近期加密市场乏善可陈,保守稳健的收益再次成为市场需求,因此结合自己近些年的投资心得及去年底对稳定币领域的集中研究成果,谈一谈稳定币收益这个古老但长青的话题。
当前加密市场的稳定币类别主要为以下几大类:
- 有条件合规但市占率最高的USDT:应用场景足够广(交易所币种交易对、加密行业公司发薪、真实国际贸易与线下支付场景),用户寄希望于大而不能倒且Tether具有兜底能力。
- 与法币1:1锚定的合规稳定币:USDC有最多链及应用场景支持是真正的链上美元,而PayPal USD、BackRock USD等其他合规稳定币的应用场景都有一定局限性。
- 超额抵押稳定币:以MakerDAO的DAI及其升级为Sky Protocol后的USDS为主;Liquity 的LUSD以0抵押借贷利率和110%的低质押率的微创新成为竞品之一。
- 合成资产稳定币:本轮周期以现象级的Ethena的USDe最具有代表性。其资金费率套利获取收益的模式亦是本文随后会重点分析的稳定币收益模式之一。
- 底层资产为美债的RWA项目稳定币:本轮周期以Usual的USD0和Ondo的USDY最具有代表性。而Usual的USD0++为美债提供流动性类似Lido之于ETH Staking具有创新性。
- 算法稳定币:Terra的UST崩盘之后赛道基本被证伪,Luna缺乏真实价值支持代币价格剧烈波动中在暴跌抛售再暴跌的死亡螺旋后脱钩最终崩盘。FRAX集合算法稳定币和超额抵押模式尚有一些应用场景,而其余算法稳定币已无市场影响力。
- 非美元稳定币:欧元稳定币(Circle的EURC、Tether的EURT等)和其他法币稳定币(BRZ, ZCHF,圆币HKDR等)目前对美元主导的稳定币市场影响甚微,笔者曾经投资的某非美元超额抵押稳定币项目已基本归零,非美元稳定币唯一的出路在于合规监管框架下的支付业务而非应用于原生加密社区。
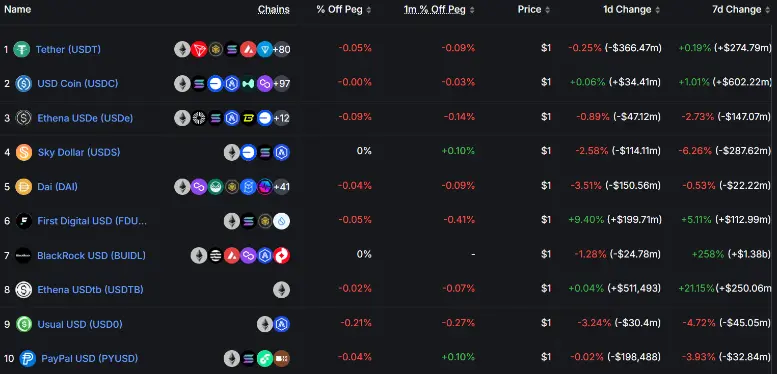
稳定币市值排行榜
