Changes in the consensus mechanism, token economics model, and unique ecosystem of Berachain

1. Introduction
Proof of Stake (PoS) as a network consensus mechanism has been widely used recently. The more native tokens staked in the network, the higher the security.
However, in PoS networks, native tokens can be used not only for staking but also for paying gas fees as the base currency within the ecosystem. This design can lead to a decrease in liquidity and network activity within the DeFi ecosystem as the amount staked on a PoS network increases, creating a self-contradictory situation.
This lack of liquidity can have a negative impact on the entire ecosystem, such as causing high slippage on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and inhibiting the development of protocols based on token deposits. Therefore, many ecosystems have been forced to conduct excessive airdrops or build their own L2 or application chains to ensure a certain level of liquidity, which has dispersed the liquidity of the entire blockchain ecosystem and reduced user experience.
On the Ethereum mainnet, the attention received by the Restaking protocol has led to a continuous increase in ETH staking, reaching a historical high of about 28%. However, we can observe a significant decrease in Ethereum network traffic, with the daily average gas fee being only about 5 Gwei.
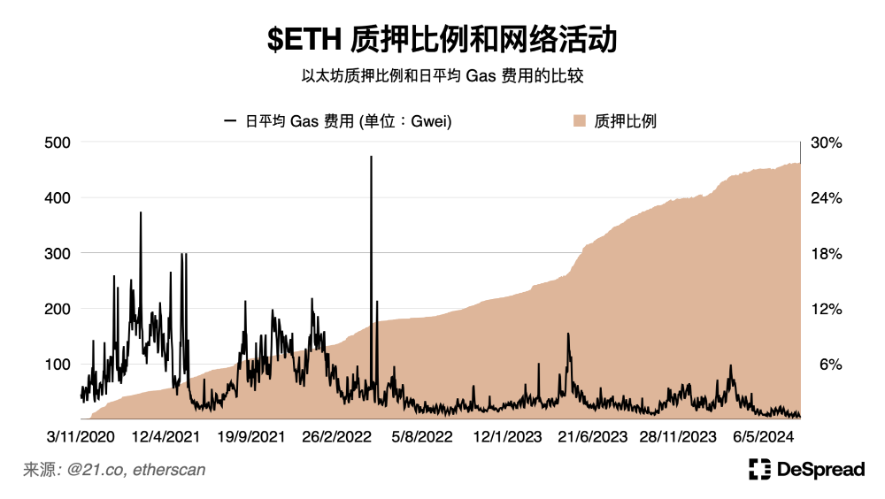
This PoS structure brings about a problem where users cannot simultaneously stake tokens in liquidity protocols and the network itself, leading to conflicting incentives for validators and protocols.
Many foundations have recognized this issue and have attempted to coordinate the interests of both parties by providing funding, technical guidance, and marketing support to protocols contributing to the ecosystem. However, this still does not fully reflect the opinions of ecosystem members such as network users and validators, and may even lead to centralization issues due to overreliance on foundations.
If one of the core ideas of blockchain is to create an environment of "Can't be evil" rather than "Don't be evil," then a new systematic improvement is needed to address the issue of PoS networks being unable to simultaneously provide liquidity to the ecosystem and network security. The goal of Berachain is to address the problems existing in PoS networks by constructing a structure that can simultaneously supplement the liquidity and network security of the ecosystem through token economics based on game theory.
In this article, we will explore the consensus mechanism and token economics model of Berachain, the main changes in the v2 testnet released in June 2024, and introduce its unique ecosystem built on this foundation.
2. Balancing Network Security and Ecosystem Liquidity in Berachain
Berachain is built using BeaconKit, a framework that utilizes Cosmos SDK to build a customizable EVM execution environment, making it an L1 network compatible with EVM.
Typically, blockchain projects release a whitepaper outlining their technical vision and recruit potential users through various activities to build a community. However, Berachain began forming its community with a NFT project called "Bong Bears."
