最近总能看到各种聊“套利”的,从“无风险年化XXX%”的资金费率,到DeFi挖矿套利组合,再到基础的“搬砖”... 似乎遍地是黄金,弯腰就能捡?
今天就来深挖一下,套利这碗饭,到底香不香,又该怎么吃?
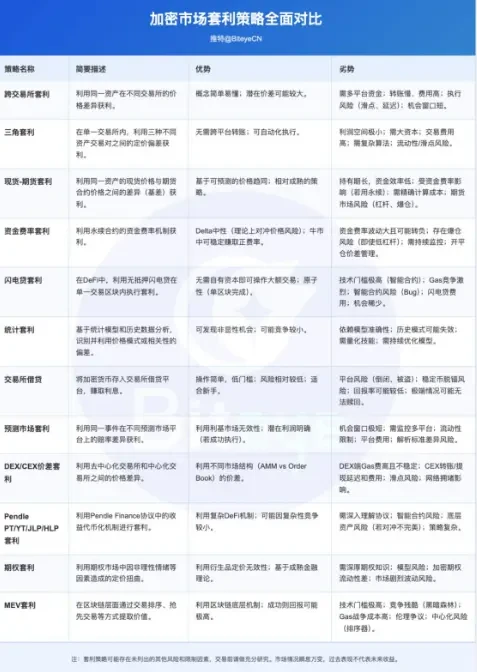
首先,基于KOL观点总结,常见套利策略类型一览
空间套利:跨交易所 (搬砖)
时间/结构套利:资金费率 (期现)、期现基差
利率套利:稳定币/借贷/LP挖矿 (DeFi/CeFi)
跨资产套利:三角套利
DeFi生态套利:跨链、聚合器、闪电贷等
特殊场景套利:预测市场
模型驱动:统计套利 (量化)
其次,KOL套利推文总结
一、节点科学家 (Ø,G) @moncici_is_girl
《币圈套利:如何在加密货币市场中寻找"免费的午餐"?【理论篇】》
提供了一个相对全面的加密货币套利理论框架,覆盖了多种主流策略。
1、跨交易所套利:利用不同交易所(CEX或DEX)对同一币种的价格差异,低买高卖。
2、三角套利:在单一交易所内,利用三个交易对(如BTC/USDT, ETH/BTC, ETH/USDT)之间的汇率定价不平衡,通过连续交易(A→B→C→A)获利。
3、现货-期货套利:利用现货市场价格与期货合约价格之间的基差(Basis)进行套利,通常是买入现货、卖出期货,预期到期时价格趋同。
4、资金费率套利 (永续合约):持有相反的现货和永续合约头寸(如买现货+做空永续合约),主要目的是赚取永续合约的资金费率(当费率为正时)。
5、闪电贷套利 (DeFi): 利用DeFi协议提供的无抵押闪电贷,在单个交易区块内完成一系列套利操作(如在不同DEX间买卖),并偿还贷款。
6、统计套利:基于统计模型和历史数据,识别价格模式或相关性的暂时偏离,进行交易以期价格回归均值。
二、 taresky @taresky
主要面向新手,对比了交易所借贷和资金费率套利。
1、交易所借贷 (理财):最基础、最适合新手的“套利”方式。用户将币存入交易所,由平台借出给他人并管理风险。详细对比了Bitfinex(订单簿)、OKX(暗池竞价)、Binance(暗池匹配)三种模式的特点和利率机制。
2、资金费率套利:通过买入现货+做空等量永续合约来对冲价格风险,从而赚取正资金费率的机制。给出了APY的估算公式:APY = (资金利用率) x (资金费率) x 3 (每天结算次数) x 365。
三、Jemima Conlon
对加密货币套利交易进行了全面梳理和定义,涵盖了从最基础的跨市场价差套利到高级的闪电贷套利。先阐明了套利的基本原理,接着重点介绍了加密领域中几类典型的套利机会:
1、跨交易所套利,包括中心化交易所之间价差(由于不同交易所定价机制不同,可能出现同一资产略有不同价格),以及去中心化交易所之间的价差(由于AMM定价和流动性原因,不同DEX价格可能暂时不一)。
2、三角套利,即通过依次兑换三种代币循环套利,解释了如何利用BTC/ETH、ETH/XTZ、XTZ/BTC三者汇率差完成套利。
3、闪电贷套利:闪电贷利用智能合约允许无抵押瞬时借款,使套利者可以放大操作规模,在一次链上交易中完成复杂套利过程
还强调了去中心化套利相对于中心化套利的优势:成本更低且无需信任托管,因为在DEX之间套利时用户始终掌控自己的私钥。
四、套利老六 @taolige666
在市场不景气、投资者偏好避险资产时,DeFi玩家会更倾向于使用稳定币和Delta中性的产品来理财。几种适合普通用户的稳健套利思路:利用LSD结合对冲赚取无风险利差、通过去中心化永续合约平台对冲波动赚取手续费等,推荐了对应项目/池子。
核心思想是尽量不承担价格波动风险(Delta中性),同时捕捉链上协议提供的收益,例如质押奖励或交易手续费。这样即便在行情低迷期,也能稳定实现两位数的年化回报。
五、林无限SamLam @samsir1997
将套利的本质归结为利用信息差进行“搬砖”,内容可能对“有基础头寸+金融能力的人”更有帮助。包括以下几种套利方式:
