Project Introduction
AltLayer is a decentralized and elastic Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) protocol that enables application developers to quickly launch highly scalable custom execution layers (also known as Layer 2) for applications. It can save application developers a significant amount of capital and development time, while encouraging innovation and rapid experimentation. Additionally, AltLayer supports multiple chains and multiple VMs, with default support for EVM and WASM. Therefore, AltLayer is not confined to a single Layer 1 or Layer 2, but can be used as a modular and pluggable extension solution for all EVM and WASM compatible chains. The project is committed to becoming a key infrastructure in the Ethereum ecosystem to address scalability challenges.
Author
JUMPENG, Senior Researcher at WJB. Master of Finance from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, with 7 years of industry experience. Specializes in areas such as Layer1, DeFi, NFT, Layer2, and Gamefi, having researched over 2000 projects and produced over 500 in-depth research reports.
1. Research Highlights
1.1. Core Investment Logic
AltLayer is expected to become the AWS of the blockchain industry, providing flexible, low-cost, and rapid deployment RaaS solutions for various application scenarios. Here are some of its core investment logics:
Excellent technical development team: This is a key factor in its investment value. The AltLayer team members have deep backgrounds, with most coming from top projects in the blockchain field. Co-founder Yaoqi Jia was a co-founder and CTO of Zilliqa and is an expert in blockchain security. Growth lead Dorothy Liu has previous experience as the head of Synthetix in China. With a team composed of blockchain technology experts, possessing profound industry experience and technical vision, they are capable of designing products that meet market demands and carrying out solid technical implementations. This is an important guarantee for AltLayer to stand out in a fiercely competitive market.
AltLayer has two major technological innovations in product design: codeless deployment and decentralized coordination. AltLayer provides a codeless graphical interface, allowing developers to launch a rollup for their application in minutes without writing any code. This significantly lowers the development threshold, enabling more people to enjoy the benefits of rollup. Additionally, AltLayer has built a decentralized Beacon Layer, which can allocate nodes to provide sorting and verification services for rollup, using tokens as incentives. This further reduces the difficulty of using rollup and enhances overall security. This codeless and decentralized design brings great convenience to AltLayer's RaaS service model, making it highly replicable and applicable to more scenarios. These technical advantages not only create value for users but also drive AltLayer to gain a higher market share and more users.
Clear market positioning and demand: AltLayer is based on the scalability needs of the Ethereum ecosystem, designing products and technological innovations based on the definite direction of rollup technology. It has a high degree of fit with the Ethereum ecosystem, meeting significant and continuously growing market demands. Compared to its competitors, AltLayer has a significant first-mover advantage in the rollup field, which is a very core investment logic. It seizes the overall trend of blockchain development, standing at a positive opportunity point with a very high-quality market positioning. This will be an important foundation for driving rapid growth for AltLayer.
Advanced technical framework design and user-friendly services and products: AltLayer has made significant usability optimizations in product design, providing a very simple and intuitive user experience and interface. These include: - Codeless Rollup launcher, deploying through a graphical interface; - Clear and concise operation processes, easily completing creation and management; - Comprehensive documentation and community support, reducing the learning curve; - Integrated ChatGPT, providing intelligent user guidance; - Support for common wallet access, maintaining user habits, etc. These usability designs greatly enhance the usability of AltLayer's products, enabling different user groups, including non-technical personnel, to easily get started. In addition to directly improving user experience, this will also help AltLayer achieve higher user activity and market penetration. Furthermore, AltLayer has made significant technological innovations in architecture design, achieving a modular and layered technical framework. This configurable design supports high customization, allowing AltLayer to flexibly optimize for different application scenarios. This advanced technical architecture will also ensure AltLayer's scalability, interoperability, and sustainable development in the future. These innovative designs not only directly improve product and service quality but also promote AltLayer to achieve outstanding commercial performance and maintain a leading technological position.
1.2. Valuation
Currently, AltLayer has not disclosed its token model and valuation, so it is not possible to accurately evaluate it.
1.3. Project Risks
The risks of AltLayer mainly come from technical, business, system, and other comprehensive aspects. For details, please refer to section 5.2 Project Weaknesses and Project Threats in this report.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Project Introduction
AltLayer is a decentralized elastic Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) protocol, committed to providing developers with highly customizable and scalable blockchain execution environments. AltLayer allows developers to easily and quickly deploy their own Rollup based on mainstream public chains such as Ethereum, while ensuring security and decentralization. This application-specific Rollup execution layer can be customized based on the actual needs of the project, such as transaction fees, consensus mechanisms, virtual machines, etc. Compared to deploying directly on the public chain or Layer 2 network, AltLayer provides projects with greater flexibility and controllability. Compared to building a standalone chain, AltLayer reduces maintenance costs and improves resource utilization. Additionally, AltLayer has elastic scalability, dynamically allocating resources and verification nodes based on the actual usage of the execution layer. It also provides cross-chain interoperability, allowing assets on the execution layer to seamlessly circulate across different chains.
Overall, AltLayer combines the security of the public chain with the customization of application chains, making it a new type of Rollup-as-a-Service solution. It has the advantages of usability, efficiency, and interoperability, and is expected to become an important infrastructure in the Web3 world, providing strong support for decentralized applications.
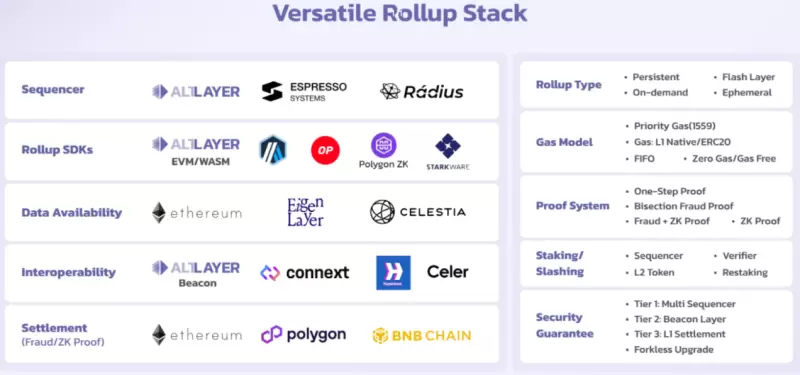
2.2. Team Overview
2.2.1. Overall Situation
AltLayer was founded by multiple senior experts in the blockchain field. Co-founder Yaoqi Jia was a co-founder and CTO of Zilliqa, with extensive experience in technical research and development. In addition to the co-founders, the core members of AltLayer include industry veterans such as Dorothy Liu, who previously served as the head of Synthetix in China. The core team members are highly capable and have unique perspectives on blockchain technology and applications.
2.2.2. Core Members

Yaoqi Jia: Former co-founder and Chief Technology Officer of Zilliqa, and one of Forbes Asia's 30 Under 30 elites. He obtained a Ph.D. in Computer Science from the National University of Singapore and has published several top-tier journal papers in areas such as network security, privacy, and distributed system security. His work has been recognized by multiple suppliers including Google and Apple, and has attracted media attention. He currently hosts advanced system seminars at the National University of Singapore and is involved in a network security research group.

Tan Jun Hao: Co-founder and CEO of AltLayer, an experienced blockchain developer and entrepreneur. He was a core developer at Synthetix, responsible for developing and maintaining smart contracts and front-end projects. He also served as a senior software engineer at Kyber Network, participating in the development and optimization of decentralized exchanges.