数据来源:https://defillama.com/stablecoins
而目前通过稳定币获取收益的模式类别主要为以下几大类,本文将进一步详细分析每类收益:
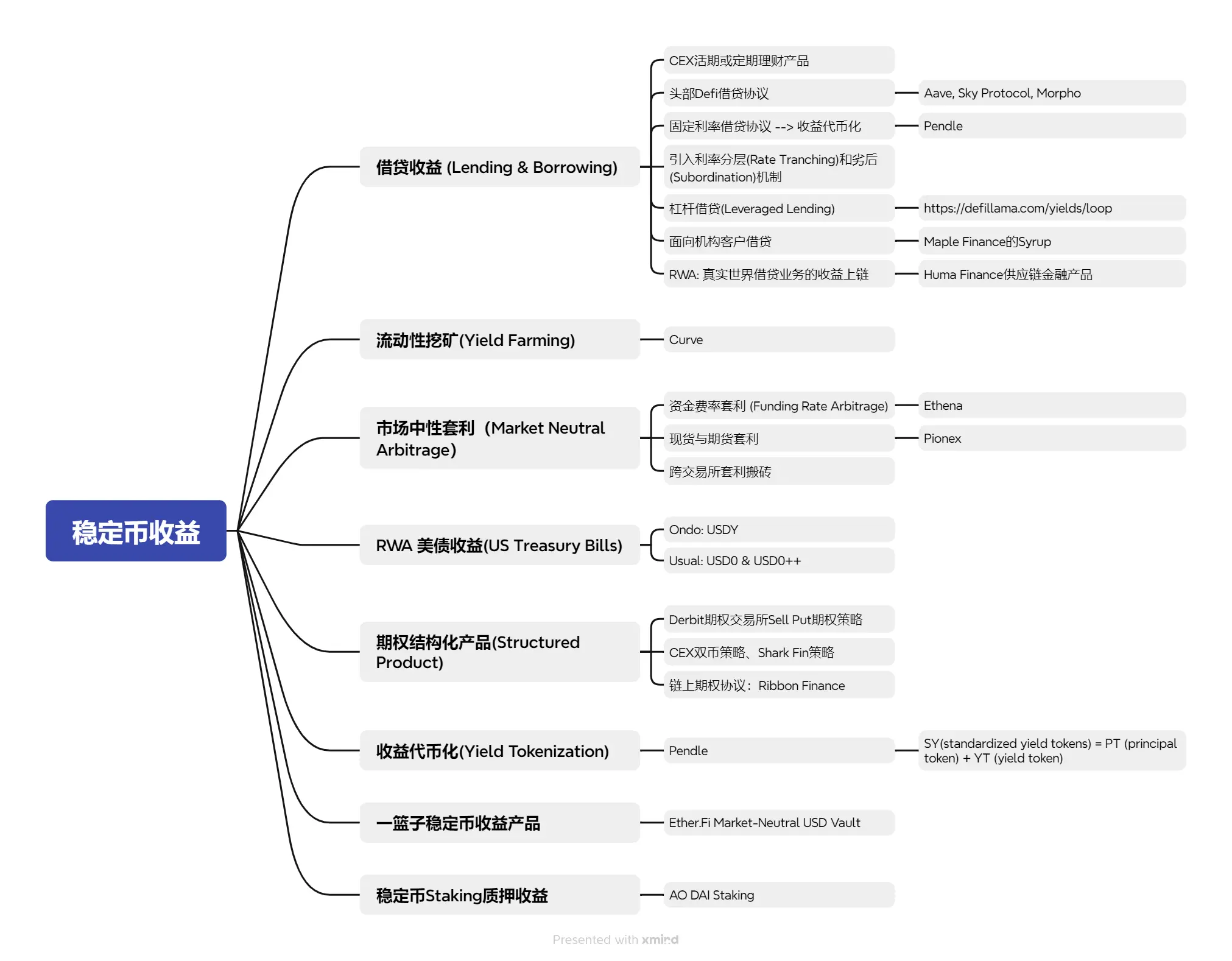
一、稳定币借贷 (Lending & Borrowing):
借贷作为最传统的金融收益模式,其收益本质来源于借款人支付的利息,需要考虑平台或协议安全性、借款人违约概率及收益稳定性。目前市场上的稳定币借贷产品:
- Cefi平台以头部交易所(Binance, Coinbase, OKX, Bybit)活期理财产品为主
- 头部Defi协议以Aave, Sky Protocol(MakerDAO升级后品牌), Morpho Blue等为主。
经历过周期考验的头部交易所的平台安全性和头部Defi协议安全性较高,在行情上涨期由于借贷需求旺盛导致U活期收益很容易飙升到20%以上,但行情淡静期普遍收益较低维系在2%-4%,因此活期借贷利率(Flexible Interest)的也是很直观的市场活跃度指标。固定利率(Fixed Interest)借贷由于牺牲流动性因此大部分时间收益高于活期,但在市场活跃期亦无法捕获活期收益的飙升。
此外,在整体的稳定币借贷市场从存在部分微创新,包括:
- 固定利率借贷Defi协议:本轮周期极具代表性的Pendle协议,始于固定利率借贷而成于收益代币化,本文后续将详细介绍;而Notional Finance、Element Finance等早期固定利率Defi项目虽未成功跑出但其设计理念值得参考。
- 在借贷中引入利率分层机制(Rate Tranching)和劣后(Subordination)机制;
- 提供杠杆借贷(Leveraged Lending)的Defi协议;
- 面向机构客户的Defi借贷协议,例如Maple Finance的Syrup收益源自机构借贷。
- RWA将真实世界借贷业务的收益上链,例如Huma Finance的链上供应链金融产品。