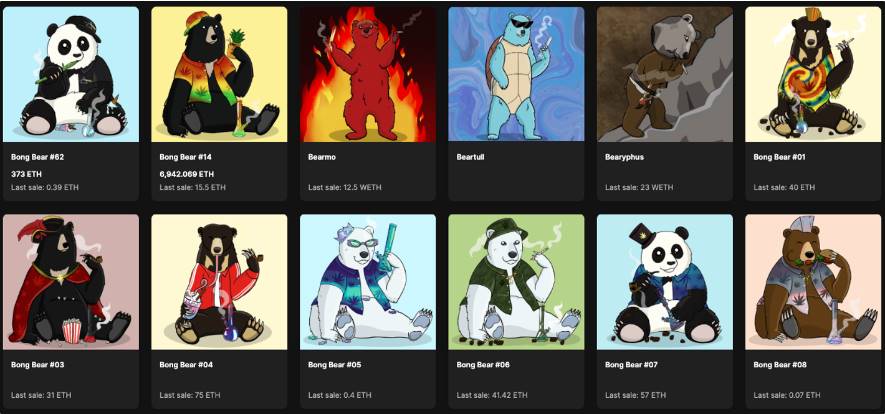
Bong Bears was launched in 2021 during the NFT market boom and received strong support from the popular DeFi project Olympus DAO community at the time. Subsequently, Bong Bears holders received airdrops of derivative NFTs such as The Bond Bears, The Boo Bears, and The Baby Bears, expanding the community.
During this period, the term "Berachain" in the Bong Bears community was just a meme, but developer Dev Bear actually began developing Berachain, which has now entered the testing phase.
Many blockchain projects, despite investing a significant amount of time and resources to build a loyal community, often lose users after token airdrops. However, the way Berachain built its community, which differed from these projects, naturally attracted the attention of many cryptocurrency users.
Another key factor that makes Berachain an anticipated L1 for many users is its "Proof of Liquidity (PoL)" design, a consensus protocol that solves the issue of PoS networks being unable to uniformly reward participants through token economics based on game theory.
2.1 Proof of Liquidity (PoL)
In Berachain's PoL consensus mechanism, participants have the following roles and relationships:
- Validators: Operate Berachain nodes and participate in network validation.
- Liquidity Providers: Provide liquidity for protocols within the ecosystem.
- Protocols: Provide specific services to users on the Berachain network and require liquidity within the network.
In Berachain's PoL mechanism, liquidity providers for specific protocol liquidity pools can receive rewards in the form of Berachain network tokens, which are issued in each block as rewards. Liquidity providers can delegate the received tokens to validators to indirectly participate in the network validation process. During this process, liquidity providers can earn interest from the liquidity they provide and also generate income through network validators.
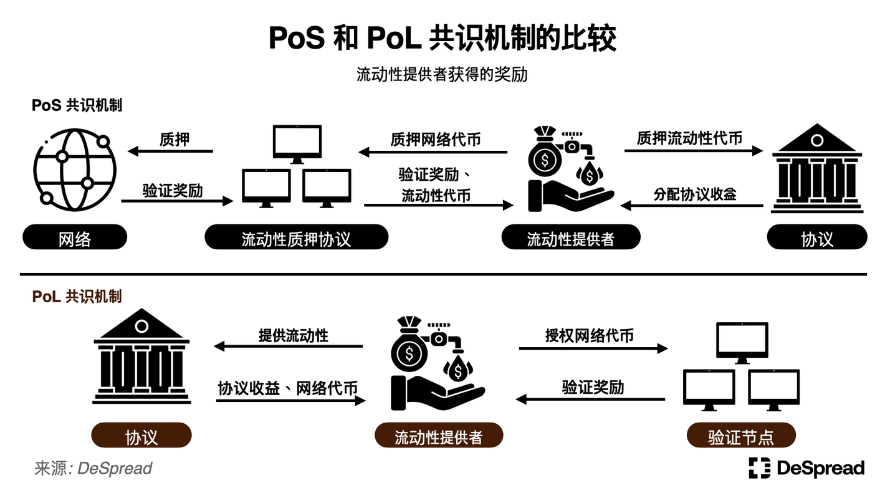
At first glance, this structure may seem similar to PoS, except for staking assets in liquidity protocols on PoS chains and then depositing the received liquidity tokens into another protocol to earn profits. However, Berachain embeds this functionality within the chain, preventing liquidity fragmentation at the base level, which is a problem in PoS.