2.3. Financing Situation
On July 1, 2022, AltLayer completed a $7.2 million seed round of financing, led by Polychain Capital, Jump Crypto, and Breyer Capital. Participants in the investment included Gavin Wood, the founder of Polkadot, Balaji Srinivasan, former CTO of Coinbase, Sean Neville, co-founder of Circle, Kain Warwick and Jordan Momtazi, co-founders of Synthetix. The funding will be used to expand its existing team of around 10 people to approximately 25 people and to launch its platform later this year.
On August 4, 2022, Binance Labs announced that it had invested in four outstanding projects, including AltLayer, KiloEx, Kinza, and Sleepless AI, but did not disclose specific details.
2.4. Past Development and Roadmap
2.4.1. Past Development
Date Event
2022-07-01 AltLayer completed a $7.2 million seed round of financing, led by Polychain Capital.
2022-08-24 AltLayer will host Dark Forest on its game-specific execution layer and hold a Dark Forest community round.
2022-10-01 AltLayer launched the Alpha developer network, allowing developers to deploy Solidity contracts and test cross-chain solutions.
2023-04-27 AltLayer's RaaS solution (Rollups-as-a-Service) supports L3 blockchain Arbitrum Orbit.
2023-05-05 AltLayer announced the launch of a multi-sorter testnet Rollup, promising to alleviate the review system and enhance the security and usability of Rollup.
2023-07-21 AltLayer announced the use of Celestia's Data Availability (DA) layer to address data availability issues and verify Rollup status in a trustless manner.
2023-07-27 AltLayer announced the deployment of over 100,000 Flash Layers as part of Altitude Phase 3.
2023-08-04 Binance Labs announced investments in four outstanding MVB VI projects, including AltLayer.
2023-08-17 AltLayer partnered with ARPA Network to integrate its on-chain verifiable random number generator Randcast.
2023-08-24 AltLayer will integrate the Sovereign SDK to optimize its Rollup.
2023-08-28 AltLayer announced the addition of OP Stack support to its rollups suite, allowing DApps to quickly launch through AltLayer's codeless rollup platform.
2023-08-30 Automata and AltLayer will collaborate to develop modular proof L2 Automata 2.0.
2.4.2. Current Progress
AltLayer has made progress in the following areas:
• In transaction sorters, AltLayer has implemented decentralized consensus, MEV prevention, and shared sorter clusters. However, the penalty mechanism and cross-rollup messaging functionality are still under development.
• In the runtime environment, AltLayer has supported EVM and WASM, but Solana and Move environments are still in development.
• In verification, AltLayer has implemented fraud proofs using the two-phase method, but fraud proofs in the mainnet environment are still under development.
• In multi-chain support, AltLayer has supported chains such as Ethereum, but Solana support is still in development.
• In the front-end, AltLayer has developed interfaces for deployment, asset settlement, and ChatGPT integration.
• The Rollup SDK is still under development.
In addition, AltLayer has provided performance test reports, case studies, testnet overviews, FAQs, tool resources, and community support documents.
Overall, AltLayer has made smooth progress in core infrastructure such as transaction sorting, runtime environment, and multi-chain support. Advanced features such as penalty mechanisms, cross-chain messaging, and mainnet fraud proofs are still under development. Front-end development and documentation support are also steadily being rolled out, and AltLayer is progressing towards its goal of creating a professional RaaS platform.
2.4.3. Development Plans and Roadmap
In addition to completing the ongoing technical features, AltLayer has the following plans:
• Plans to launch its testnet in the second half of 2023, allowing developers and users to experience the functionality and advantages of its RaaS protocol.
• Plans to launch its mainnet in the first half of 2024, officially launching its RaaS protocol services, allowing developers and users to deploy and use its execution layer and applications.
• Plans to launch its cross-chain bridging service in the second half of 2024, allowing the transfer and communication of execution layers and applications across different underlying chains.
• Plans to launch its governance DAO in the first half of 2025, allowing community members to participate in protocol governance and decision-making using native tokens.
• Plans to launch its ecosystem incentive program in the second half of 2025, allowing developers and users to earn protocol rewards and incentives using native tokens.
2.5. Social Media Data
As of September 2, 2023, AltLayer has performed well on social media platforms, indicating high project popularity. The main operating channels for the project include Twitter, Discord, Telegram, and Medium. Currently, AltLayer's Discord account has attracted nearly 550,000 followers, with a daily online presence of nearly 10,000 people, making it one of the most popular channels. Additionally, the Twitter updates have frequent interactions. The specific data for each platform is as follows:
Media Channel Twitter Discord Telegram Medium
Followers 448,701 552,010 3,675 7,600
Online/Active Frequent updates 9,907 895 7 updates
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
To address the scalability issues faced by blockchain, various scaling solutions have been proposed by the community, including sidechains, state channels, Plasma, etc. Among them, Rollup technology, which increases throughput by batching transactions and moving computation off-chain, is considered one of the most promising paths. Rollups are mainly divided into two categories: Optimistic Rollup, which ensures security through fraud proofs, and ZK Rollup, which uses zero-knowledge proofs to verify transaction validity. Despite improving scalability, Rollups still face challenges such as high development complexity, environmental constraints, resource wastage, and reduced composability.
To address these pain points, AltLayer has emerged as a Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) protocol. It provides a decentralized framework that allows developers to easily launch and manage dedicated Rollup execution layers. Compared to deploying directly on-chain, AltLayer gives developers greater flexibility and control, mitigates the risk of significant transaction fee fluctuations, and achieves low latency and high throughput. It also helps internalize transaction fees for tokens, providing more practical use cases. AltLayer makes it easier to develop Rollups and integrates its economic design into the protocol, aiming to become a flexible and efficient Rollup infrastructure that provides strong support for decentralized applications.
3.2. Project Principles
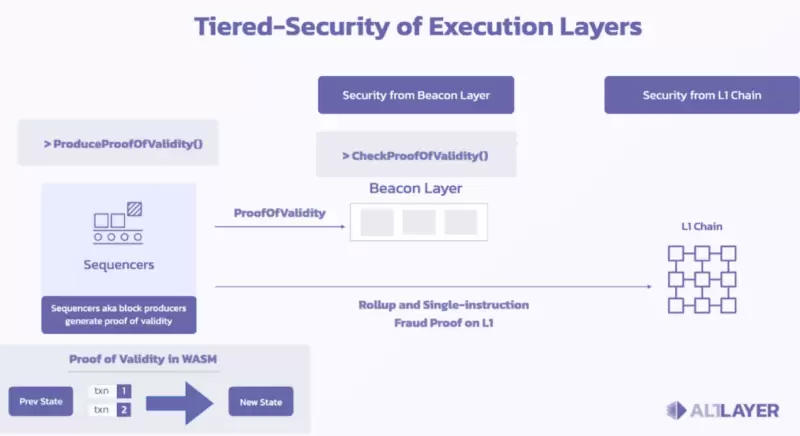
AltLayer utilizes Optimistic Rollup technology to build a fast and scalable application chain layer that can be easily deployed on public chains while ensuring security. It supports EVM and WASM and serves as a flexible scaling solution, providing support for different public chains and applications.
Due to its reliance on Optimistic Rollup technology, AltLayer is also compatible with ZK-Rollup technology. To facilitate understanding, let's first explain the working principle of Optimistic Rollup:
Running an execution environment (such as EVM or WASM) on Layer2, allowing users to deploy and execute contracts on Layer2 and send and receive transactions.
