As the futuristic concept of DAO stirs waves of innovation in the Web3 world, this innovation paradigm rooted in blockchain technology not only reshapes our understanding and imagination of traditional organizations but also incubates star projects like Compound and MakerDAO that change industry rules. From project teams to institutional investors and ordinary crypto players, there is keen attention and strong interest in DAOs, which act like a key to unlock the mysterious door of future organizational forms. However, every time we attempt to define a DAO, it morphs into new forms in different contexts and application scenarios, making it elusive.
So, what exactly is a DAO organization? What are its advantages and limitations?
How can one create a DAO organization? What processes need to be followed?
Which countries or regions have clear laws and regulations to supervise DAO organizations?
Can a DAO organization serve as the token issuance entity for RWA projects?
The Crypto Salad team has been deeply involved in the cryptocurrency industry for many years and has rich experience in handling complex cross-border compliance issues in the cryptocurrency sector. In this article, we will combine the laws and regulations of various countries with the team's practical experience to clarify and answer the above questions from a professional lawyer's perspective.
### What Exactly is a DAO Organization? What are its Advantages and Limitations?
For many outsiders, DAO organizations are quite novel, so there is no so-called "strict definition" of this concept. Specifically, the DAO organization referred to by crypto players, the DAO organization in the context of blockchain technology, and the DAO organization in terms of legal norms may have completely different conceptual connotations.
Therefore, returning to the expression of DAO itself for semantic analysis is necessary to understand its common essence in different scenarios and contexts. DAO refers to Decentralized Autonomous Organization. Thus, organizations that possess the following two characteristics can theoretically be recognized as DAO