作者:念青,ChainCatcher
近日,链上信用借贷协议 3Jane 公布白皮书。白皮书内容显示,3Jane 是一个基于信贷的货币市场,可实现零抵押借款。通过零知识证明技术验证钱包地址和银行账户来给予信用贷额度,再通过罚没信用分,和拍卖违约债的方式,来实践零抵押贷款的风控违约。
尽管无抵押信贷市场在传统金融中已经趋于成熟,但在 DeFi 中,仍以超额抵押借贷为主,即“押100借50”的模式。此外,已存在Maple Finance、Goldfinch等无抵押借款协议,也主要面向机构、做市商等,普通用户难以高效借贷。
据白皮书显示,3Jane 将打造 peer-to-pool(点对池) 的基于信用的货币市场,支持算法、实时无担保的 USDC 信用额度,为 famer、交易员、企业和 AI 代理提供资金。
简单来说,3Jane 在做的就是传统金融中很常见的信用贷产品,比如支付宝中凭借“芝麻信用”分数来获得相应额度贷款的“借呗”。但在缺乏中心化机构支撑的加密体系中,这个产品则显得大胆激进。
目前,3Jane 产品还处于开发阶段,官方已经开放早期使用者申请通道,可填写相关申请早期测试。但需要强调的是,3Jane 合作的链下信用的技术平台例如 Plaid 目前支持的地区有限(例如美国、欧洲等地),主要支持的是美国的信用体系,因此,3Jane产品上线初期,可能仅支持少部分地区,亚洲等地可能被排除在外。
3Jane 具体如何运作?
据白皮书,3Jane最终将建立在以太坊生态,其目标受众为加密原生用户(比如收益农民、交易员、商家、AI代理),靠信用评估未来现金流、链上链下资产和信用评分来放贷,使他们通过无抵押贷款解锁资本效率。
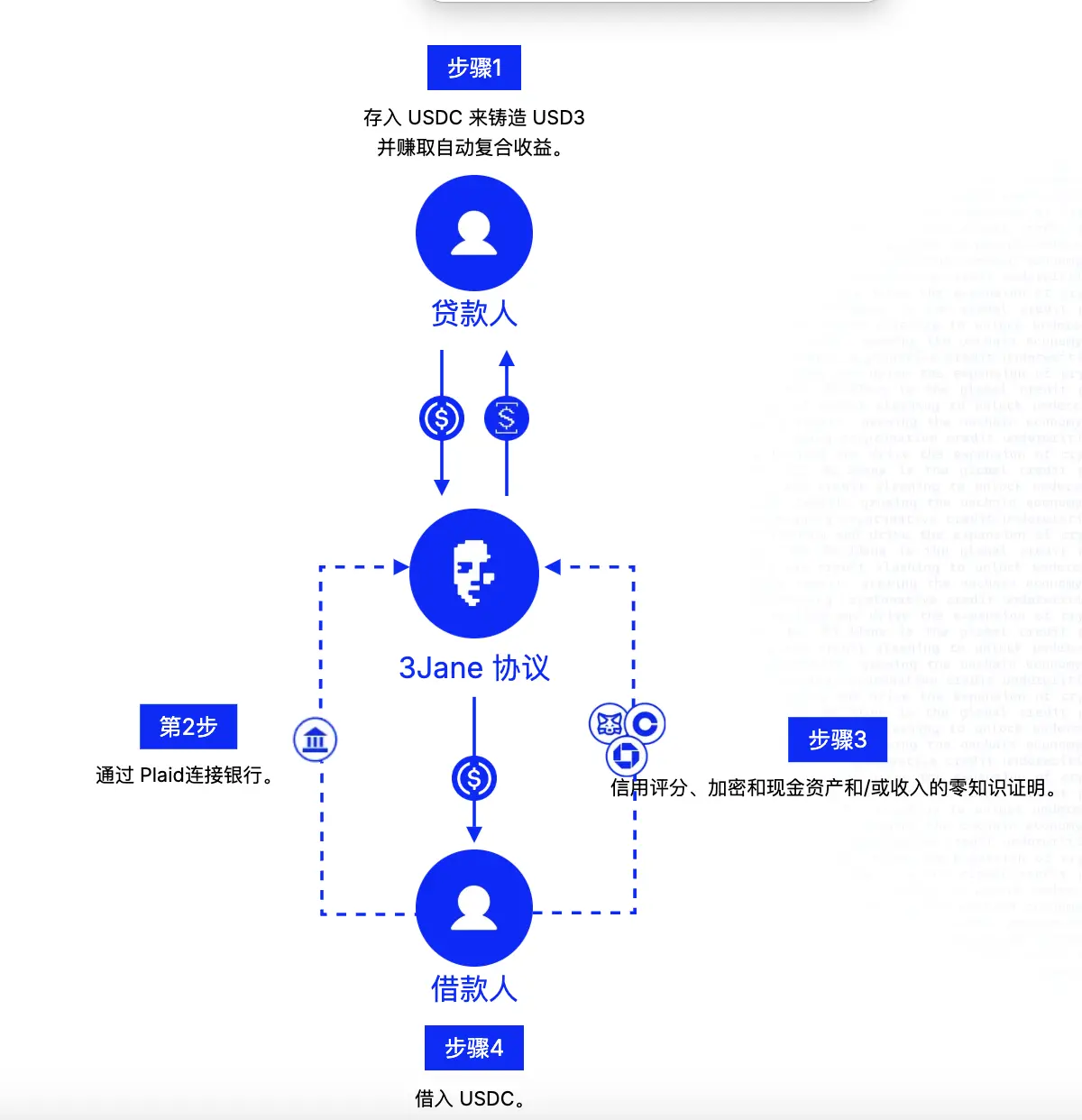
如何运作?