In addition, validators on Berachain have the authority to vote on the allocation of block rewards to liquidity pools, meaning network validators have the power to directly increase the rewards for specific liquidity pools. Compared to PoS, this feature allows liquidity providers and protocols to more closely participate in the PoL consensus mechanism.
2.1.1. Ecosystem Flywheel
It is predicted that protocols launched on Berachain will use investment funds, self-issued tokens, and protocol fees to provide incentives to validators, in order to secure their votes and ensure the initial growth of the protocol.
This will also incentivize validators to allocate rewards received from the protocol to network token delegators to ensure they have more voting power. Allocating rewards received from the protocol to liquidity providers will encourage them to provide liquidity to the protocol again, creating a virtuous cycle that further strengthens network security.
Through this approach, Berachain's PoL mechanism, with projects and liquidity providers as the main participants, addresses the issue of traditional PoS structures where they do not directly participate in the network consensus mechanism. These three entities are closely interconnected, exchanging liquidity and incentives, forming an ecosystem flywheel where value flows from liquidity providers to the protocol, from the protocol to validators, and then back to liquidity providers.
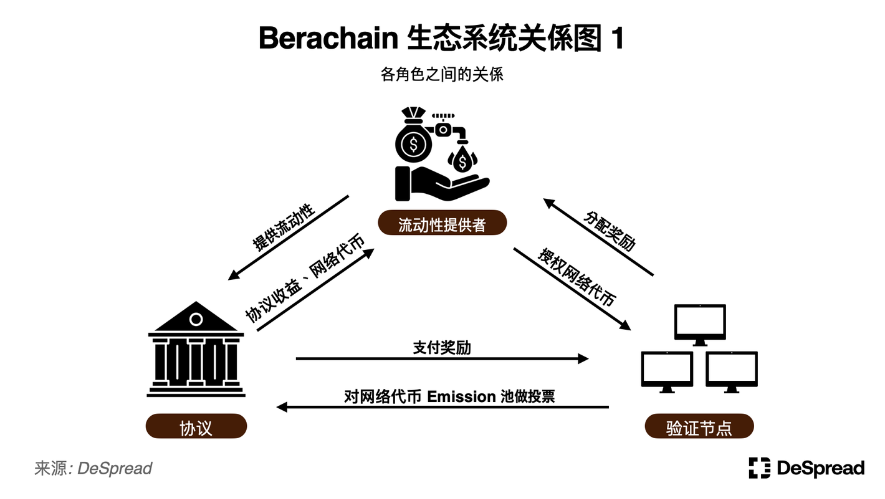
2.2. Tri-Token Model
To better utilize the flywheel characteristics of PoL, Berachain adopts a Tri-Token Model, utilizing the following three types of network tokens:
- $BERA: This token serves as the network fee for Berachain, and gas fees are burned. Validators must stake 69,420 $BERA to activate a node.
- $BGT: Inflation rewards allocated by validators to liquidity pools, this token is non-transferable and non-tradable, tied to the account. After providing liquidity, liquidity providers can take the following actions with the received $BGT:
- Burn $BGT at a 1:1 ratio and receive $BERA
- Delegate to validators
- $HONEY: A stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, serving as the reserve currency in the Berachain ecosystem. Currently issued in the form of wrapped (Wrapping) USDC on the test network, it may be converted to over-collateralized form in the future. A 0.5% fee is charged upon issuance, and this fee is distributed to $BGT holders.
By incorporating the above Tri-Token Model into the participant relationship diagram of Berachain, we can summarize the following points.