Running a sequencer node (also known as a sequencer) on Layer2, responsible for collecting user transactions, packaging them into blocks in a certain order, and submitting the block's hash and state root to the smart contract (also known as the validator contract) on Layer1.
Running a validator contract on Layer1, responsible for receiving and storing the block's hash and state root submitted from Layer2, providing a fraud proof mechanism for anyone to challenge and verify blocks on Layer2.
Establishing a bridging protocol between Layer1 and Layer2, allowing users to transfer and exchange assets and data between the two layers. The bridging protocol typically requires a certain delay period (also known as the challenge period) to ensure that blocks on Layer2 are not challenged or proven invalid.
In summary, the operation of Optimistic Rollup involves batch processing transactions on L2 without the need to process each transaction on-chain, and then periodically submitting this batch transaction data to the Ethereum mainnet. The Ethereum mainnet is only responsible for checking the validity of the submitted data without the need to execute each transaction. This design significantly increases transaction throughput and reduces gas costs.
AltLayer has made some innovations and optimizations based on Optimistic Rollup, including:
• Building an independent sequencer network, Beacon Chain, responsible for sorting Rollup transactions.
• Developing core components using the Substrate framework from scratch, supporting EVM and WASM execution.
• Supporting interaction with multiple public chains as a general scaling solution.
• Introducing a disposable execution layer: AltLayer allows developers to start and dispose of execution layers as needed, optimizing resources and composability. This new concept of a disposable execution layer allows developers to launch an execution layer in a short period of time when demand surges, complete transactions on the execution layer, and settle assets on Layer1 once demand decreases. This model is suitable for short-term use cases such as NFT minting and gaming activities.
In specific terms, AltLayer divides the transaction lifecycle into aggregation, block generation, and verification:
The aggregator collects transactions from different channels, timestamps, and sorts them, and then submits the batched transactions to the block producer according to load balancing requirements.
The block producer selects the transaction order, locally executes these transactions, and generates new blocks. AltLayer defaults to using a single producer mode to achieve low latency, but can also configure multiple producers to increase decentralization. Consensus among block producers is achieved through the GRANDPA consensus protocol.
Validators first verify the newly generated blocks for validity, then periodically generate block data packets and submit them to the main chain. Before submission, validators need to generate transaction and instruction-level state roots for on-chain verification. Validators are also responsible for fraud proofs and dispute resolution.
AltLayer provides layered transaction finality guarantees, including execution-level, verification-level, and aggregation-level, allowing users to choose finality requirements based on their security needs. After the challenge period ends without disputes, the block is confirmed as final.
AltLayer also has a Beacon layer, serving as a shared distributed sorting node cluster. When a user requests to launch a Rollup, the Beacon layer selects sorting nodes to provide services based on the nodes' staking weights.
Considering the potential for disputes in OP-Rollup execution, AltLayer uses a binary search method to gradually narrow down the scope, efficiently resolving disputes.
In summary, AltLayer supports multiple chains and processes transactions in three steps: aggregation, block generation, and verification. It uses a single or multiple producers to achieve consensus in block production. Validators not only verify blocks but also submit data to the main chain. It offers three levels of finality, allowing users to choose the desired security level. Additionally, it has a shared sorting node cluster in the Beacon layer and uses a binary search method to efficiently resolve disputes in OP-Rollup execution.
Overall, AltLayer combines the high performance and scalability of Optimistic Rollup with its own customization and portability. It provides a flexible scaling framework for different chains, allowing dynamic resource adjustments while ensuring security. This technical design makes it a highly valuable and feasible Rollup-as-a-Service solution.
3.3. Project Technical Features
The main technical features of the AltLayer project include:
• Modularity: AltLayer's modular design allows for customization for different applications. It separates different functions and components, allowing developers to choose and combine based on their needs and preferences. AltLayer provides various customization options and templates, allowing developers to choose different deployment types, virtual machine types, data availability modes, sequencer modes, etc.
• Elasticity: Elastic scalability and efficient resource utilization. AltLayer can dynamically adjust and optimize its parameters and mechanisms based on different network and market conditions. It can adjust its deployment type, data availability mode, sequencer mode, etc., based on Layer 1 data availability and Layer 2 transaction demand. Additionally, it can adjust its service fees, staking rates, reward distribution, etc., based on user feedback and community voting. For example, developers can choose to start a Flash Layer during high traffic to increase throughput and close it during low traffic to save costs.
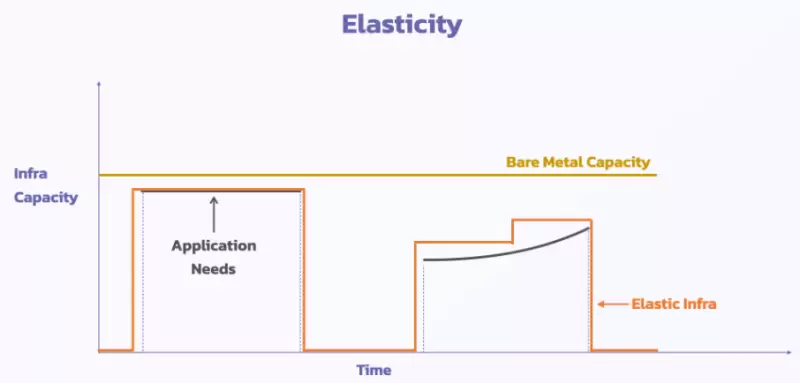
• Multi-Virtual Machine Support: Providing developers with more choices. AltLayer can support different virtual machine types, such as EVM and WASM. This allows AltLayer to be compatible with different smart contract languages and applications, such as Solidity, Rust, C++, etc. It also enables developers to use different virtual machine types on the same Rollup for increased flexibility and efficiency.
• Fraud Proof: Built-in fraud proof mechanism to ensure security. AltLayer can use cryptographic methods to ensure the correctness of Layer 2 transactions without relying on challenge periods or zero-knowledge proofs. AltLayer uses a fraud proof scheme based on RSA signatures, requiring sequencer nodes to provide a signature when submitting data to prove its correctness. If someone discovers that a sequencer node has submitted incorrect data, they can provide a fraud proof, i.e., a counterexample transaction, to prove that the sequencer node's signature is forged. This allows AltLayer to improve efficiency and reduce costs without sacrificing security.
• Decentralized Sequencer: Increased reliability. AltLayer implements a decentralized sequencer through the Beacon Layer, allowing anyone to join the network as a sequencer and have the opportunity to be selected to serve dedicated launch programs. This increases network security and decentralization while providing incentives for sequencers.
• Layered Finality: Balancing security and performance. AltLayer adopts a layered finality mechanism, allowing Layer 2 transactions to achieve finality in a short time, while Layer 1 transactions require a longer wait, improving user experience and efficiency while ensuring Layer 1 security. This allows AltLayer to balance the trade-off between efficiency and security.
• Codeless Dashboard: Simplifying Rollup deployment. AltLayer provides a codeless dashboard (Rollup Launchpad) that allows non-professional developers to easily create and launch their own Rollups. The codeless dashboard offers various customization options and templates, allowing users to choose different deployment types, virtual machine types, data availability modes, sequencer modes, etc., through simple clicks and drags. It also provides common application scenarios and examples, such as games, NFTs, social media, enabling users to quickly deploy and run their applications.
