional Web2 applications, making it easier for more non-technical users to use.
Protect Layer1 security: Offloading a large number of transactions to Layer2 can reduce the burden on Layer1 and improve security.

How does Layer2 work: Channels, sidechains, Validiums, rollup
Common Layer2 protocol technologies mainly include the following:
1. Channels (state channels, payment channels)
Channels are the earliest form of Layer2 technology. They allow two or more parties to conduct multiple transactions off-chain without broadcasting each transaction to the entire network. By reducing the number of transactions that need to be processed, it significantly improves the scalability of the blockchain and reduces costs.
For example, the Lightning Network operates on the Bitcoin blockchain as Layer2. Through the Lightning Network, users can quickly make payments between each other and settle many transactions at once without the need to transmit on the main chain each time.
This greatly increases the throughput of the Bitcoin blockchain and reduces transaction costs and waiting time. The user experience is almost the same as traditional payment apps, but with the security and auditability of the blockchain.
2. Sidechains
Sidechains operate independently with their own consensus mechanism and can interact with the main chain. They provide a fast channel for assets to flow between the main chain and the sidechain at specific times.
However, because sidechains operate independently and are not protected by the main chain, they are responsible for maintaining their own security. This requires additional computational power or resources, such as proof of stake (POS) or proof of work (POW) consensus mechanisms.
Currently, well-known sidechain solutions for Ethereum are xDai and Gnosis chains. These sidechains provide a high-speed channel for Ethereum. Developers can use the free nodes of these sidechains to develop dApps.
Although sidechains do not need to submit state data to the main chain, many sidechains still choose to do so to leverage the security of a larger and more decentralized chain.
3. Validiums
Similar to sidechains, Validiums are independently operated blockchains closely connected to the main chain, but they primarily use zero-knowledge proofs instead of traditional proof of work or proof of stake.
While Validiums use encryption technology with zero-knowledge proofs, the difference from zk-Rollup is that transaction data is not stored on Layer1, so Validium can prove the validity and compliance of transactions without exposing real transaction information.
However, like sidechains, Validium also has limitations. Because it does not rely on the security of the main chain, it requires a self-built consensus layer, which places higher demands on developers. Smart contract support is also relatively limited.
In short, Validium is a technology between sidechains and Layer2 Rollup. It has a bridge to the main chain for asset interaction but requires self-assurance of security.
Projects using the Validium Layer2 solution include StarkWare, Immutable X, ApeX, and others.
Rollups – Optimistic Rollup, zk-Rollup
Rollup is the most popular Layer2 technology today, and the basic concept is to package transaction data and submit it to Layer1 in the form of Rollup. It mainly consists of two types:
Optimistic Rollup
Optimistic Rollup is the most widely used Layer2 solution at present, with representative projects such as Arbitrum and Optimism. Its advantage is easy development and deployment, which can quickly attract applications, but it has a certain risk of fraud and requires economic mechanisms to prevent it.
zk-Rollup
zk-Rollup
zk-Rollup uses zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-proofs) to verify the authenticity of transactions, which can be used to improve privacy on the blockchain by allowing verification of transactions without revealing sensitive information about the transactions. The downside is that it is less developer-friendly. Representative projects include zkSync, Polygon zkEVM, and Linea.
The emergence of zero-knowledge proof technology may become a future adoption solution for enterprises, as it allows the transmission of messages to third parties (users) while securely transmitting sensitive data without revealing it.
Differences
Overall, ZK rollups can bring higher efficiency. The biggest difference between Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup is that Optimistic can be directly compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), so anything possible on Layer1 can be directly implemented on Layer2.
To address the EVM compatibility issue of ZK rollups, the zkEVM solution gradually emerged. For information about zkEVM, please refer to "What is zkEVM? What are the projects and airdrops?"
What are the popular Layer2 projects and tokens?
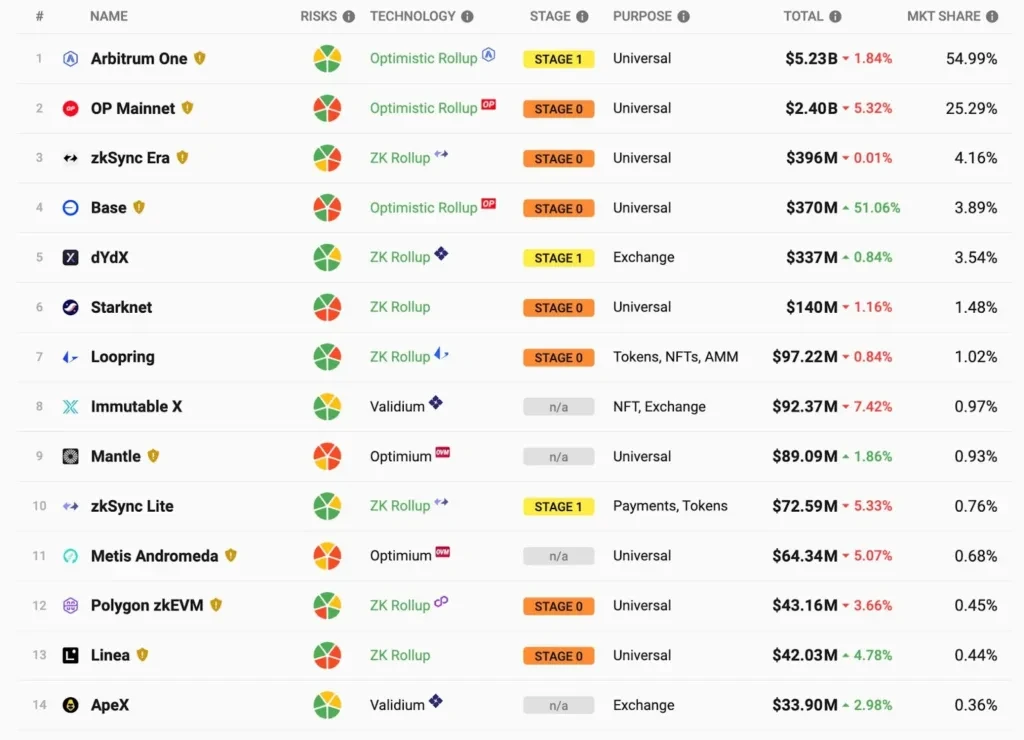
According to the data from the cryptocurrency data website L2BEAT, as of now, Arbitrum and OP Mainner are the projects with the largest locked-in value in the market. Here are introductions to some of the popular Layer2 projects in the market:
Optimism
Optimism is one of the earliest Optimistic Rollup projects in the Ethereum ecosystem, focusing on building an efficient EVM execution environment. Although it has a long development history, it is currently accelerating upgrades and providing a set of developer-friendly software tools called OP Stack.
OP Stack is mainly managed and maintained by Optimism Collective, simplifying the process of creating Layer2 blockchains and significantly reducing development costs. Developers can use the OP Stack toolkit to assemble a customized Layer2 network according to their own needs, and this network is the OP Superchain.
Currently, well-known institutions such as Coinbase, a16z, and BNB Chain have started to create superchain networks based on OP Stack.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: OP
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is Optimism (OP token)? What is OP Stack ecosystem?