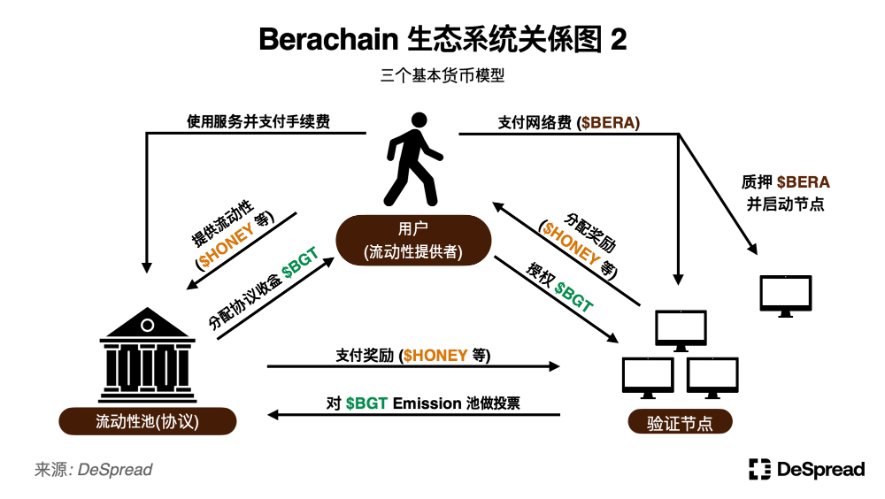
Since the non-tradable $BGT determines the allocation of inflation rewards and can only be obtained by providing liquidity, Berachain's structure prevents whales from acquiring large amounts of $BGT in a short period to influence governance. This structure encourages protocols seeking to attract liquidity in the Berachain ecosystem to persuade validators with significant voting power through the allocation of incentives.
This social consensus behavior among participants in the Berachain ecosystem leads to increased network security and liquidity, helping to attract more users to join the Berachain ecosystem.
As more users join the ecosystem and network usage increases, the amount of $BERA burned for gas fees will also increase. Furthermore, as demand for collateral and trading assets in ecosystem protocols increases, the demand for $HONEY will also increase, resulting in profits for $BGT holders.
3. bArtio Testnet
With a loyal community and a unique PoL mechanism, Berachain has gained widespread attention and achieved remarkable results. In January 2024, it launched the first test network, "Artio Testnet," and within 8 days, the number of active wallets reached 1 million.
However, as Berachain uses the CometBFT consensus mechanism based on Cosmos to run EVM, compatibility and scalability issues with EVM were discovered during the test network. In June 2024, Berachain launched the second test network, "bArtio Testnet," to address these issues encountered in the first test network and improve other deficiencies related to the PoL mechanism.
3.1. Full EVM Compatibility
During the chain's development, the Berachain team constructed a compatibility EVM framework called "Polaris" to connect the CometBFT consensus mechanism based on Cosmos and the EVM execution environment. The Artio test network of Berachain was built using this framework.
However, limitations of Polaris were discovered during testing.
- The Cosmos SDK's consensus engine waits for EVM to complete transaction processing before creating blocks, leading to bottlenecks when processing a large number of transactions simultaneously.
- Polaris cannot function properly when performing precompiles for algorithms that have not been constructed, leading to EVM compatibility issues.
To overcome these issues with Polaris, the bArtio testnet introduced BeaconKit, an EVM-compatible framework derived from the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain.
3.1.1. BeaconKit
Unlike Polaris, BeaconKit explicitly separates the execution layer (EVM) and the consensus layer (CometBFT), connecting and making them compatible through the EngineAPI. This architecture allows BeaconKit to work in collaboration with standard Ethereum execution clients (Geth, Erigon, Nethermind, etc.).
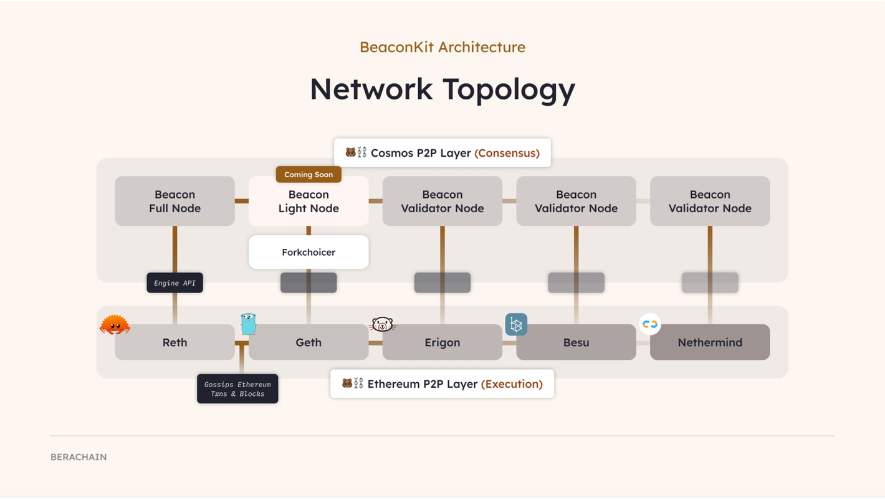
The use of the same execution client as Ethereum in the bArtio testnet allows for a 100% identical EVM execution environment. When the Ethereum execution environment is updated, Berachain only needs to install and run the client provided by Ethereum to replicate the effects of the EVM execution environment updates from the Ethereum mainnet, without the need for any special operations on the Berachain network.