3.4. Beacon Layer
The Beacon Layer is one of the core components of AltLayer, providing coordination and verification functions between the execution layer and data availability layer. The Beacon Layer offers the following main services:
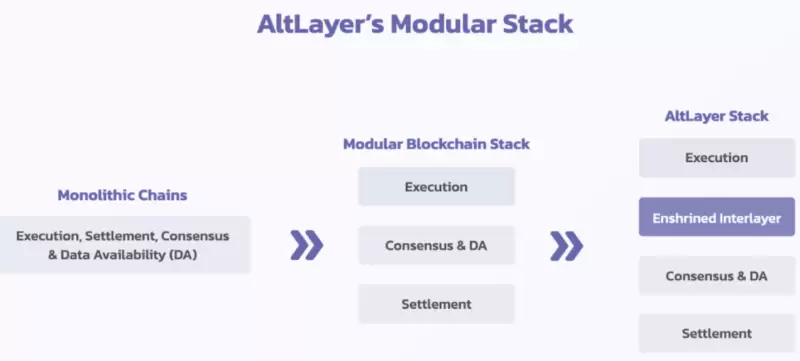
• Shared Sequencing Layer: The shared sequencing nodes in the Beacon Layer provide transaction sequencing services for Rollups in AltLayer. It is the bottom layer of the Beacon Layer, a decentralized network where anyone can join as a sequencer to collect and execute Layer2 transactions, and submit block headers and Merkle roots to the smart contract on Layer1. The shared sequencing layer uses a staking/slashing mechanism to incentivize and penalize sequencer behavior, ensuring network security and activity.
• Verification Layer: Verification nodes are responsible for verifying transactions in Rollup, ensuring the security of the execution layer. The Beacon Layer provides a verification layer for AltLayer, allowing non-professional developers to create and launch their own Rollups through a codeless dashboard and be serviced by dedicated sequencer nodes allocated by the Beacon Layer. The verification layer uses a data availability sampling (DAS) based verification scheme, allowing Layer 2 verifiers to verify transaction correctness without downloading or storing all Layer 1 data, but by randomly sampling a portion of data from the Beacon Layer network. The verification layer also provides a fraud proof mechanism for verifiers to punish sequencer nodes and restore the correct state of Layer 2 when incorrect data is discovered.
• Staking/Slashing Layer: The Beacon Layer provides a staking/slashing layer for AltLayer, allowing users to participate in the staking and slashing of the AltLayer protocol by holding the native token. The staking/slashing layer uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) based staking/slashing scheme, allowing users to stake the native token into the Beacon Layer network to receive corresponding rewards or losses. The staking/slashing layer also provides a dynamic adjustment mechanism for users to adjust their staking rates and rewards based on network and market changes.
• Interoperability Layer: Enables easy cross-chain transfer of assets on Rollup. The Beacon Layer provides an interoperability layer for AltLayer, allowing users to perform cross-layer transactions and data transfers between different Rollups or other Layer 2 solutions. The interoperability layer uses a Hyperlane-based interoperability scheme, allowing users to utilize Hyperlane's cross-chain protocol for permissionless interoperability. The interoperability layer also provides a cross-chain bridging mechanism, allowing users to utilize Biconomy's meta-transaction service for cross-chain transactions without holding or paying any tokens.
• Upgradeability Layer: Smoothly upgrades various components of the Beacon Layer. This is the fifth layer of the Beacon Layer, a centralized layer composed of smart contracts on Layer1, where each smart contract can upgrade various sub-layers of the Beacon Layer based on social consensus. The upgradeability layer uses governance tokens to achieve social consensus, ensuring network flexibility and adaptability. It also provides a compatibility guarantee mechanism for developers to upgrade and optimize without affecting users and applications.
• Social Consensus Layer: Governance on-chain based on ALT holders' voting, etc. This is the top layer of the Beacon Layer, a decentralized community of AltLayer Token holders, where each holder can participate in the governance and upgrade of the Beacon Layer. The Social Consensus Layer uses a voting mechanism to achieve social consensus, ensuring network democracy and fairness.
3.5. Rollup Types on AltLayer
AltLayer provides two types of Rollups: Flash Layer and Persistent Rollups.
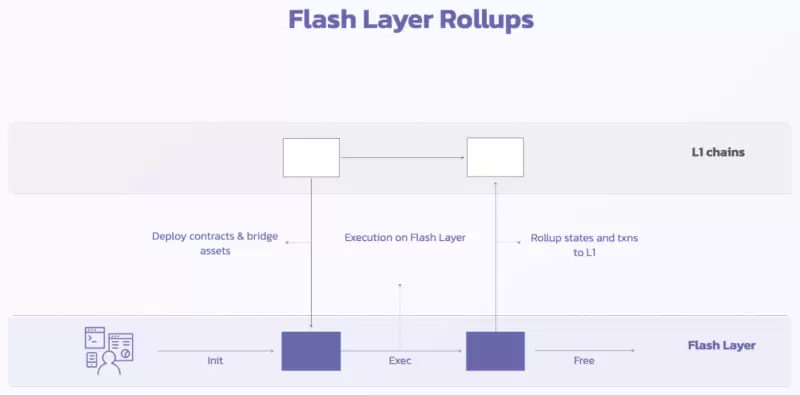
3.5.1. Flash Layer Rollups
The Flash Layer is a temporary, one-time rollup provided by AltLayer, with optional fraud proof. It can be quickly created when there is a short-term surge in dApp demand, such as during airdrop events. The Flash Layer can rapidly scale to prevent congestion on the base chain, and after the event, it can transfer states and assets back to the base chain and then be deleted to release resources. The Flash Layer provides an instant scaling solution to avoid the waste of maintaining a chain or contract permanently, utilizing the advantages of rollup to provide elastic scaling. It has the following characteristics:
• Deposit/Withdrawal Not Required: Users can use the services of the Flash Layer without depositing or withdrawing funds on Layer1. They only need to use their wallets and wallet addresses and signatures on Layer1 to transact on the Flash Layer.
• No Challenge Period Required: The Flash Layer does not need to set a challenge period to prevent fraud because it uses a trust-based mechanism. Users can only transact with sequencers they trust, and if a sequencer cheats, users can arbitrate on Layer1 and receive compensation.
• No Data Publication Required: The Flash Layer does not need to publish data to Layer1 to ensure security. It uses a signature-based mechanism, allowing users to transact on the Flash Layer using their wallet addresses and signatures on Layer1. If a sequencer loses data, users can provide evidence on Layer1 and receive compensation.
3.5.2. Use Cases of Flash Layer Rollups
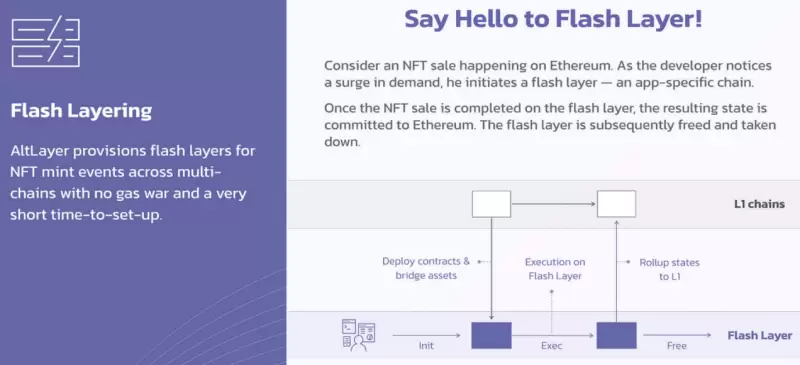
1) NFT Mint Event
One of the suitable use cases for AltLayer is NFT mint events. Since NFTs are usually limited in supply, each NFT mint event leads to a short-term surge in high TPS demand, resulting in a large number of transaction failures and network congestion. In the past, general chains provided a shared block space model, often leading to a popular dApp consuming too much block space, resulting in poor user experience for other dApp users due to high fees and settlement times.
