The supply of Ethereum continues to grow, with an annual growth rate of 0.805%. Despite the burning of a large amount of ETH, the issuance still exceeds the amount burned.
Written by: Lawrence, Mars Finance
Introduction
As the world's leading smart contract platform, Ethereum has attempted to achieve deflationary goals since the introduction of the burning mechanism through EIP-1559.
However, as of April 13, 2025, research shows that its supply is still growing at an annual rate of 0.805%, increasing by 3,477,830.85 ETH, despite burning 4,581,986.52 ETH. This report analyzes this phenomenon from a research perspective, exploring the historical context, current dynamics, influencing factors, and future outlook.
Historical Context
The London hard fork introduced EIP-1559, changing the way transaction fees are managed. Previously, all transaction fees were rewards for miners; under the new mechanism, the base fee is burned, and the remaining "tip" is distributed to validators (previously miners before the merge). This mechanism aims to counteract the inflationary effect of new ETH issuance, ultimately making ETH a deflationary asset.
The merge in September 2022 transitioned Ethereum from PoW to PoS, significantly reducing the issuance rate. Before the merge, miners received about 13,000 ETH daily; after the merge, based on approximately 14 million ETH staked, the issuance dropped to about 1,700 ETH/day. This change laid the foundation for achieving deflation, but the actual effect of the burning mechanism depends on network activity and fee levels.
Current Supply Dynamics
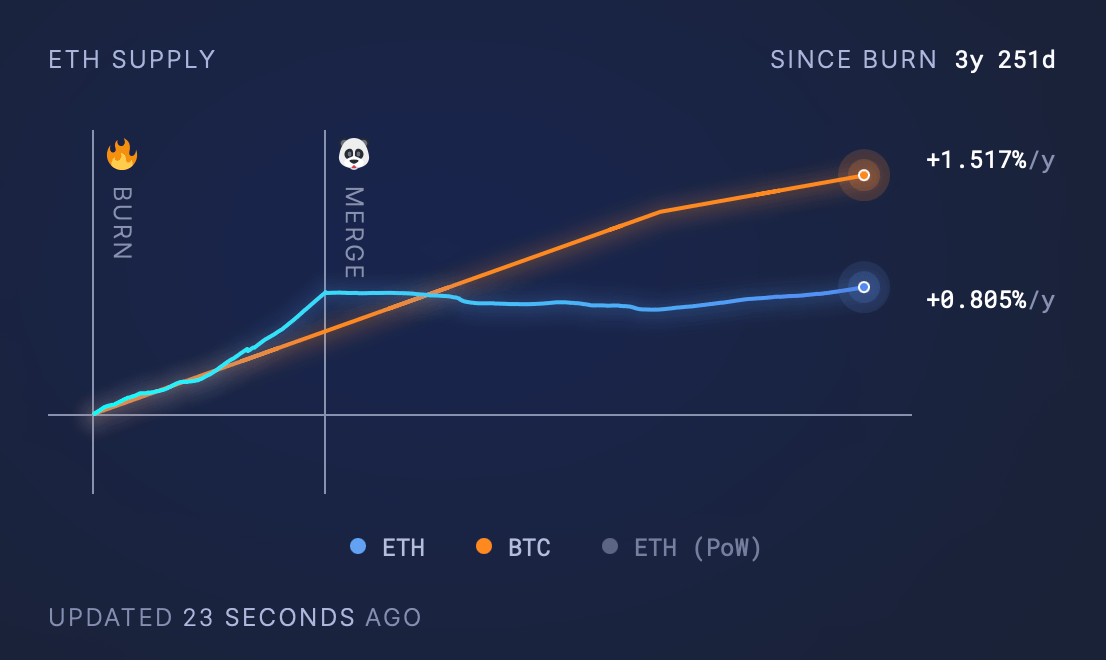
Since August 2021, Ethereum worth $7.3 billion has been burned.
As of April 13, 2025, the circulating supply of Ethereum is approximately 120,690,000 ETH, with an annual growth rate of 0.51%. Since the London hard fork, 4,581,986.52 ETH has been burned, with a total value of about $7.3 billion (based on historical ETH prices). However, the net supply has increased by 3,477,830.85 ETH, indicating that issuance exceeds the amount burned.
In comparison, Bitcoin's annual inflation rate during the same period (three years and eight months) is 1.517%, despite Bitcoin having a fixed cap of 21 million coins, while Ethereum theoretically has an unlimited supply.
Analysis of Influencing Factors
The following factors influence the balance between burning and issuance:
Network Activity and Transaction Fees:
- The burn rate is directly related to transaction volume and fees. High activity periods (such as NFT booms or DeFi surges) may lead to temporary deflation. The Dencun upgrade in 2024 reduced Layer 2 transaction fees by introducing proto-danksharding, improving user experience but also reducing the amount burned.
- For example, Dencun reduced transaction costs for Layer 2 solutions (such as Optimism and Arbitrum), indirectly decreasing the burn on the main chain.