organizations: "Decentralization" + "Autonomy." The following will compare DAO organizations with traditional companies and analyze the core essence of DAO organizations from the perspectives of "decentralized" organizational structure and "autonomous" governance model, allowing everyone to better understand the uniqueness of DAO organizations.
1. "Decentralized" Organizational Structure
Under the traditional corporate system in our country, the highest decision-making power of a company is held by the shareholders' meeting. Shareholders delegate the management power over specific company affairs to the board of directors, forming a centralized management institution responsible for decision-making on important matters during the company's operation. Finally, the board of directors implements decisions through the hiring of corporate executives and employees.
The decentralized characteristic of DAO organizations is reflected in the fact that DAOs do not have a centralized decision-making management institution as in traditional corporate systems; instead, all members within the organization collectively share the management and decision-making power of the DAO organization.
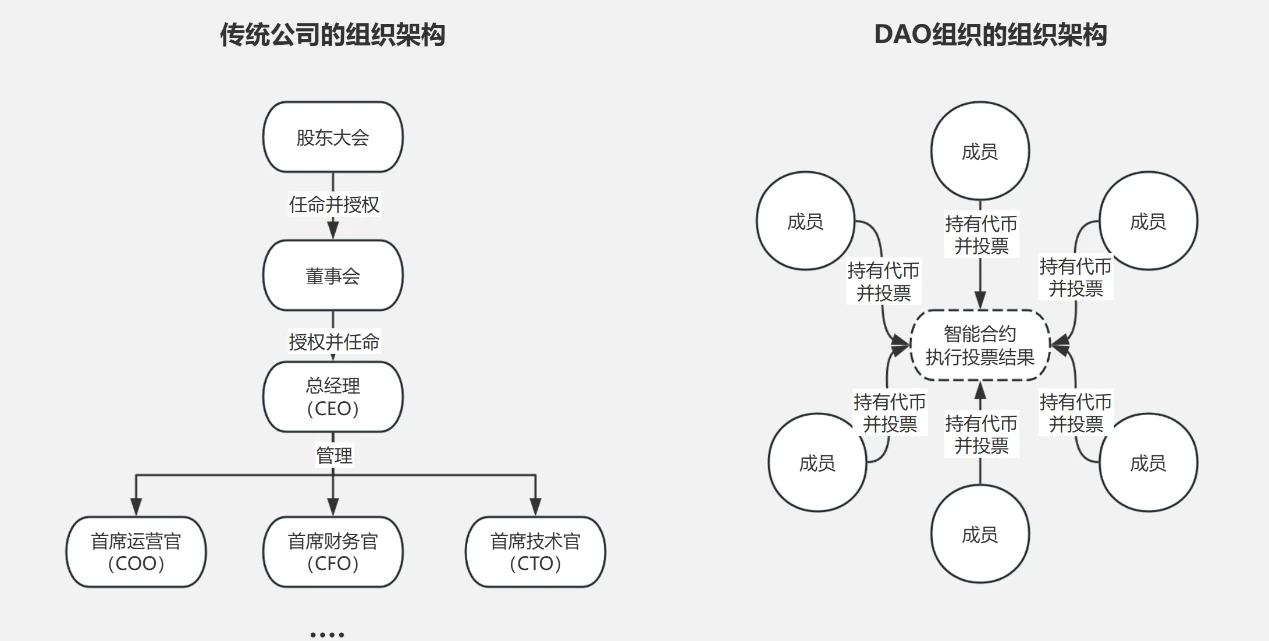
(Comparison diagram of organizational structures between traditional companies and DAO organizations, for reference only)
At the same time, DAO organizations are not required to be accountable for the interests of specific stakeholders (such as shareholders) and do not possess a centralized profit orientation. Each member holding governance tokens of the DAO organization can share the benefits of the organization's development through token appreciation or internal incentives. For example, Uniswap, as one of the largest DeFi trading platforms on-chain, has seen its governance token UNI bring considerable returns to its members and further incentivize them to build the entire organization.
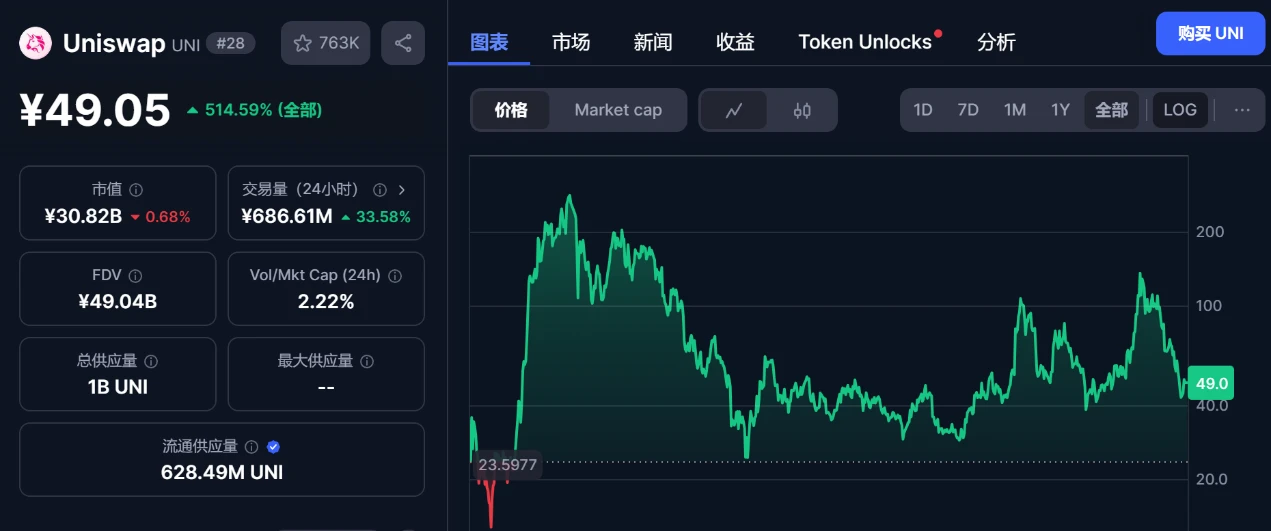
(The above image shows the price trend of the UNI token) Resource: CoinMarketCap
So, how does a DAO organization achieve a decentralized organizational structure?