AltLayer proposes an elastic scaling solution to better meet the short-term high TPS demand of NFT projects and alleviate the long-term burden. AltLayer can flexibly allocate resources based on dApp requirements, addressing the impact on dApp experience due to resource competition in a single network.
Specifically:
• Rapidly launch a Layer1-secured Rollup solution during peak dApp usage.
• Mitigate the risk of congestion on Layer1 using Rollup.
• Settle and clear on Layer1 after the Rollup task ends.
This model customizes an independent Mint layer for each NFT project. In addition to eliminating congestion, it provides an exclusive high-throughput, low-latency environment, significantly improving user experience. Overall, it optimizes resource allocation, covering NFT short-term peaks, balancing efficiency and cost, and truly achieving demand-driven upgrades.
AltLayer offers the following advantages:
• Automatic Settlement: After the NFT mint event ends, the system automatically settles all assets from the Rollup layer to the base chain without user intervention, reducing security risks.
• Multi-Chain Compatibility: Default support for EVM and WASM standards, compatible with a wider range of projects.
• Complete Liquidity: All NFTs automatically drop to the base chain after the mint event, ensuring that participants in the secondary market can find the desired NFT without the need for cross-chain transactions.
• Avoiding Congestion: Each NFT project has a dedicated execution layer, completely isolated from other activities, ensuring productivity.
Through automatic settlement, multi-chain support, liquidity assurance, and exclusive resource sharing, the AltLayer solution helps NFT projects efficiently complete minting while balancing user experience and system efficiency, truly achieving demand-driven upgrades.
2) GameFi
Running blockchain games on-chain faces certain challenges, including:
• Insufficient performance of general public chains to meet the scale and requirements of games.
• Customization required for games to optimize the chain's rules for a better user experience.
• Independent control of the ecosystem for tokens essential to game operation.
In response, AltLayer's Flash Layer solution is excellent:
• Provides dedicated on-chain space for different games, isolating them from interference and ensuring high performance.
• Game developers can customize rules according to their requirements, focusing on the gaming experience.
• After the game ends, assets automatically roll back to the base chain, saving development costs.
It is suitable for two common types of games:
• Short-term event mini-games, such as "kill games." The Flash Layer can start and end promptly after the event.
• Independent small studio-developed standalone games with a short lifecycle, where the Flash Layer starts and ends periodically according to the game's cycle.
In summary, the Flash Layer shields games from on-chain disturbances, reduces costs, truly focuses on the user experience, and is conducive to the popularization of Web3 games.
3.5.3. Persistent Rollups
AltLayer provides persistent and secure rollups, which are application-specific and compatible with EVM and WASM. Persistent rollups are well-suited for long-term applications such as GameFi, SocialFi, MetaFi, and DeFi. Compared to transient Flash Layer, persistent rollups provide a customized execution environment for these long-running applications. They inherit the security of optimistic rollup and have the ability to be parameterized and customized for specific applications, as well as support for multiple virtual machines, making them particularly suitable for the aforementioned long-term applications such as GameFi, SocialFi, MetaFi, and DeFi.
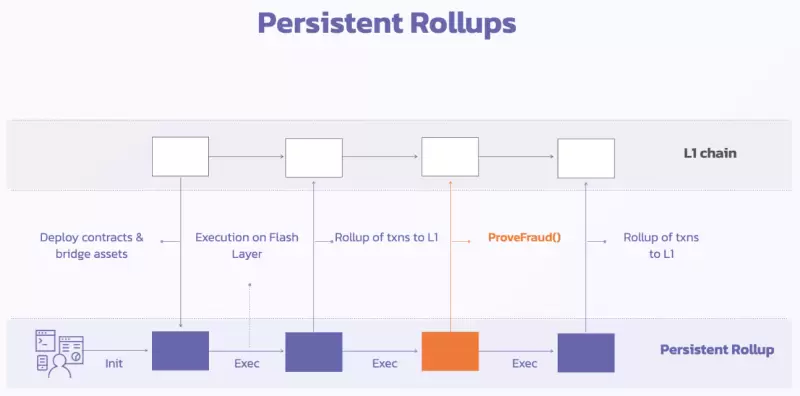
3.6. Ecosystem Collaboration
AltLayer is collaborating with external projects to enhance user experience and data availability. Here are some details about the collaborations:
1) Account Abstraction Using Biconomy
AltLayer uses Biconomy's Meta-Transaction API to achieve account abstraction, allowing users to use AltLayer's services without creating or managing Layer2 accounts. Users only need to use their wallet address and signature on Layer1 to transact on Layer2.
2) Using Celestia for Data Availability (DA)
Celestia is a modular consensus and data network designed to provide a lightweight blockchain framework for anyone to deploy and manage their own blockchain easily. Celestia's core function is to provide Data Availability (DA) layer, ensuring the integrity and accessibility of Layer 1 data. AltLayer can utilize Celestia's DA layer to implement Data Availability Sampling (DAS), allowing Layer 2 validators to verify transactions' correctness without downloading or storing all Layer 1 data, by randomly sampling a portion of data from the Celestia network. This significantly improves Layer 2 scalability and efficiency while ensuring the security of Layer 1.
3) Achieving Permissionless Interoperability with Hyperlane
Hyperlane is a cross-chain protocol based on Optimistic Rollup, enabling fast and cost-effective asset transfers between any Layer2 chains. It uses a cross-chain protocol based on state channels and zero-knowledge proofs, allowing users to perform atomic swaps and generic calls between different blockchain networks. AltLayer uses Hyperlane's cross-chain bridge to achieve permissionless interoperability with other Layer2 solutions, expanding its ecosystem and user base.
3.7. Project Data
According to data released by AltLayer's official Twitter account, as part of the third phase of Altitude, over 100,000 Flash Layers have been deployed. However, since its Testnet and Mainnet have not been officially launched, there are currently no publicly available project-related data such as user numbers, transaction volume, and revenue. Nevertheless, it is anticipated that AltLayer will have significant market demand and potential upon its launch.
4. Industry Space and Potential
4.1. Industry Overview
4.1.1. Project Categories
AltLayer can be classified as a blockchain scalability solution and Web3 infrastructure, specifically as a RaaS protocol.
• Blockchain Scalability Solution: AltLayer is a blockchain scalability solution based on Rollup technology, enabling off-chain transaction execution and on-chain result verification to improve blockchain throughput and efficiency.
• Web3 Infrastructure: AltLayer serves as Web3 infrastructure, providing an efficient, flexible, and secure scalability solution for Web3 applications while reducing development and operational costs and complexity.
• RaaS Protocol: AltLayer is a decentralized and flexible RaaS protocol, allowing application developers to quickly deploy and customize their own execution layer (Layer 2).
4.1.2. Market Size
According to reports on the blockchain technology market, the global blockchain technology market is expected to grow from $34.9 billion in 2020 to $394.6 billion in 2028, with a compound annual growth rate of 48.4%. Scalability is one of the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology and a major driver of market growth. As more applications enter the blockchain space, the demand for efficient, low-cost, and user-friendly scalability solutions will continue to increase. As a RaaS protocol and Web3 infrastructure based on Rollup technology, AltLayer has tremendous market potential and competitive advantages.