Arbitrum
Arbitrum is one of the most mature Optimistic Rollup solutions in the Ethereum ecosystem. It provides high EVM compatibility, allowing Ethereum dApps to seamlessly migrate to Arbitrum Layer2, achieving higher transaction throughput and lower gas fees. ARB is the governance token of Arbitrum.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: ARB
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is Arbitrum token: popular ecosystem introduction, tutorials, investment strategies

Starknet
Starknet is a zk-Rollup type developed by StarkWare, using efficient Stark zero-knowledge proofs to verify Layer2 transactions. Unlike other zk-Rollups, it inherently supports EVM compatibility.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: Unknown
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is StarkNet token: airdrop tutorials, ecosystem introduction

zkSync
zkSync is a representative project of zk-Rollup, created by Matter Labs. It focuses on providing high-speed, low-cost, and private transactions for Ethereum. However, zkSync has recently faced controversy, such as on-chain data falsification and soft rug exit scams.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: Unknown
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is zkSync: token airdrops, operation tutorials, ecosystem introduction

Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM is a zk-Rollup solution launched by the well-known public chain project Polygon, providing dual advantages of EVM and zkRollup for Polygon.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: MATIC
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is Polygon chain: future potential, exchanges, ecosystem introduction, zkEVM development

Scroll
Scroll is another zk-Rollup solution that uses unique ZK nodes to enhance security and focuses on EVM compatibility. Scroll is currently in the final testnet Sepolia and is expected to launch its mainnet later this year.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: Unknown
Mainnet status: In testing
Further reading: What is Scroll chain: token airdrops, operation tutorials, ecosystem introduction

Linea
Linea is also one of the zk-Rollup solution projects, created by the development team behind MetaMask at Consensys, a highly influential Ethereum development company in the market. The network is already preset in the popular wallet Metamask, allowing users to directly interact with it.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: Unknown
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is Linea network: token airdrops, wallet tutorials, ecosystem interaction

Base
Base is an Ethereum Layer2 network launched by Coinbase, supported by Optimism's OP Stack, providing a high-speed, secure, and low-cost transaction environment.
Utilizing the Coinbase team's extensive experience in cryptocurrency products, they have developed a complete ecosystem, providing a new DeFi environment for the Ethereum developer community and existing Coinbase users.
Native token: ETH
Governance token: Unknown
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: CoinBase: What is the Base chain? Are there any airdrops? Wallet tutorials
Mantle
Mantle Network is a Layer2 network launched by one of the top decentralized autonomous organizations in the market, "BitDAO," using the OP Stack technology provided by Optimistic Rollups to provide a faster and cheaper transaction experience than Ethereum, and using modular blockchain design to create greater scalability.
Native token: MNT
Governance token: MNT
Mainnet status: Launched
Further reading: What is Mantle Network: tokens, ecosystem introduction, and its relationship with BitDAO/Bybit?

opBNB
opBNB is a Layer2 solution officially launched by BNB Chain, built with OP Stack, and is an important part of BNB Chain's network upgrade plan, capable of achieving transaction speeds of up to 10,000 TPS. opBNB will significantly enhance the performance of the BNB ecosystem.
Native token: BNB
Governance token: Unknown
Mainnet status: In testing
Further reading: What is opBNB? Are there token airdrops? BNB Chain's L2 scaling solution

Conclusion
It is foreseeable that as ETH 2.0 gradually upgrades, Layer2 solutions will play an increasingly important role. However, the current challenge for blockchain is the lack of actual users.
Although these projects have their own characteristics and are supported by well-known investment institutions, the competition between them will become increasingly fierce, such as OP Stack, ZK Stack, zkEVM series, etc. Perhaps only a few projects may stand out and become the cornerstone of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Of course, as these Layer2 solutions are expected to reshape the use cases of public chains, they have the opportunity to become the foundation that supports the metaverse and the Web3 world in the future. This will also be the key to the widespread adoption and commercialization of blockchain technology.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