总之,借贷业务作为最传统的金融收益模式通俗易懂,承载最大资金体量将继续是最主要的稳定币收益模式。
二、流动性挖矿(Yield Farming)收益:
以Curve为代表,其收益来源于AMM交易分给LP的手续费及代币奖励。Curve作为稳定币DEX平台的圣杯,成为Curve Pools中支持的稳定币成为衡量新稳定币在行业采用度的重要指标。Curve挖矿的优势在于安全性极高而不足在于收益过低缺乏吸引性(0-2%),如果非大额且长期资金参与Curve的流动性挖矿可能收益甚至无法覆盖交易Gas Fee。
而Uniswap的稳定币池交易对面临相同问题,Uniswap的非稳定币交易对存在流动性挖矿亏损可能性, 而其他规模较小DEX的稳定币池交易对即便收益较高依然有Rug Pull顾虑,皆不符合稳定币理财谨慎稳健的原则。我们可以看到目前Defi稳定币池依然以借贷模式为主,Curve最经典的3Pool(DAI USDT USDC)仅为TVL排名前二十。
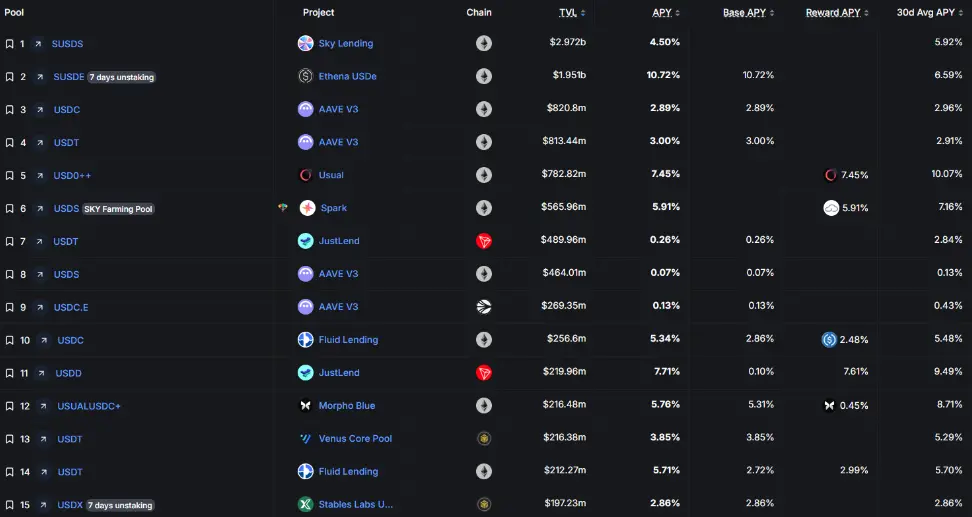
稳定币池TVL排行榜
来源: https://defillama.com/yields?token=ALL_USD_STABLES
三、市场中性套利收益:
市场中性的套利策略一直长期广泛的应用于专业交易机构中,通过同时持有多头(Long)和空头(Short)头寸,使投资组合的净市场暴露(Net Exposure)接近于零。具体于Crypto的主要为:
- 资金费率套利(Funding Rate Arbitrage):永续合约(Perpetual Futures)没有到期日,其价格通过资金费率(Funding Rate)机制与现货价格保持一致。资金费率需要定期支付,缩短现货与永续合约的短期价差。
- 当永续合约价格高于现货价格(升水),多头支付空头,资金费率为正。
- 当永续合约价格低于现货价格(贴水),空头支付多头,资金费率为负。