Issuance Rate:
- After the merge, the issuance rate is based on staking rewards, approximately 1,700 ETH daily, with an annual issuance of about 620,500 ETH (assuming stable staking participation). Although this is a significant reduction from pre-merge levels (13,000 ETH/day), the current burn rate during low activity periods is still insufficient to offset it.
Major Contributors to Burning:
Data shows that the sources of burning mainly include:
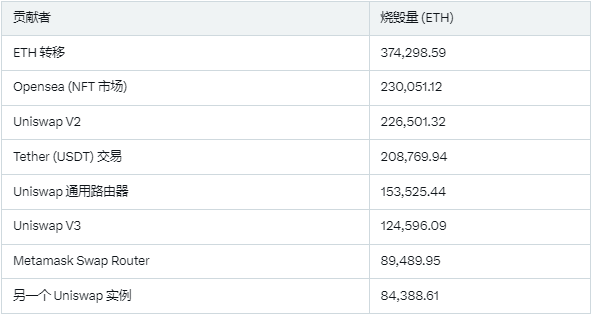
These platforms drive a large number of transactions, but activity levels are influenced by market conditions, such as NFT trends and fluctuations in DeFi usage.
Market Conditions:
- High activity periods may achieve temporary deflation, while low activity periods (such as Q2 2024, with an increase of 75,301 ETH) turn into inflation. Data from Q2 2024 shows an issuance of 228,543 ETH, a burn of 107,725 ETH, and a net increase of 120,818 ETH.
Analysis of Ongoing Inflation Reasons
The current supply dynamics of Ethereum may be influenced by the following factors:
"Expectation Trap" in Technological Evolution
Limitations of EIP-1559 Mechanism Design
Although the burning mechanism creates a new paradigm for value capture by destroying base fees, its effectiveness is constrained by the nonlinear fluctuations in network activity. Data shows that after the Dencun upgrade in 2024, Layer 2 transactions accounted for over 83%, leading to a 72% drop in daily Gas fee revenue on the mainnet.
Implementation Challenges of Sharding Technology
The planned Pectra sharding upgrade, originally scheduled for Q1 2025, has been delayed due to ZK-Rollup compatibility issues, resulting in TPS remaining in the range of 15-45, unable to support high-frequency trading scenarios.
"Value Dissipation" in Ecological Competition
Value Diversion in Multi-Chain Ecosystems
Solana, with 9,000 TPS and a transaction cost of $0.0001, captured 38% of the public chain market share in 2024, with daily active users reaching 2 million, 5.6 times that of Ethereum's mainnet.
Structural Decline of DeFi and NFT
Sales of NFTs on the Ethereum chain have dropped from a peak of $1.23 billion/month in 2023 to $125 million in 2025, while Uniswap v4's full transition to Layer 2 has resulted in the mainnet DEX trading volume accounting for less than 9%. More critically, in the RWA (real-world assets) sector, institutions like BlackRock have chosen Polygon to issue tokenized funds, causing Ethereum to miss out on trillion-dollar market entry.
Reflexivity Paradox of Economic Models
Imbalance in Staking Mechanism Incentives
The designed staking yield of 3.2% post-merge has lost its appeal in a macro environment where the Federal Reserve's benchmark interest rate reaches 5.25%, leading to a decrease in the number of validating nodes from 3.495 million to 3.4 million, with the staking rate dropping to 27%.
Asymmetric Effects of the Burning Mechanism
Data modeling shows that the deflation threshold for ETH needs to meet: burn amount > issuance amount (approximately 1,600 ETH/day). However, during market downturns, the number of active addresses on the network drops to 360,000/day, only able to maintain an average daily burn of 800 ETH.
Structural Suppression of Regulatory Environment
Shadow of Securities Classification
The SEC has classified 75% of ERC-20 tokens under securities regulation and prohibited ETH ETFs from participating in staking, directly leading to a 22% year-on-year decrease in institutional capital inflow. In contrast, Bitcoin, with its clear positioning as "digital gold," attracted $30 billion in ETF capital inflow, exacerbating the regulatory arbitrage gap and causing the ETH/BTC exchange rate to drop to a historical low of 0.02.
Cost Transfer Effects of Compliance
To meet KYC/AML requirements, compliance modifications such as account abstraction have increased smart contract Gas consumption by 27%, further suppressing network activity.
Conclusion: The Midlife Crisis of Blockchain
The deflationary dilemma of Ethereum is essentially a microcosm of the collision between technological idealism and commercial realism. When the market cap share of ETH remains at a historical low of 17.5%, it reflects not only an imbalance in monetary policy but also the growing pains of the entire industry transitioning from "proof of concept" to "value creation." The path to breaking the deadlock in the future may not lie in a mechanical pursuit of deflationary models, but in constructing a new paradigm that accommodates efficiency, fairness, and regulatory sustainability. Just as Satoshi Nakamoto did not foresee the ETF frenzy when creating Bitcoin, Ethereum's value discovery also needs to break out of existing frameworks and find a dynamic balance between technological ideals and market realities.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