贷款人存入USDC,换成USD3(稳定收益)或sUSD3(高收益但风险更高),借给借款人。借款人通过连接钱包和银行账户完成链上和链下的信用认证,在3Jane快速评估后得出信用分数,并拿到无抵押信用额度。
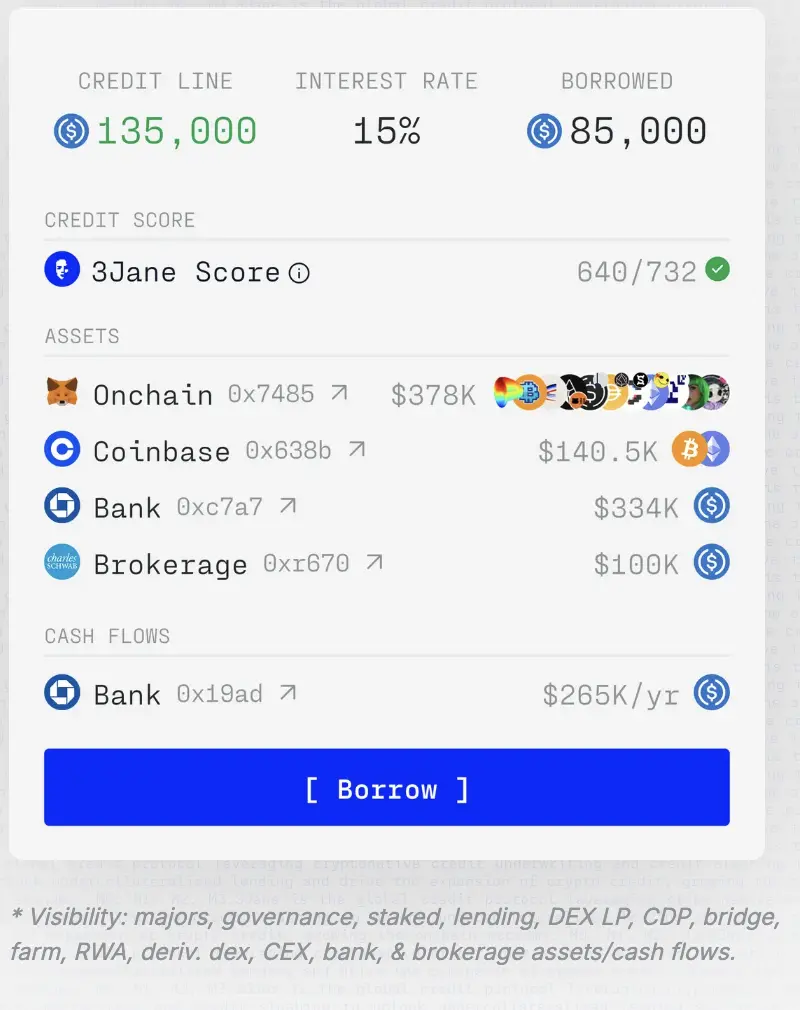
3Jane 信用评分是如何得出的:
- 链上:3Jane 通过 Cred Protocol 和 Blockchain Bureau 评估链上信用,综合分析 EVM 链上的借贷、清算、持币、交易所交互等行为。Cred Protocol 和 Blockchain Bureau都是链上信用评分工具,通过分析链上数据(比如你的钱包交易记录)来给加密用户打信用分数,两个工具可覆盖超过5亿个地址、8条EVM链、100多个DeFi协议,分析大量交易数据,并生成300-1000的信用分数。
- 链下:用zkTLS(零知识技术)从链下(银行、Credit Karma)拉取资产和信用数据,保护隐私。通过 ReclaimProtocol 和 EigenLayer 获取 Transunion、Equifax 信用评分和 Credit Karma 记录(VantageScore3.0,VantageScore 3.0 是一个在美国广泛使用的信用评分模型,类似“芝麻信用分”),且在这个过程中无需提供社保号。此外,3Jane 通过使用现有的基础设施实现法币到加密货币的入网。Plaid 是 3Jane 最初将链下声誉与链上以太坊地址连接起来的方式。Plaid 提供连接用户的银行账户与各种金融应用程序的API服务。
3Jane 资金市场架构
- 资金流:
- 存入的USDC先放Aave V3赚基础收益,再分配给借款人。
- USD3是优先级高的代币,sUSD3是次级债,先承担损失。
- 借贷合约:
- 基于Morpho Blue改造,把抵押逻辑换成信用评估。
- 利率=基础利率(IR_Base)+风险溢价(IR_DRP)+逾期罚息(IR_LP)。
隐私与透明度
- 隐私:借款人数据(姓名、电话等)加密分片存储,只有违约时解锁给催收机构。
- 透明度:链上证明(zkTLS Proofs)让放贷人能审计借款池健康。
无抵押状态下如何防止坏账?