- 历史回撤数据,资金费率为正的的概率长期大于资金费率为负的概率。因此收益来源主要是正资金费率场景下现货买入,永续合约卖空,收取多头支付的费用。
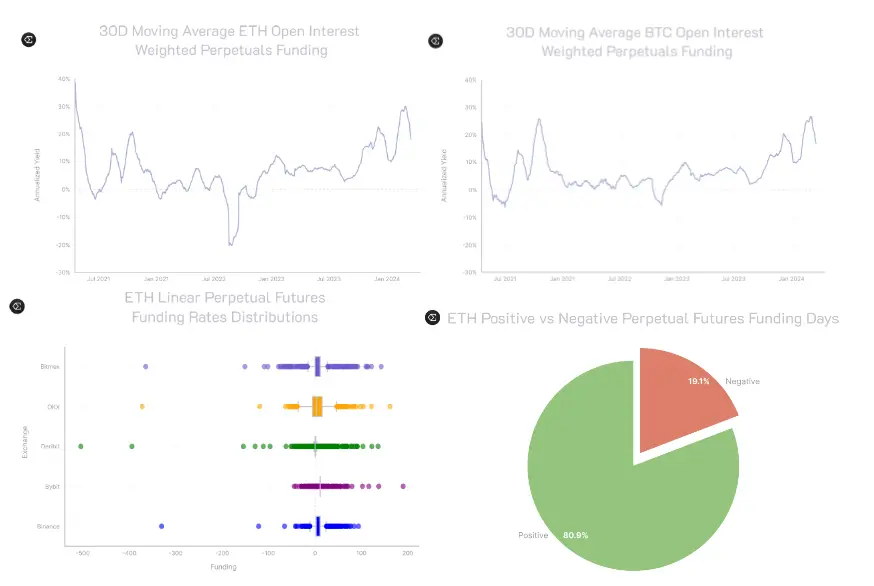
- 现货与期货套利(Cash-and-Carry Arbitrage):期现套利利用现货市场(Spot)和到期期货市场(Futures)之间的价格差异,通过对冲头寸锁定利润。核心概念为“基差”(Basis)即到期期货价格与现货价格的差额。通常在升水(Contango,期货价格高于现货)或贴水(Backwardation,期货价格低于现货)市场中操作。期现套利适合资金量较大、能接受锁定期且看好基差收敛的投资者,常见于传统金融思维的交易者。

- 跨交易所搬砖套利:在不同交易所间利用价格差异构建中性头寸,是Crypto行业早期主流套利方式,但目前主流交易对在不同交易所间的价差已经极低,需要依赖于自动化搬砖脚本且更加适合高波动市场及小市值币中,散户参与门槛高,可参考Hummingbot平台。
- 此外市场上存在着三角套利、跨链套利、跨池套利等套利模式本文不做额外延展。
市场中性的套利策略,由于其专业度极高大部分受众限于专业投资者。而本轮周期Ethena的出现,将“资金费率套利(Funding Rate Arbitrage)”这一成熟模式搬至链上,普通零售用户可参与。
用户在Ethena协议存入stETH会Mint收到等值的USDe代币,与此同时在中心化交易所开等值的空单对冲赚取正向资金费率,依照历史统计数据80%以上时间为正向资金费率而负资金费率场景下Ethena会通过储备金弥补亏损;Ethena协议65%以上的收入对冲资金费率此外亦有部分以太坊Staking、链上或交易所借贷收益(35%)作为补充收益;此外,用户资产托管到第三方托管机构OES(Off Exchange Settlement)并定期出具审计报告,有效隔离了交易所平台风险。