Once the operational management rules of a DAO organization are established, they will be written into the corresponding smart contracts and autonomously run through blockchain technology. In theory, once a smart contract is written and deployed on the chain, it will continue to run automatically, and the operational management rules within it cannot be arbitrarily changed, thus eliminating the possibility of intervention by centralized management institutions.
At the same time, the smart contracts that write governance rules are fully open-source on-chain. Therefore, all community members, including other players on the chain, can query the DAO organization's smart contracts and all its operational management rules through the blockchain. Through this technological tool of smart contracts, DAO organizations achieve complete transparency of management rules, breaking free from the "black box" decision-making model of centralized management institutions.
(The above image shows the relevant information and partial code of the "Governor" smart contract of the DAO organization Compound) Source: Compound project official website
What advantages does a decentralized organizational structure bring to DAO organizations compared to traditional companies?
In the management model of traditional companies, how to avoid moral hazards of corporate directors and executives and ensure that they act in the overall interest of the company is a problem that cannot be completely solved.
To ensure that these individuals or centralized management institutions holding the main power of the company do not act against the overall interests of the company for personal gain, regulations need to be imposed from various aspects, including internal governance models and external regulatory frameworks.
Establishing a supervisory board within the corporate structure is, to some extent, aimed at solving this problem. For example, Article 78 of our country's Company Law stipulates that the supervisory board exercises the following powers: "When the actions of directors and senior management harm the interests of the company, they may require the directors and senior management to correct them." However, a new problem arises — if the supervisors are responsible for overseeing the company's directors and executives, who supervises the supervisors, and how can we ensure that supervisors effectively fulfill their supervisory duties? At this point, merely addressing the issue from the internal structure of the company is no longer sufficient, necessitating the intervention of an external regulatory system. Article 180 of our country's Company Law explicitly stipulates the diligence and loyalty obligations of directors, supervisors, and senior executives. Even so, this combination of internal and external methods still cannot completely resolve the issue.
However, DAO organizations, based on blockchain technology, replace centralized management decision-making institutions with coded, automatically running operational management rules. At the same time, DAO organizations allow members to share the benefits of organizational development through governance tokens, aligning the interests of decision-makers with the overall interests of the organization. Therefore, DAO organizations fundamentally avoid the moral hazard issues mentioned above.
2. "Member Autonomy" Governance Model
Here, "member autonomy" refers to an internal governance system within the organization that allows members to achieve self-governance, breaking free from the hierarchical governance model of traditional corporate systems.
How is internal autonomy achieved within the organization?
In short, DAO organizations generally achieve autonomy through internal voting. Members holding governance tokens of the DAO organization can propose and participate in voting. Specifically, under the framework of governance rules, organizational members can initiate time-limited votes on specific proposals, and the final decision on whether to implement a proposal is determined by the public voting results of the organizational members (i.e., governance token holders). The entire process is automated through smart contracts.