4.1.3. Core Competitive Factors
Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) is primarily used to enhance transaction processing capabilities on Ethereum and other public chain networks. The core competitive factors among RaaS protocol products include technical capabilities, product usability, supported features, ecosystem collaboration, decentralization, and performance levels.
Technical Capabilities: The technical team behind the RaaS platform directly determines the quality of its products and services. A team with high technical expertise is more likely to develop higher-performing and more stable solutions.
Product Usability: The convenience and ease of use of the Rollup deployment tools and services provided by the RaaS platform are important. A good user experience can increase developer retention.
Supported Features: The comprehensiveness of supported chain types, virtual machine types, and functional modules is also a competitive factor. The richer the functionality, the wider the applicability.
Ecosystem Collaboration: Different RaaS protocols may collaborate with different public chain platforms, data service providers, developer communities, etc., to build the entire Rollup ecosystem. Ecosystem collaboration determines the market size and influence of the RaaS protocol, as well as affecting customer trust and loyalty.
Decentralization: Different RaaS protocols need to ensure the decentralization of their components such as sequencers, validators, and settlement layers to prevent centralization failure or attack risks. The higher the level of decentralized consensus mechanism and transaction ordering, the better the reliability and security.
Performance Levels: Different RaaS protocols need to ensure the throughput, latency, and other performance metrics of their Rollups to meet increasingly complex business requirements. Performance levels directly impact user experience, with superior performance being more favored.
In addition, network effects, project resource support, and token model design are also influencing factors.
4.2. Track Analysis
Rollups-as-a-Service (RaaS) projects aim to innovate Rollup deployment by providing easy-to-use Rollup development tools and service SDKs, abstracting technical complexities, designing no-code/low-code Rollup construction interfaces, and sharing sequencers to lower the threshold for users, ensure efficient and seamless transaction processing, and provide one-click Rollup rapid deployment solutions.
In simple terms, RaaS is similar to Software as a Service (SaaS). Developers do not need to build the underlying infrastructure themselves. By using RaaS services, they can create and manage Rollups, greatly reducing the threshold for developing and maintaining Rollups. This is similar to the emergence of Amazon Web Services (AWS), which allows enterprises to obtain elastic, convenient, and efficient computing power through cloud services without building their own services and storage infrastructure. Similarly, RaaS provides elastic and scalable Rollup execution layers, allowing on-chain applications to achieve higher transaction throughput and lower usage costs when necessary, giving blockchain applications a significant competitive advantage.
The current competition for AltLayer mainly includes competition with application chain construction facilities and competition among segmented products within the RaaS track.
4.2.1. Competition with Application Chain Construction Facilities
More and more dApps are choosing to build their own application chains to gain greater customization and control, addressing the performance and scalability issues of public chains. Currently, application chains are mainly built on Cosmos SDK, Polkadot, and Avalanche, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. AltLayer, as a cross-chain Optimistic Rollup solution, aims to provide temporary elastic scaling capabilities. When an application chain experiences a short-term surge in demand, it can quickly obtain scaling support using AltLayer without the need to permanently build an application chain. AltLayer allows application chains to migrate their state back to the application chain after scaling, achieving composability with public chains. AltLayer can be seen as a complementary solution for application chains, helping them cope with short-term peaks. Both can coexist and collaborate. Additionally, AltLayer itself can support the construction of application-specific Persistent Rollups, creating some competition with application chains.
Overall, AltLayer provides a new type of scaling and resource optimization solution for application chains through its flexibility and interoperability. While they have different positioning, there is also a competitive-cooperative relationship between the two.
4.2.2. RaaS Track Landscape
The current RaaS projects in the market can mainly be divided into three categories: SDK, no-code solutions, and shared sequencers.
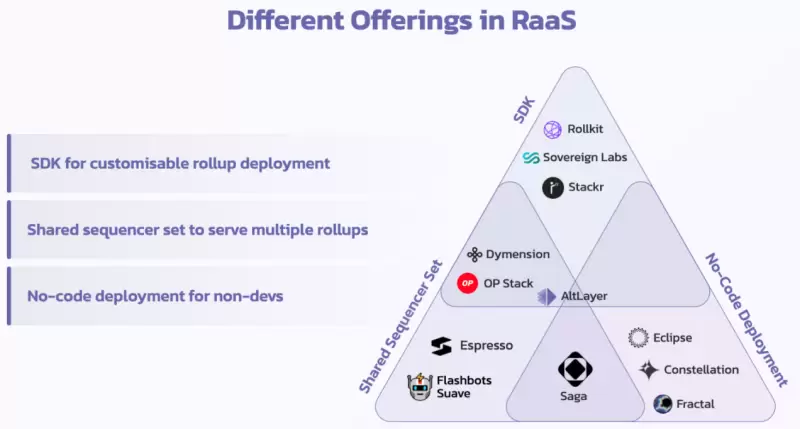
1) SDK
The SDK solution provides developers with a complete set of general software development kits, making deploying Rollups as easy as deploying smart contracts. There are currently various SDKs available to meet different needs and scenarios. Here are some representative SDK projects:
Rollkit by Celestia: It uses Cosmos SDK and communicates through IBC to provide a solution for deploying sovereign Rollups. Developers have complete control over execution and settlement and use Celestia as the data availability layer.
OP Stack: It utilizes OP Rollup technology to organize the network into three different layers: consensus, execution, and settlement. To simplify development, these three layers are standardized through APIs, allowing developers to easily fork and assemble components to meet their specific needs.
RollApp Kit by Dymension: It provides compatibility with various virtual machines, allowing developers to choose from different smart contract platforms such as CosmWasm or Ethermint, or any other platform supported by the Cosmos ecosystem.
Sovereign SDK: It aims to simplify the creation of zk-Rollups, similar to how Cosmos SDK simplified App-chain development. It will be the first Rollup framework to eliminate zero-knowledge complexity, allowing developers to easily build applications without requiring advanced cryptographic skills.
The availability of these SDKs indicates the maturation of the RaaS market, with increasing demand for easy-to-use, user-friendly Rollup deployment solutions. Each SDK offers unique advantages, allowing developers to choose the most suitable one based on their needs and requirements.
2) No-Code Solutions
No-code Rollup deployment solutions aim to make it easier for developers to create and manage Rollups. Current no-code deployment products mainly include:
Constellation: Based on OP Stack, it allows developers to easily customize EVM-compatible Optimistic Rollups, with a block explorer and asset bridging, customizable through options such as block time and account permissions.
AltLayer: It supports Rollup as a service platform for multiple chains and multiple virtual machines, serving as a universal scaling solution for various chains. Each Rollup is customized for a specific application, and the platform is designed to work with multiple blockchains and virtual machines. It supports Ethereum (EVM) and WebAssembly (WASM) for versatility. AltLayer is a flexible scaling solution for all compatible chains, not limited to a single layer1 or layer2.
Eclipse: Based on Cosmos SDK, it provides a customizable Rollup framework for developers to easily customize Rollups suitable for different chains. As a modular blockchain infrastructure, it can provide a universal settlement layer solution for any public chain. It aims to be a universal Layer2 platform compatible with multiple Layer1 blockchains. Currently, Eclipse supports Ethereum Virtual Machine and Solana Virtual Machine.
Caldera: A customizable Rollup framework built on op-rollup, focusing on building high-performance, customizable, and application-specific Layer1 blockchains. These customized blockchains offer high throughput, low latency, and customizable features to optimize the performance and user experience of decentralized applications. Caldera Chains can choose any EVM-compatible chain.