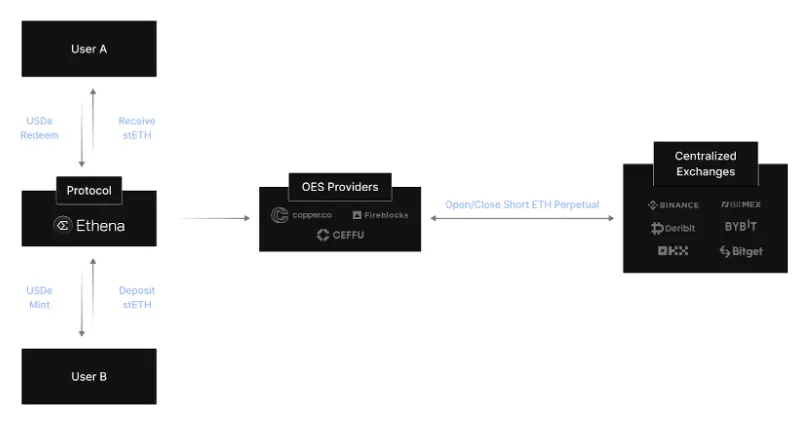
之于Ethena风险的思考,除去交易所平台与托管机构事故、智能合约安全问题或锚定资产脱钩等项目方不可控因素,更重要的核心点在于“长期负资金费率场景下的亏损且协议预留资金无法覆盖”,根据历史数据的回撤我们可以理解为概率较低,即便发生也意味着业内普遍适用的“资金费率套利”交易策略失效。因此,在团队不作恶的前提下,Ethena协议并不会出现Terra算法稳定币的死亡螺旋模式,而有可能出现的是由代币补贴的高收益率逐渐下降回归至正常套利收益范围。
与此同时,我们不得不承认Ethena做了最大程度的数据透明度,在官网可以清晰的查询到历史收益、资金费率、不同交易所的头寸以及每月托管审计报告,优于市场上其他资金费率套利产品。
除去Ethena的“资金费率套利”模式,Pionex交易所亦有“期限套利”模式的稳定币理财产品。令人遗憾的是,除去Ethena外,目前市场上并未看到太多零售客户可低门槛参与的市场中性套利产品。
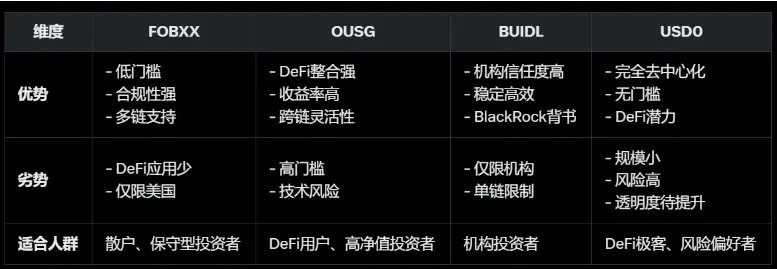
四、美债收益 RWA 项目(US Treasury Bills)
美联储2022-2023年的加息周期将美元利率推至5%以上,即便当下已转向逐步减息但4%以上的美元利率在传统金融行业依然是难得的兼顾高安全性与较高收益的资产标的。RWA业务具有高合规要求和重运营模式,美债作为高成交量的标准化标的是为数不多业务逻辑成立的RWA产品。
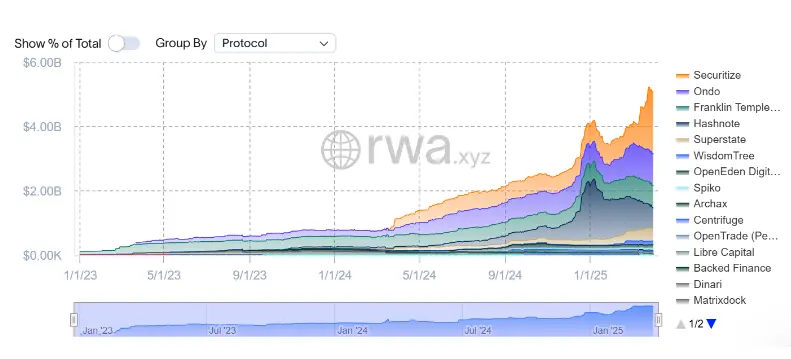
以美债为底层资产的Ondo,其USDY面向非美国通用零售客户、OUSG面向美国机构合资格客户收益均为4.25%,在多链支持和生态应用上属于RWA赛道一哥,但在监管合规层面相比Franklin Templeton推出的FOBXX和BlackRock的BUIDL略有不足;而在本轮周期中异军突起的Usual协议,在一篮子美债作为底层资产的 USD0之上,增加了流动性代币USD0++,类似于Lido之于以太坊质押,为4年期锁定的美债提供了流动性,并且可参与稳定币流动性挖矿或借贷池获取额外收益。