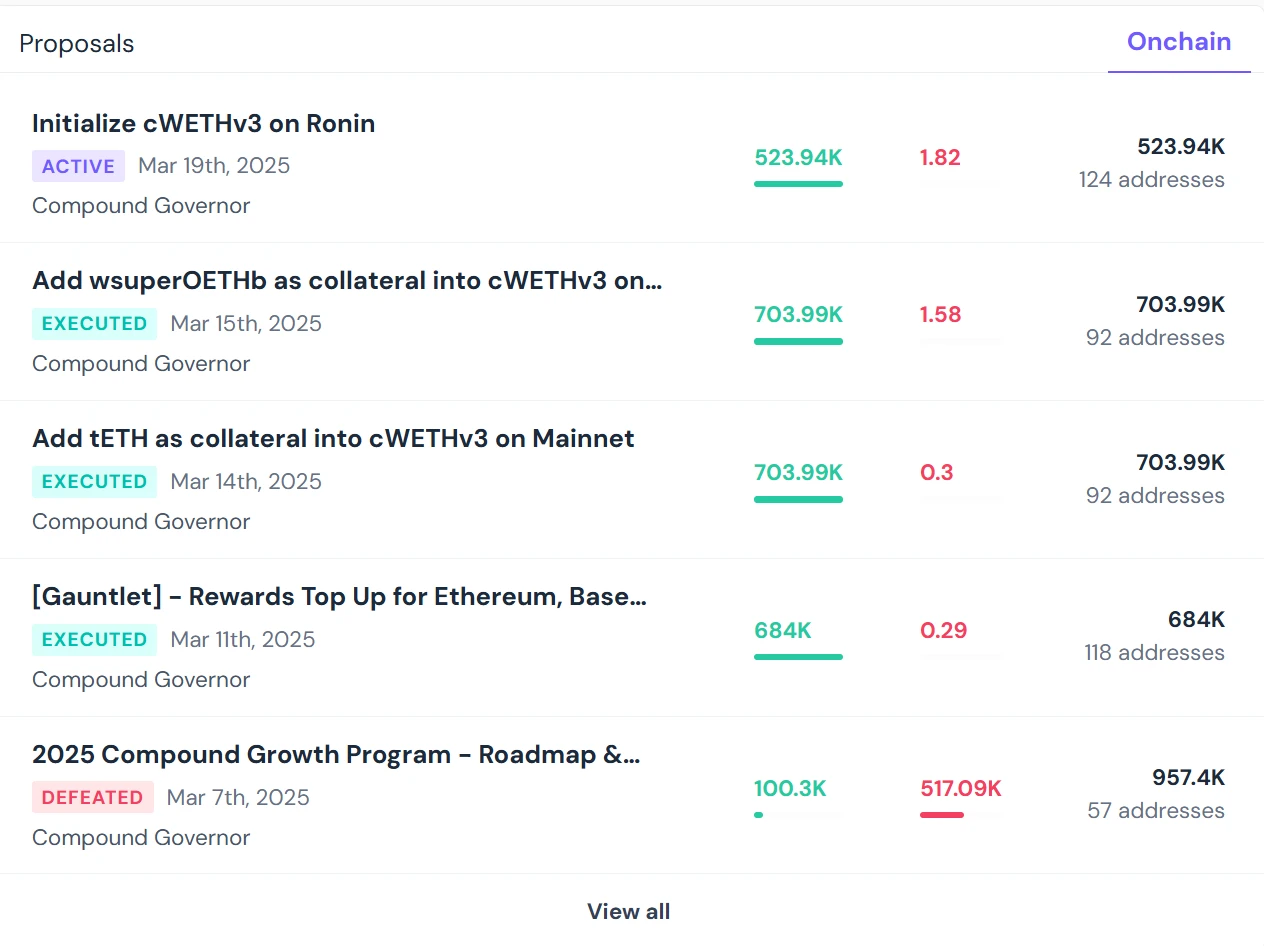
(The above image shows the public interface of the proposal voting situation in the DAO organization Compound) Source: Compound project official website
Although the voting models of DAO organizations are quite similar, the specific voting rules vary. Some DAO organizations adopt a "one token, one vote" approach to set voting weights. Others may use special calculation methods to determine voting weights, such as quadratic voting mechanisms, to reduce the influence of large token holders on the final voting results. Meanwhile, mainstream DAO organizations often adopt representative voting (Delegate) methods, allowing token holders to delegate their voting rights to corresponding representatives for unified voting, thereby improving the overall voting efficiency of the organization.
It is important to note that DAO organizations do not initially adopt a completely community autonomous system in practice. For many newly established or early-stage DAO organizations, considering that the governance structure of the DAO organization is not yet fully developed and that the number of members is small, the founding team of the DAO organization generally opts for a temporary centralized governance approach, with the founding team responsible for the initial operation management and decision-making of the project. Once the DAO organization matures, the founding team gradually transfers management authority to other members of the organization through the distribution of governance tokens and other means.
