作者:Kevin, Caiya researcher from BlockBooster
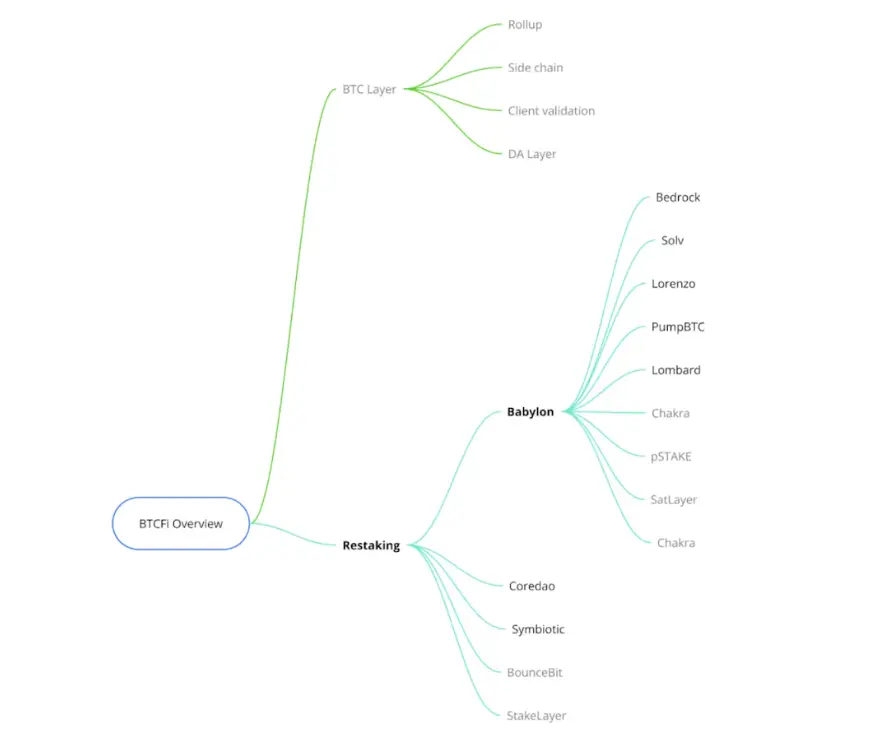
比特币因其工作量证明(PoW)共识,其收益方面的应用潜力一直受限。与权益证明(PoS)不同,比特币缺乏原生质押机制。然而,随着BTCFi的崛起,新的方式正在逐步形成,允许比特币在不牺牲安全性的前提下产生收益。BTCFi生态系统大致分为两部分:BTC层与重质押,以及诸如ARC20和BRC20等资产协议。本文将探讨BTCFi领域的新兴参与者如何重塑比特币重质押格局,并比较它们的主要优势。
当前比特币重质押的格局
比特币重质押在本轮周期中并非新话题,已有BounceBit、Coredao、Stakelayer等知名项目,以及近期受到广泛关注的Babylon和Symbiotic。
首先,我们来分析Babylon的方案。Babylon的比特币质押方案包含多个旨在增强安全性和用户体验的创新,令其在众多协议中脱颖而出:
- 远程质押:Babylon采用比特币的UTXO模型和脚本系统进行质押、削减和奖励分配。一个显著的优势是,质押比特币的用户不会面临削减惩罚风险,只有节点运营者会受到影响。这意味着用户的比特币没有损失风险,只是无法提前解锁质押的资金,安全性较高。
- 时间戳服务器:Babylon的时间戳服务器将来自PoS链的事件记录到比特币主网上,提供防篡改的时间戳记录。尽管比特币主网确保这些记录一旦上链无法更改,但时间戳的准确性仍依赖于Babylon的PoS网络。
- 三层架构:Babylon的架构分为三层——以比特币为基础层,Babylon为中间层,PoS链为顶层。Babylon将PoS链的检查点记录到比特币区块链上,确保数据的不可篡改性。通过使用Cosmos作为中间层,增强了其可扩展性和灵活性,吸引了节点运营者,并使原生比特币质押能够为Babylon的PoS网络提供支撑。
虽然Babylon在原生比特币质押领域处于领先地位,但它并不是唯一一个探索重质押的协议。让我们一起看看另外2个明星项目的比特币质押方案:
- Symbiotic:由Lido和Paradigm联合创立,Symbiotic被认为是EigenLayer的直接竞争对手。Symbiotic最近宣布支持比特币重质押,但目前仅接受WBTC质押。与Babylon提供的原生比特币质押不同,Symbiotic要求用户将比特币转移到第三方托管地址。到目前为止,Symbiotic已质押1,630枚WBTC,并通过积分奖励激励用户参与。
- CoreDAO:CoreDAO提供了两种质押方式:一种是原生质押,允许比特币持有者将比特币委托给Core验证者而无需转移资金;另一种是托管质押,用户将比特币发送到锁仓地址并在CORE链上铸造coreBTC。目前,CoreDAO仅支持托管质押选项。
上述三者都希望为比特币生态带来更多应用场景,激发比特币与其他链之间的跨链通信或者数据分享。再质押平台本身通过模块化的思想来共享底层网络的安全性,并向上赋能AVS,为广泛应用提供基础设施,大幅提高区块链的效率和性能。
优点:
- Babylon和CoreDAO通过比特币的时间戳机制,缩短Pos链的质押流程;
- Symbiotic有Lido和Paradigm的支持,在协议合作和生态推进上占据优势;
- Babylon率先实现原生质押,在比特币质押上实现了去信任。
不足方面:
- CoreDAO和Symbiotic依然依靠第三方托管来解决信任假设;
- Babylon的 PoW+PoS架构在安全性逻辑上存在不足,只能被动依靠比特币网络实现记账的功能,不能主动利用比特币网络的安全性。
和以太坊再质押平台不同,比特币再质押平台没有直接将比特币网络的安全性传导给各自的 Pos 网络,而这也是未来发展的重点方向。
比特币重质押生态系统
已有多个协议与比特币重质押生态系统合作,这些项目旨在提升质押比特币资产的流动性和实用性:
- Bedrock:作为Babylon的首轮预质押领头项目,持有约30%的份额,Bedrock支持质押WBTC以铸造uniBTC。在Babylon主网上线后,用户将能够从uniBTC和Babylon质押中获得奖励,并有可能通过Bedrock的Diamonds计划获得空投。
- Lombard:Lombard允许用户通过Babylon质押比特币,且Lombard负责管理重质押过程。当用户质押比特币时,Lombard在以太坊上铸造等量的LBTC。用户可使用LBTC参与DeFi活动,享受跨链收益的灵活性。
- Lorenzo:Lorenzo通过本金-收益分离模型提供流动质押和重质押,允许用户质押比特币或BTCB来获得stBTC(流动性本金代币)和YAT(收益代币)。该双代币系统使用户能够在积累Lorenzo积分的同时获得Babylon的原生质押奖励。
- Pell Network:Pell是首个基于比特币重质押构建的安全网络,并运行在Babylon的AVS网络上。Pell的TVL在三周内已超过2亿美元,拥有超过41万个独立地址。Pell提供四种重质押方式,涵盖从原生比特币质押到质押包含流动性BTC衍生品的LP代币,其AVS架构使其能够从中间件、预言机、模块化链等领域捕获大量收入。
- PumpBTC:允许用户质押WBTC或BTCB,并1:1获得pumpBTC代币。PumpBTC的独特之处在于,由第三方托管机构(如Cobo和Coincover)处理重质押流程。用户无需直接与协议交互即可享受收益,简化了质押流程。
- Solv Protocol:Solv开发了一个跨多条链的比特币资产流动性层,支持在Arbitrum上的WBTC、BNB链上的BTCB及Avalanche上的BTC.b的跨链桥接。用户可以通过持有solvBTC、参与借贷协议或向流动性池添加流动性来赚取XP积分。此外,尽管Babylon主网尚未上线,用户仍可通过Solv的vault桥接到Babylon以获取更多积分。
- Stakestone:预计将采用类似于ETH-STONE的模式,用户将原生比特币质押至Babylon并铸造收益型的STONEBTC,用于跨链流动性。用户可以从各种生态系统中赚取积分,例如2倍Scroll积分。
结论
将比特币转化为一种能产生收益的资产具有重要意义,比特币重质押是对比特币“数字黄金”定义的有效补充,极大地提升了其流动性。与以太坊生态不同,BTCFi协议,如Babylon、Symbiotic和Coredao,不依赖预先存在的基础设施,这既带来挑战,也提供了机会。Solv、Lombard和Lorenzo等平台正逐步发展,分别专注于多重奖励、安全灵活性及双重激励系统。BTCFi仍处于早期阶段,技术和生态系统发展迅速,我们将继续关注这一领域的动态。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