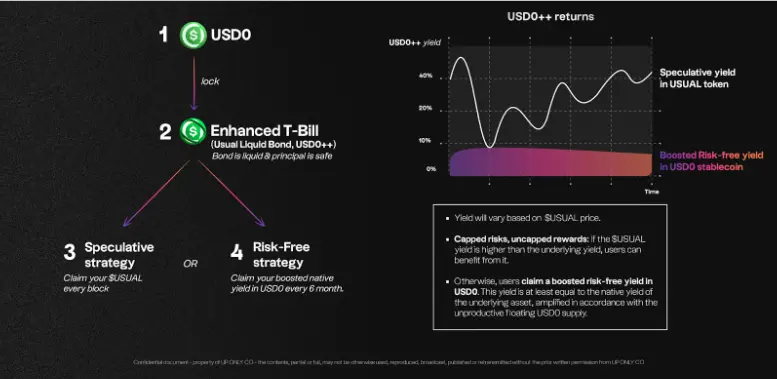
需要特别指出的是,大部分美债RWA项目收益稳定在4%左右,而Usual稳定币池的较高收益主要源于Usual代币补贴、Pills (Point)激励、流动性挖矿等偏投机性的额外收益不具有可持续性,作为与Defi生态最完备的美债RWA项目,在未来依然面临收益缓慢下降但不至于暴雷的风险。
虽然2025年初USD0++的赎回机制调整导致的价格脱钩和抛售事件,根源在于其债券属性与市场预期的错位叠加治理失误,但其流动性设计机制作为行业创新依然值得其他美债RWA项目借鉴。
五、期权结构化产品(Structured Product)
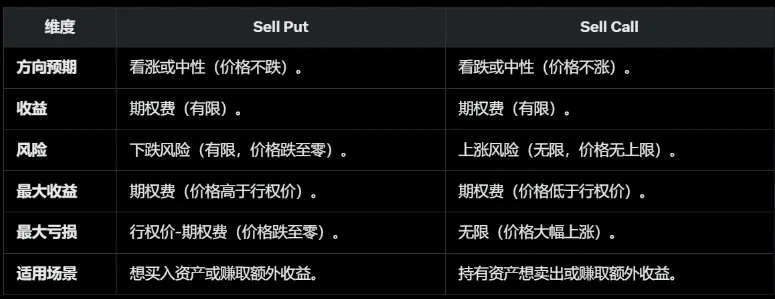
目前在大部分中心化交易所流行的结构化产品及双币策略,源于期权交易里“卖期权赚保费”的Sell Put或Sell Call策略。U本位的稳定币主要为Sell Put策略,收益源于期权买方支付的期权金,即赚取稳定USDT期权金或以更低的目标价格购买到BTC或ETH。
在实操实践中,卖期权策略更加适合于区间震荡行情,Sell Put目标价为震荡区间下限、Sell Call目标价为震荡区间上限;对于单边上涨行情,期权金收益有限容易踏空而选择Buy Call更为合适;对于单边下跌行情,Sell Put容易成为买在半山腰后持续亏损的状态。对于卖期权交易的新手,容易陷入追求短期“高期权金收益”陷阱而忽视币价大幅下跌带来的风险敞口,但将目标价设置过低,期权金收益率又缺乏足够的吸引力。结合笔者多年的期权交易,Sell Put策略主要在市场下跌恐慌情绪弥漫时设置更低的买入目标价操作以赚取高期权金收益,而市场上涨期选择交易所活期借贷收益率更为可观。
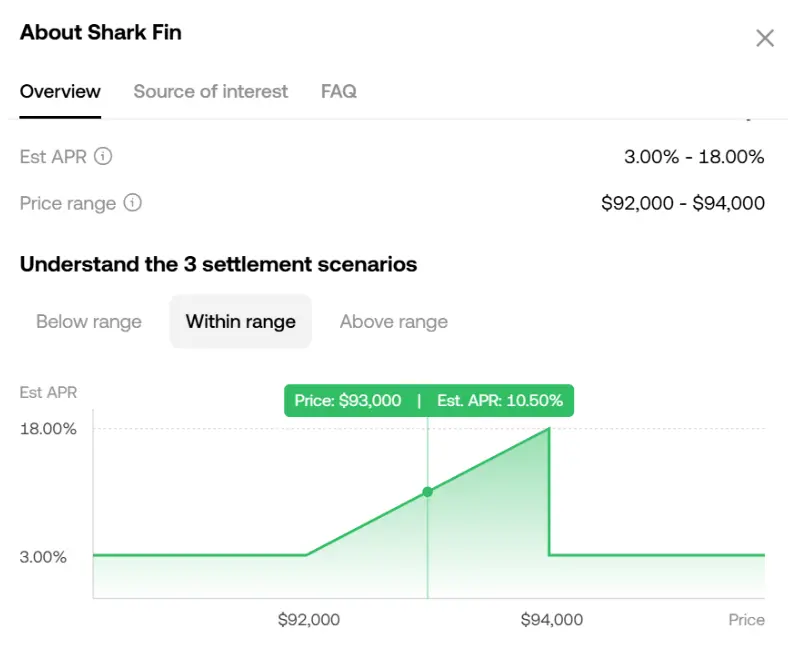