So, what advantages does member autonomy have compared to the governance model of traditional companies?
Under the hierarchical system of traditional companies, operational decisions largely depend on the business judgments made by directors or executives. However, the judgments and decisions of executives inevitably encounter deviations when communicated to the execution level, which is an unavoidable issue when directives are transmitted from top to bottom. Moreover, the information and situations known by employees at the execution level are difficult to directly convey to decision-makers, and the channels for bottom-up information exchange may be blocked. Therefore, this governance method in traditional companies is likely to lead to subtle "misalignments" between high-level decisions and actual business operations. If this "misalignment" is not corrected in a timely manner, it may lead to the entire company losing its competitiveness and heading towards failure.
In contrast, DAO organizations eliminate differences and barriers in rank and level among organizational members through member autonomy, thus promoting equal communication and interaction among members, creating a community-like atmosphere and model for exchange. At the same time, DAO organizations complete decision-making through public voting on proposals, ensuring that the decisions reflect the views and perceptions of the majority of members within the organization. Although the majority's views may not always be correct, this mechanism theoretically avoids the negative impact of "dictatorship" and enhances members' enthusiasm for participating in organizational construction and communication.
Once community voting decisions are completed, smart contracts will faithfully and automatically execute the contents of the proposals, thus solving the problem of "decision-execution" implementation difficulties.
In summary, the two core characteristics mentioned above complement each other and are both indispensable. Without a decentralized organizational structure, the so-called autonomy of organizational members would inevitably become a mere performance due to the intervention of centralized management institutions, lacking practical significance and value. Conversely, if it deviates from a rigorous, reasonable, and sustainable autonomous model, then a decentralized organization becomes a rootless entity, struggling to maintain normal operations and development.
From a higher level of humanistic care and organizational development philosophy, the significance and value of DAO organizations extend far beyond the internal organization.
Traditional companies, in pursuit of maximizing shareholder interests, tend to focus on unlimited capital appreciation and scale expansion. While companies strive for higher profits and larger scales, they inevitably work to diminish the importance of individuals within the entire system; otherwise, the development of the entire enterprise would be exposed to significant risks. Consequently, traditional companies ultimately lead to individuals within them being increasingly instrumentalized, ultimately becoming "cogs in the machine." This organizational form inherently places the company and its employees in opposition to each other, continuously exacerbating the conflicts and contradictions between the two.
However, DAO organizations, relying on blockchain technology, break free from centralized management institutions and hierarchical management models, to some extent subverting the traditional paradigm of "opposition between organization and individual" and "opposition between managers and employees" found in corporate systems. The two core characteristics of DAO organizations introduced above allow the purpose and goals of DAO organizations to return to the self-exploration and social needs of individuals, rather than blindly pursuing the profitability and expansion of the organization itself.
"Humans as ends rather than means" — this humanistic ideal and vision is one of the deeper reasons why so many Web3 entrepreneurs and participants are willing to follow and even believe in DAO organizations.
However, DAO organizations also have their own limitations.
First, since the smart contracts of DAOs are deployed on-chain and fully open-source, this ensures transparency of operational rules for organizational members but also provides convenience for malicious attacks by hackers. If there are vulnerabilities in the DAO organization's smart contracts and these are exploited by hackers, it could lead to significant losses for the DAO organization. A typical case illustrating this limitation is the massive theft incident involving "The DAO."
Around 2016, a DAO organization called "The DAO" was created on the Ethereum mainnet. This DAO organization was essentially a community-controlled, decentralized investment fund. "The DAO" raised over 11.5 million ETH by selling its community tokens, which served as its investment fund and was managed collectively by its organizational members.