1、还款激励
- 信用评分惩罚:
- 不还钱,3Jane信用评分被“砍”,以后借钱额度低、利率高。
- 逾期收益共享:
- 逾期罚息分给其他借款人,鼓励大家监督和还款。
- 债务拍卖(NPL Auction)
- 流程:
- 借款人逾期后,信用额度进入违约状态。
- 启动链上荷兰式拍卖,美国持牌催收机构竞标接手坏账。
- 催收机构追回钱后拿提成(比如20%),剩下的还给资金池。
- 怎么追:
- 催收机构用TLOxp(债务追踪工具)找人,能上报信用局影响借款人现实信用,还能上法庭强制还款。
3、风险管理
坏账估值与减记
- 动态减记:
- 违约后不立刻把债务价值记为0,而是用公式算概率加权后的市场价值(M(t))。
- 公式考虑损失概率(L(t))和回收率(R(t)),随时间递减,避免市场恐慌。
- 例子:
- 刚违约时可能值50%,拖久了降到10%,最后可能是0。
资金池分层
- USD3:85%资金池,优先拿利息,风险低。
- sUSD3:15%资金池,高收益但先亏,缓冲坏账冲击。
还款规则
- 最低还款:
- 每月还利息+本金的一部分,但不会超过资产增值或现金流。
- 有宽限期(G_p),过期加罚息,再不还就拍卖。
- 保障:
- 还款跟借款人实际收益挂钩,降低还不起的风险。
- 信用筛选
- 门槛:
- 3CA算法综合资产、现金流和信用评分,不合格直接拒贷。
- 用zkCoprocessor防欺诈地址(Sybil攻击)。
3Jane 团队背景及发展现状
3Jane 由 3yakov(@_yakovsky)于2024年 创立,3yakov曾在 Ribbon Finance工作三年,最初作为智能合约工程师加入,随后转向增长策略。除了创始人外,暂无其他团队成员信息披露。
目前,3Jane 产品还处于开发阶段,但据官网显示,其已获得 Coinbase、Lagrange、Reclaim、CRED 和 EigenLayer等机构的支持。Circle 联创兼CEO Jeremy Allaire 对 3Jane 评价到“3Jane人工智能驱动的实时无担保 USDC 信贷的想法非常酷”。

链上无抵押借贷发展现状
加密无抵押借贷是DeFi发展的新方向,因为风险管理困难、技术实现比较复杂等原因,这一领域还在早期。已有的一些协议,包括Goldfinch、TrueFi 、Maple Finance 等。
Goldfinch重点是给现实世界的人和企业放贷,比如发展中国家的小生意。Goldfinch 对借款人信用审核引入了去中心化审计师批准机制,资金效率相对低一些;TrueFi 主打链上信用贷款,用社区投票和信用评分决定谁能借钱,不一定非得抵押。借款人多是机构或有信用记录的实体,其风险控制靠人工审核多一些;Maple Finance 面向机构的无抵押借贷,靠专业团队评估借款人的信用,不是完全去中心化,借款人需要提供财务报表,因此存在隐私上的问题。
综合来看,3Jane是最新、最激进的尝试,基于以上协议的困境有一些优化。但风险控制仍是加密无抵押借贷最核心的阻碍之一。尽管 3Jane 设置了信用评分惩罚和追债制度,但其约束力究竟有多大?链上信用评分的威慑力实际有限,毕竟使用信用评分的DeFi协议还比较少。此外,鉴于加密货币的全球性,尚不清楚这种拖欠行为的威慑力有多强。
以Goldfinch 为例,其目前已经遭遇了三次违约,违约金额达上千万美元。多次违约凸显了无抵押贷款的难度,放贷者和协议本身都面临巨大的风险。
(本文只介绍早期项目,不作为投资建议。)
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