1、利率套利 (Interest Rate Arbitrage):以传统外汇为例,借入低利率货币(如日元),兑换并投资于高利率货币(如美元)的资产,赚取息差。
2、USDT与法币套利 (Stablecoin Arbitrage):特指利用不同交易所(如Bitfinex vs Kraken)上USDT对法币(示例中为美元)的价格差异进行买低卖高。
3、正向掉期套利 (Positive Swap Arbitrage):在外汇市场,持有能赚取正隔夜利息(掉期/Swap)的货币对头寸,并通常通过反向现货或其他工具对冲汇率风险。
4、跨市场套利 (Cross-Market Arbitrage):利用同一资产(以外汇对USD/BRL为例)在不同地理市场(如巴西市场 vs 美国市场)的价格差异进行套利。
5、三角套利 (Triangular Arbitrage):在(通常是同一)市场内,利用三种货币(如USD, EUR, GBP)之间的交叉汇率定价偏差,通过连续兑换实现增值。
6、统计套利 (Statistical Arbitrage):基于历史数据分析,发现两种或多种相关资产(如USD/JPY与USD/EUR)之间的价格关系(如价格比),当关系偏离均值时进行反向交易,期待其回归均值时平仓获利。
六、 Aliez Ren @aliez_ren
Aliez Ren 开发了Taoli Tools | 套利工具,核心目的是为对套利感兴趣或正在实践的用户提供一个集中的信息导航和工具箱。按照套利类型进行了清晰分类,主要涵盖了跨所搬砖套利、永续合约资金费套利、套保对冲等等,还包含了基础知识与教程部分。详情:https://renzholy.notion.site/Taoli-Tools-18c64b000c25808e862bd0c61b193eb1
Biteye对套利工具不作背书推荐,仅供参考,DYOR
七、Brak @0xbrak
讨论了套利策略及机制(包括有争议的)
1、资金费套利:跨交易所对冲,赚取费率差。
2、期现套利:利用交割日期货与现货的价差收敛获利(举例BN-0328-BTC期货与现货BTC)。
3、价差套利: 涵盖DEX/CEX价差、三角套利、闪电贷等利用价格直接差异的策略。
4、PT套利 (Pendle): 通过交易Pendle的本金代币(PT),将空投预期换为固定收益,需研究底层资产并对冲非美元PT风险。
5、JLP/HLP套利 (Pendle): 持有Pendle流动性凭证,对冲底层资产风险,赚取手续费、空投奖励等(指出多数人不做对冲)。
6、YT Flow (Pendle): 在判断Pendle收益代币(YT)价格有足够安全边际时买入,博弈未来收益(举例早期$ENA、$USDC挖矿)。
7、期权Flow: 利用期权市场因情绪等因素造成的定价扭曲,通过价差、跨式等策略套利。
8、MEV/科学家流: 在链上通过交易排序(如三明治攻击)等方式提取价值。
八、Pix @PixOnChain
How I Made $100k Arbitraging Between Prediction Markets (Full Guide)
分享的核心策略是预测市场套利,即利用不同平台对同一事件结果给出不同定价(赔率)的无效性来获利,而非赌博。
方法论关键在于:
1、首先,在多个预测市场上寻找同一事件,尤其关注结果较多的市场。
2、找出该事件所有可能结果在各平台上的最低可购入价格并加总;若总成本低于1美元(或100%),则存在套利机会。执行时必须极其迅速,因为价格差异转瞬即逝(“延迟游戏”),推荐使用自动化工具,在相应平台买入所有结果的最低价份额以锁定利润。
倾向于选择预期年化收益率(APY)高的机会(如>60%),并且不一定持有到期,若持有的所有份额组合的市场卖出价高于成本,会考虑提前退出以提高资金效率。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