However, shortly after "The DAO" began operations, it was attacked by hackers due to a vulnerability in its smart contract, resulting in the theft of approximately 3.6 million ETH. Based on the ETH price at that time, the total loss from this hacking incident exceeded $60 million, making it the largest hacking incident globally at that time. This event dealt a significant blow to the Ethereum community, and to recover the related losses, the Ethereum community had to vote to approve a hard fork. In summary, the security risks of DAO organizations cannot be ignored.
Second, decision-making in DAO organizations requires voting, and to ensure that organizational members can fully participate in the voting process, DAO organizations generally set longer durations for proposal voting. Therefore, overall, the efficiency of their operational decision-making is lower than that of traditional corporate entities.
Finally, although DAOs are widely recognized and used in the blockchain field, in most countries and regions, there is no well-established financial and legal regulatory framework for DAOs. This leads to potential legal compliance risks when establishing and operating DAOs on-chain in the real world, such as issues related to liability, taxation, and financial compliance. However, a small number of countries and regions have adopted a relatively open and advanced attitude toward this organizational form and have established corresponding regulatory frameworks, which will be elaborated on later.
### How to Create a DAO Organization? What Processes Need to be Followed?
After understanding the characteristics of DAO organizations, we can further analyze how to create a DAO organization in practice. Although the creation methods and processes for each DAO organization vary, they generally include the following four steps:
Establish the purpose and operational management rules of the DAO organization.
Write the operational management rules of the DAO organization into smart contracts.
Since contracts cannot be modified once created and operational, technical personnel need to conduct strict testing and auditing of the smart contracts before they can go live.
Inject funds into the DAO organization.
The DAO organization will set fundraising methods based on a pre-established governance framework, typically completing initial financing through the sale of governance tokens of the DAO organization.
Deploy the smart contracts to the corresponding blockchain, officially establishing the DAO organization.
After completing the above steps, theoretically, the creation of a DAO organization is complete. However, it is important to note that the "completion of the creation of a DAO organization" does not mean registering and establishing a DAO organization within a legal regulatory framework. In most cases, on-chain DAO organizations do not possess legal person status and corresponding capacity for action under real-world legal frameworks. The details on how to register a DAO organization recognized by official laws and regulations, as well as the relevant provisions in various countries and regions, will be elaborated on later.
### Which Countries or Regions Have Clear Laws and Regulations to Supervise DAO Organizations?
1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
RKA DAO, located in the UAE, is a free zone established specifically for virtual asset companies, created by the government of Ras Al Khaimah (one of the emirates in the UAE). By the end of 2024, RKA DAO released a set of regulations titled "DAO Association Regulations," providing a clear legal framework for DAO organizations in the UAE.
Within this legal framework, DAO organizations are explicitly granted independent legal personality. According to Article 8 of the "DAO Association Regulations" and related provisions, DAO organizations adopt the underlying legal form of a limited liability company, with their legal personality completely independent of organizational members and token holders. Specifically, DAO organizations can legally and independently acquire, hold, or dispose of property and independently generate legal relationships and bear corresponding legal responsibilities.

(The above image shows the original text of Article 8 of the "DAO Association Regulations")
At the same time, this legal regulation also imposes clear technical requirements on DAO organizations, requiring them to be deployed on permissionless distributed ledgers and that all software code remains open-source. This provision further clarifies the unique technical aspects of DAO organizations compared to other traditional organizational forms.

(The above image shows the original text of Article 14 of the "DAO Association Regulations")
In addition, this law and regulation also provide detailed provisions and explanations regarding the internal governance structure and external regulatory framework of DAO organizations in the UAE. For example, Articles 92 and 99 of the "DAO Association Regulations" stipulate that official registrars and third-party auditors are responsible for compliance supervision and financial audits of DAO organizations.

(The above image shows the original text of Article 92 of the "DAO Association Regulations")
Analyzing the "DAO Association Regulations" reveals that the UAE government places a high emphasis on the Web3 industry, with its regulatory and governance measures leading the world. Coupled with the recent news of the Abu Dhabi sovereign fund investing $2 billion in Binance, the future development prospects of the Web3 industry in the UAE and the Middle East are highly anticipated.