至于近期OKX等交易所流行的Shark Fin本金保护策略,采用Bear Call Spread策略(Sell Call 收取期权金 + 更高行权价 Buy Call 限制上涨幅度)+ Bull Put Spread(Sell Put 收取期权金 + 更低行权价Buy Put限制下跌幅度),令到整个期权组合在区间内赚取期权金收益,在区间外买入与卖出期权互相对冲无额外收益,对于注重本金安全又不追求期权金或币本位收益最大化的用户来说不失为一种合适的U本位理财方案。
链上期权的成熟度有待开发,Ribbon Finance曾经上一轮周期成为最头部期权金库协议,Opyn和Lyra Finance等头部链上期权交易平台亦可手动交易期权金策略,奈何当下已经风光不再。
六、收益代币化 (Yield Tokenization)
本轮周期极具代表性的Pendle协议,始于2020年的固定利率借贷而成于2024年的收益代币化,通过将收益资产拆分为不同的组成部分,让用户能够锁定固定收益、投机未来收益或对冲收益风险。
- 标准化收益代币 SY(standardized yield tokens) 可拆分为主体代币PT和收益代币YT
- PT(Principal Token):代表底层资产的本金部分,到期时可按 1:1 赎回基础资产。
- YT(Yield Token):代表未来收益部分,随时间递减,到期后价值归零。
Pendle的交易策略主要为:
- 固定收益:持有 PT 到期可获得固定收益,适合风险厌恶者。
- 收益投机:购买 YT 押注未来收益上升,适合风险偏好者。
- 对冲风险:卖出 YT 锁定当前收益,规避市场下跌风险。
- 流动性提供:用户可将 PT 和 YT 存入流动性池,赚取交易费和 PENDLE 奖励。
目前其主推的稳定币池,除了底层资产原生收益外亦叠加了YT投机收益、LP收益、Pendle代币激励、Points等激励措施令其总体收益率可观。美中不足之一就是Pendle的高收益池普遍期限较中短期,无法像Staking或流动性挖矿或借贷池一样一次操作一劳永逸,需要经常性的链上操作更换收益池。