These products provide developers with graphical interfaces and configuration options, allowing them to deploy the Rollup that suits their project needs in minutes without programming. They represent the transformation of Rollup technology towards no-code deployment, significantly lowering the development threshold.
Compared to traditional hand-coding, these no-code Rollup solutions make it easier for developers to independently manage scaling requirements. They have the ability to optimize parameters for specific applications or scenarios. As the industry develops, it is expected that more comprehensive and user-friendly no-code Rollup deployment solutions will emerge.
3) Shared Sequencers
The transaction sequencer is a core component of Layer 2 architecture, aggregating transactions off-chain, generating blocks, and submitting data to the main chain. The solution of shared sequencers involves sharing decentralized sequencing services among multiple Rollup networks. Rollup sequencers are responsible for grouping and compressing transactions, then submitting them to the main chain. This decentralized design enhances the network's resistance to censorship and ensures efficient and seamless transaction processing, enabling the secure and stable operation of the Rollup system.
Currently, most Ethereum Rollup solutions use centralized sequencers. However, some RaaS projects are developing decentralized shared sequencers, including:
Optimism Collective: It provides shared sequencer nodes for the OP Stack chain, managed collectively by Optimism.
Dymension: Based on Cosmos, it is a modular blockchain project aimed at simplifying the deployment of RollApps through Dymension Chain (settlement layer), RDK (RollApp Development Kit), and IRC (Rollup Inter-Chain Communication). Sequencer nodes need to stake DYM tokens in their settlement layer and are elected through voting.
Espresso: It can provide sequencing services for different Rollups. The Espresso Sequencer is designed as a platform that can deploy any zk-VM or optimistic VM. In the future, it can serve as a cross-chain interoperability layer, supporting multiple virtual machines.
The advantage of decentralized shared sequencers is their ability to serve multiple Rollups, improving resource utilization efficiency. They are also more reliable, avoiding single points of failure. Additionally, mechanisms such as staking and POS can ensure the reliability of nodes.
Overall, shared sequencers are a key infrastructure for achieving multi-chain interoperability and cross-chain communication. With the maturity of technology, it is expected that decentralized shared sequencers will gradually replace centralized sequencers, providing strong support for the development of Rollups and Layer 2.
4.2.3. Overall Advantages and Disadvantages of the RaaS Track
The future of the cryptocurrency industry is multi-chain and multi-Rollup, and as more projects emerge, they will seek public chains with higher performance, lower costs, and the ability to provide customized services. The development of RaaS lays the foundation for this trend.
1) From the overall perspective of the RaaS track, RaaS currently has the following advantages:
Greater control and customization: RaaS allows developers to highly customize their own Rollups according to specific business needs, rather than using generic solutions, to meet specific project requirements.
Avoidance of significant fluctuations in transaction fees: RaaS can minimize the risk of sudden increases in Gas fees due to network congestion, allowing developers to avoid the risk of soaring fees.
Achieving low latency and high throughput: RaaS can provide higher transaction throughput and lower network latency, which is particularly important for applications requiring high-frequency trading.
Empowering developers to realize their technical vision: RaaS allows developers to achieve their envisioned product features and user experience within existing constraints.
Internalization of MEV and transaction fee economic benefits: Developers can obtain economic benefits such as MEV and transaction fees through RaaS.
Adding more practical scenarios for tokens: RaaS can design more usage scenarios for project tokens, increasing their value.
Meeting the continuous growth demand for scaling solutions for on-chain applications: With more dApps in use, the demand for RaaS solutions will continue to grow.
2) From the overall perspective of the RaaS track, its disadvantages mainly manifest in the following aspects:
Technical risk: Rollup technology is still developing, with uncertainties, and core technologies such as fraud proof and security need commercial validation. Technical challenges such as multi-chain interoperability and performance improvement also require continuous efforts.
Business risk: The RaaS model needs to validate its commercial viability in practice, and the user base and commercialization path are uncertain. Pricing strategies for track products also need continuous optimization in competition.
Systemic risk: There is a certain degree of centralization tendency, reliability needs to be considered, and there are security vulnerabilities in bridge design. Additionally, fluctuations in the crypto economy may affect ecosystem development, and potential regulatory risks need attention.
Comprehensive risk: The project is still in the early stages of development, and various elements have not fully matured. Continuous iteration and progress are needed in technology, product, and business aspects. Additionally, dynamic changes in competitors, market position maintenance, and uncertainties in funding and talent also exist.
Overall, AltLayer, as an innovative RaaS platform, faces challenges and risks at various levels from technology to business. It needs to maximize opportunities while addressing risks to achieve evolution from concept to commercialization and infrastructure.
4.2.4. AltLayer Competitive Advantages
AltLayer is the only RaaS platform that provides temporary Rollup services. Its Flash Layer allows developers to quickly create disposable Rollups to handle short-term traffic peaks. This avoids wasting resources on building an entire chain for temporary needs.
AltLayer has built a decentralized Beacon layer as a shared sequencer network, making it one of the few RaaS platforms with decentralized sequencers. Decentralized sequencers enhance the security and reliability of Rollups.
AltLayer has implemented fraud-proof mechanisms such as binary fraud proof and has effectively operated on multiple public chains. This ensures the secure execution of AltLayer Rollups and makes it one of the few RaaS platforms capable of running fraud proofs.
AltLayer has been committed to supporting a multi-chain environment from the beginning, while also supporting mainstream virtual machines such as EVM and WASM. This allows developers to flexibly deploy AltLayer Rollups in different networks, positioning it as an industry-leading platform with multi-chain and multi-virtual machine support.
The above content is mainly sorted based on core competitive factors and may be subjective. Readers can evaluate it themselves. It is evident that compared to other RaaS competitors, AltLayer has unique advantages and leading technology in areas such as Flash Rollup, decentralized sequencing, fraud-proof mechanisms, and multi-chain support, making it a comprehensive and technologically advanced RaaS provider.
4.3. Token Economic Model Analysis
4.3.1. Token Total Supply and Distribution
AltLayer has not released token information.
4.3.2. Token Value Capture
Potential value capture for AltLayer tokens:
1) Platform service usage fees: AltLayer, as an RaaS platform, can charge a service fee based on the number of times users use the Launcher to start Rollups, providing a continuous source of income. As the user base and application scenarios grow, this value capture space will continue to expand.
2) Staking and rewards for coordinating nodes: Running consensus nodes on AltLayer's Beacon chain requires staking native tokens. Honest sorting nodes can also earn rewards through block production and fees. This will drive the demand for holding and circulating ALT tokens.
3) Governance rights: Token holders will have voting rights for platform governance. They can participate in formulating important decisions regarding the platform's development direction, economic parameters, new features, etc., giving the tokens regulatory governance value.
4) Additional application scenarios: ALT tokens can be designed for more application scenarios, such as running nodes, accessing data, paying fees, etc., continuously enhancing the token's role in the ecosystem. This provides further expansion possibilities for ALT.
In summary, ALT tokens capture value through platform service fees, consensus mechanisms, governance rights, and additional applications, closely linking them to the growth of the AltLayer platform and providing a sustainable empowerment mechanism.
4.3.3. Core Demand for Tokens
1) AltLayer platform users: The no-code Rollup launcher of AltLayer will attract developers, enterprises, and individual users who need to use ALT tokens to pay for platform usage fees. As the user base and application scenarios grow, this demand will continue to rise.