2. United States
On April 21, 2021, Wyoming Governor Mark Gordon officially signed Senate Bill No. 38, known as the "Wyoming Decentralized Autonomous Organization Supplement Act." First, this act provides a clear definition of DAO organizations: "A decentralized autonomous organization is a limited liability company whose articles of organization contain a statement that the company is a decentralized autonomous organization as described in this subsection (c)."

(The above image shows the original text of Section 17-31-104 of the "DAO Organization Supplement Act")
It can be seen that the DAO organizations defined in this act can be directly registered as limited liability companies. Additionally, to highlight the unique characteristics of DAO organizations and free them from the various restrictions imposed by the limited liability company format, the act specifically requires that DAO organizations must include the following statement in their articles:
"The rights of DAO organization members may differ significantly from the rights of other limited liability company members. The Wyoming DAO Organization Supplement Act, the underlying smart contract, the articles of organization, and the operating agreement (if applicable) may define, reduce, or eliminate fiduciary duties and may restrict the transfer of ownership interests in the DAO organization, the exit from the DAO organization, and the dissolution and liquidation of the DAO organization."

(The above image shows the original text of Section 17-31-104 of the "DAO Organization Supplement Act")
In addition, this act also provides relevant regulations for the establishment, operation, and dissolution of DAO organizations at various stages. However, a comparison shows that the completeness and rigor of this regulation are slightly inferior to the "DAO Association Regulations" of the UAE.
Tennessee in the United States also amended Title 48 of the "Tennessee Code" on April 20, 2022, which explicitly states in §48-250-103(a) that limited liability companies (LLCs) can register as "Decentralized Organizations" by adding a specific statement in their articles of organization. In terms of the legal nature of DAO organizations, the legislative model in Tennessee is quite similar to that of Wyoming.
Additionally, countries such as the Marshall Islands and Malta have also introduced laws and regulations related to DAO organizations, but due to their limited influence, they will not be discussed here.
### Can DAO Organizations Be Used as Token Issuers for RWA Projects?
Regarding this issue, it is necessary to analyze it in conjunction with the definition of DAO organizations mentioned earlier. If the DAO organization has been registered as an independent legal entity according to local laws and regulations, theoretically, as long as the DAO organization meets local financial compliance requirements, it can complete the token issuance. Of course, the specific situation should be comprehensively judged based on the project itself and local regulatory policies, laws, and regulations.
If the DAO organization only exists on-chain and does not have a corresponding legal entity off-chain, then such DAO organizations cannot directly serve as token issuers for RWA projects. They need to undergo legal wrapping (Legal Wrapper) in the early stages of the project. This is because an on-chain DAO organization, as a token issuer, would face tax risks and is likely unable to pass the financial compliance review of relevant financial institutions. The so-called "legal wrapping" specifically involves establishing a separate legal entity such as a limited liability company or foundation, and through agreements or specific structural designs, transferring some functions of the DAO organization to the off-chain legal entity, ultimately completing the token issuance.
### Interpretation by the Crypto Law Team
This novel organizational form of DAO has developed quite maturely on-chain and has given rise to many star projects. However, if DAO organizations want to further deepen their links and interactions with the real world, relevant laws, regulations, and regulatory frameworks still need to be improved. At the same time, DAO organizations currently in operation or projects interested in DAO organizations should pay more attention to compliance requirements in the real world.
The Crypto Law team is dedicated to providing the most professional legal services to practitioners in the crypto industry, maximizing the protection of clients' legal rights and avoiding unnecessary legal risks. Our goal is to help clients make more money while avoiding pitfalls; if they win, they win comfortably, and even if they lose, they can lose clearly.
The views expressed here are solely those of the author and do not constitute legal advice or opinions on specific matters.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