七、一篮子稳定币收益产品:
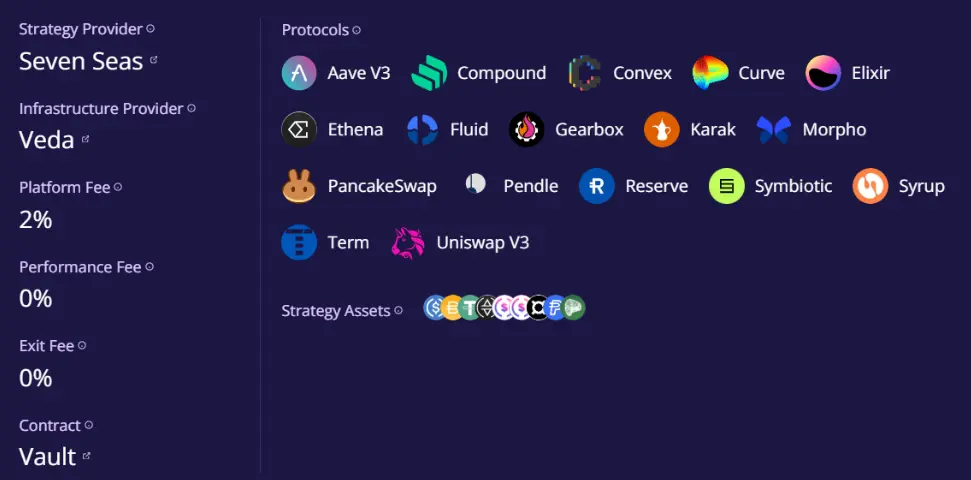
Ether.Fi作为Liquid Restaking的头部协议,在Restaking赛道进入饱和下行趋势后,积极拥抱变化产品转型推出了在BTC、ETH和稳定币的诸多收益产品,持续保持了其全Defi行业领先地位。
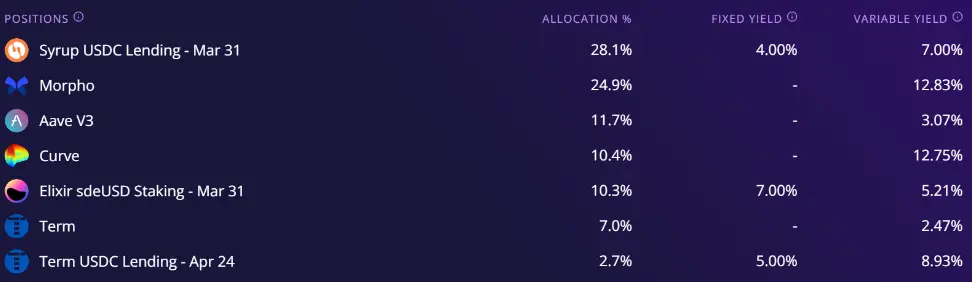
而在其稳定币Market-Neutral USD池中,其以主动管理基金的形式为用户提供借贷生息(Syrup, Morpho, Aave)、流动性挖矿(Curve)、资金费率套利(Ethena)、收益代币化(Pendle)等一篮子稳定币收益产品。对于追求稳定链上收益、资金体量不足且不愿频繁操作的用户来说,不失为一种兼顾高收益与分散风险的方法。
八、稳定币 Staking 质押收益:
稳定币资产并非ETH等POS公链具有Staking属性,然而Arweave团队推出的AO网络在代币Fair Launch发行模式上接受了stETH和DAI的链上质押,且DAI的质押具有最高的AO收益资金效率。我们可将此类稳定币质押模式归为另类稳定币收益模式,即确保DAI资产安全的前提下赚取额外的AO代币奖励以小博大,而其核心风险在AO网络发展及代币价格的不确定性。
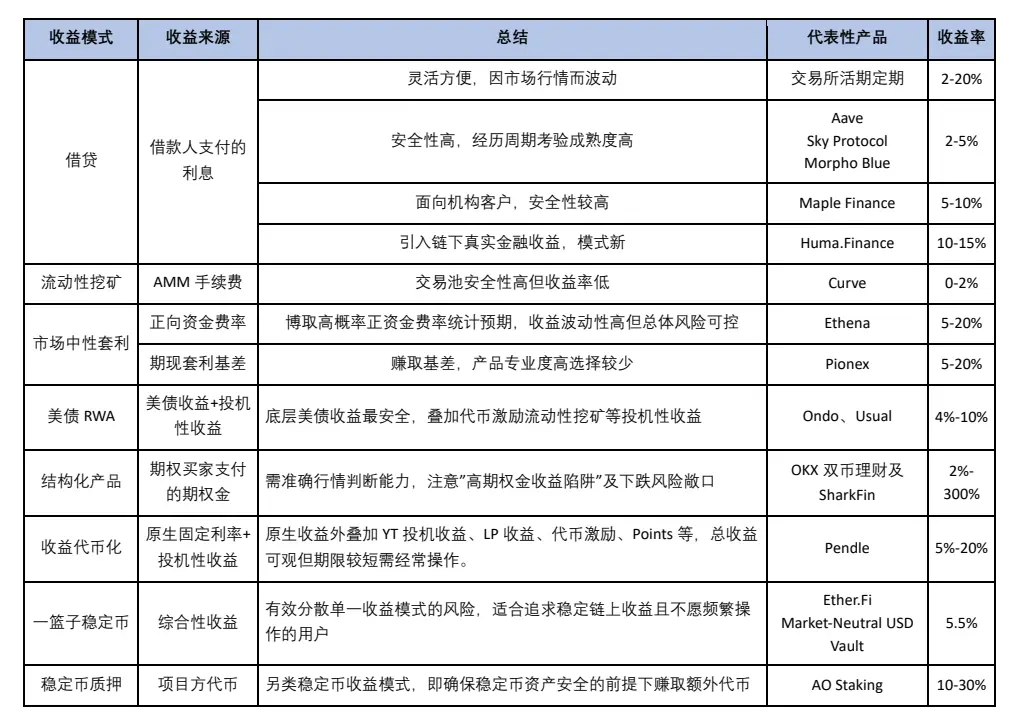
综上所述,我们将当前加密市场上主流的稳定币收益模式总结如上表。稳定币资产是加密市场从业者最熟悉但又最容易忽略的市场,理解清楚稳定币的收益来源进而合理配置,方可在财务基石稳健的基础之上更加从容的应对加密市场的不确定性风险。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