2) Rollup node operators: Running consensus nodes on AltLayer's Beacon chain will require the use of ALT tokens for staking. Nodes can also earn rewards through block production, driving the demand for holding and circulating ALT.
3) Ecosystem partners: Collaboration with other projects can bring more scenarios, enhancing the demand for ALT tokens. This will also attract more users and funds into the ecosystem.
4) Potential users: With the increasing influence of the platform, more potential users will join, driving the demand for service and node fees.
5. Preliminary Valuation
As an emerging RaaS service platform, AltLayer has a broad market space, currently with a low valuation, and is expected to achieve several-fold growth in the rapidly developing industry.
5.1. Core Issues
At which stage of operation is the project? Is it in the mature stage or in the early to mid-stage of development?
AltLayer, as an innovative RaaS solution provider, is currently in the early stage of development.
1) Product features are still rapidly iterating, mainly using the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach to gather user feedback and iterate the product quickly. 2) The technical framework is also continuously being optimized and improved, with some core components such as consensus mechanisms and cross-chain support needing further strengthening. 3) The user base is still relatively small, mainly consisting of early adopters and tech enthusiasts. 4) There is a need to expand the user base, especially the adoption by application developers. The business model needs further validation, and matters such as pricing strategies and profit methods need to be determined. 5) The token economic model design is still being perfected and needs to be combined with user incentive mechanisms. 6) The project's influence is limited and needs brand building through community development, content marketing, etc. 7) The organization still heavily relies on the founding team and needs to gradually achieve power decentralization and community governance. In summary, AltLayer is in the early stage of rapid growth, with some distance from maturity, but it is in a high-growth track, with promising future potential.
Does the project have reliable competitive advantages? Where do these competitive advantages come from?
AltLayer has the following reliable competitive advantages:
- Early entry into the RaaS field: AltLayer can be considered one of the early explorers of the RaaS model, giving it a certain first-mover advantage in this track.
- Strong technical capabilities: AltLayer is developed by blockchain technology experts, and the team has rich experience in blockchain underlying technology, capable of developing future-oriented technology.
- User-friendly product design: AltLayer has significantly improved product usability, from no-code deployment to user interface optimization. This helps in acquiring users faster and establishing a leading position.
- Technological innovation capabilities: AltLayer has innovated in consensus mechanisms, fraud proofs, etc., maintaining a leading technological position.
What are the main variable factors in the operation of the project? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
- User base growth: The number and activity of users are key variable factors in project operations. Their growth trend can be quantitatively measured through registered user data, active user data, transaction data, etc. User growth is an important indicator of the project's network effect.
- Number of supported public chains: The number of public chains supported by AltLayer reflects the breadth of the project's applicable scenarios. This variable can be directly quantified by counting the number of supported public chains. Its growth will enhance the versatility of AltLayer.
- Transaction volume handled: The number of transactions processed on AltLayer's Rollup reflects resource utilization and service scale. Transaction volume data can be directly obtained from on-chain data. The size of transaction volume is also related to operational income.
- Number of developers: The number of developers represents the recognition of the product by developers. This variable can be obtained by counting the number of registered developer accounts. An increase in the number of developers indicates an increase in platform influence.
All of the above indicators can be quantified and measured, and they are key variables for evaluating AltLayer's operational performance. Their changes are directly related to the project's growth.
What is the project's management and governance approach?
Currently, AltLayer is managed and operated by the founding team, with the core team having decision-making power over the project's strategic planning and technical roadmap. As the project develops, AltLayer plans to gradually decentralize power and implement community governance. In the future, AltLayer will transition to a DAO governance structure, allowing token holders to participate in discussions and voting mechanisms to collectively determine the platform's development direction.
5.2. SWOT Analysis
5.2.1. Strengths
The project's strengths are detailed in section 1.1 Core Investment Logic:
- Excellent technical development team
- Two technological innovations in product design: no-code deployment and decentralized coordination
- Clear market positioning and demand
- Advanced technological framework design and high usability of services and products
5.2.2. Weaknesses
- Early stage of the project: AltLayer's related products are in the development and trial operation stage, and further technological accumulation and market cultivation are needed before large-scale commercial use. The project is in a stage of rapid iteration and requires time to grow and accumulate.
- Limited user base and influence: As a new project, AltLayer's user base is still in the early stages of formation. Its brand influence and industry recognition are limited, requiring product optimization and market promotion to expand the user base.
- Numerous competitors: The RaaS market has many participants, and other excellent teams are also developing similar products. AltLayer needs to continuously optimize its product performance and user experience to maintain competitiveness.
- Limited funding and resources: As a new project, AltLayer's funding and resource allocation are relatively low, which will have a certain impact on the development process. Continuous fundraising is needed to expand resources.
In addition, AltLayer's token economic model has not been disclosed and needs to be validated. Additionally, there are technical challenges in multi-chain interoperability, fraud proof, off-chain performance, etc., which pose risks.
5.2.3. Opportunities
- Strong and continuous demand for public chain scalability: The transaction volume of public chains such as Ethereum is rapidly increasing, creating a huge and continuously growing demand for scalability solutions. This provides ample market space for Rollup solutions.
- Prosperous development of L2 technologies such as Rollup: Rollup technology is rapidly developing and becoming more widely adopted, providing broad demand space for RaaS platforms like AltLayer.
- Rapid growth of the crypto economy: With an increasing number of capital and users entering the space, the crypto economy is experiencing rapid growth. New application scenarios and various dApps are constantly emerging, all of which require scalable solutions, promoting the development of RaaS services and providing huge opportunities for RaaS infrastructure.
- Rapid expansion of user base and increased industry collaboration opportunities: The rapid growth of crypto users will bring a broader user base to AltLayer, making network effects easier to achieve. As the industry develops, the opportunities for collaboration between different infrastructure projects will increase, bringing new cooperation and application scenarios to AltLayer.
5.2.4. Threats
The main threats to AltLayer's project are the challenges currently existing in the RaaS track (see section 4.2.3). In addition, AltLayer also faces some specific threats:
- Challenges from new competitors and the risk of falling behind in technological development: In the rapidly developing field of blockchain technology, AltLayer faces the risk of being surpassed by competitors in technology. As the prospects of the RaaS market are proven, it will attract more competitors to enter this track, putting direct competitive pressure on AltLayer. If AltLayer's pace of technological innovation does not keep up with the industry's forefront, its products and services may be surpassed by competitors. Blockchain technology iterates and updates at an astonishing speed every day, and if AltLayer cannot sustain large-scale investment in talent, funding, etc., its technological accumulation will struggle to keep up with the progress of blockchain technology, leading to competitors catching up with and even surpassing AltLayer's technological advantages.
- Threats of security and technical vulnerabilities and business model validation: AltLayer's RaaS protocol involves various technical and business scenarios, and may encounter some technical challenges and security risks. If security and technical vulnerabilities occur, it may cause user asset losses or exploitation by hackers. The RaaS protocol also needs to undergo thorough testing and validation to prove its feasibility and reliability. Additionally, if AltLayer cannot rapidly expand its user base and its growth rate slows down, its business model will not be validated, and the demand for tokens will be affected. Faced with various competitors, AltLayer needs to continuously expand application scenarios and attract users.
6. References
- AltLayer Project Official Website
- AltLayer Official Twitter
- AltLayer Official Medium
- AltLayer Related Reports on Forkast News
- AltLayer Telegram
- AltLayer Documentation
- Rollup as a Service: A New Era of Blockchain Scalability, the Next Modular Battlefield
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