Furthermore, unlike Polaris, BeaconKit runs the execution layer and the consensus layer independently, so a bottleneck in one layer does not affect the other. Additionally, when a validator creates a block, they propagate the state of all completed transactions in that block to other validators. This "Immediate Execution" mechanism significantly improves transaction processing speed, addressing Polaris's scalability issues.
3.2. Strengthening the PoL Mechanism
In addition to changing the EVM-compatible framework to BeaconKit, the Berachain team made the following changes to strengthen the PoL mechanism of the bArtio testnet.
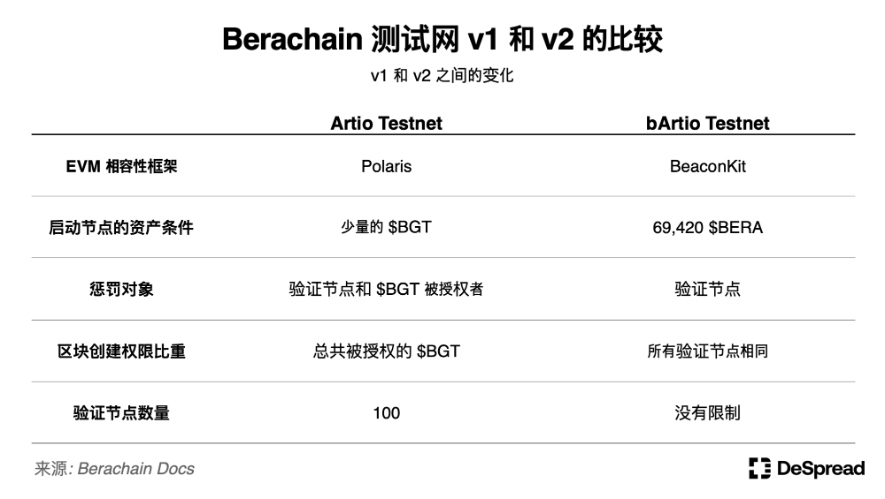
Changes to Validator Participation Requirements: In v1, activating a validator node only required a small amount of $BGT staking, but the bArtio testnet changed this requirement to 69,420 $BERA to increase the staking amount and network security.
Changes to Penalty Conditions: In v1, incorrect behavior by validators would collectively affect both the validator node and the liquidity providers delegating $BGT to that validator, reducing the $BGT of these participants. In v2, the penalty conditions were changed to only reduce the staked $BERA of the validator, separating the roles of $BGT and $BERA in the PoL ecosystem and strengthening the responsibility of validators.
Changes to Block Creation Authorization Criteria: In v1, the authorization for validators to create new blocks would change based on the amount of authorized $BGT they received. In v2, the amount of authorization no longer affects the permission to create new blocks, giving each validator an equal opportunity. However, block rewards still change based on the authorized amount of $BGT.
Increase in Validator Cap: To enhance network decentralization and security, the Berachain team removed the limit of 100 validators. As of July 16th, a total of 150 validators are participating in validating the Berachain network.
The table below summarizes the changes from the Artio testnet to the bArtio testnet (conditions are subject to change before the mainnet launch).
After testing the PoL mechanism of the Artio testnet, the bArtio testnet is currently fine-tuning the details and parameters of PoL in preparation for the actual mainnet launch.
Since its launch, the daily transaction volume of the bArtio testnet has gradually increased, with approximately 3.2 million transactions and 860,000 active wallets. Over 150 projects are also preparing to build new protocols on Berachain to leverage the advantages of EVM compatibility, scalability, and the PoL mechanism.
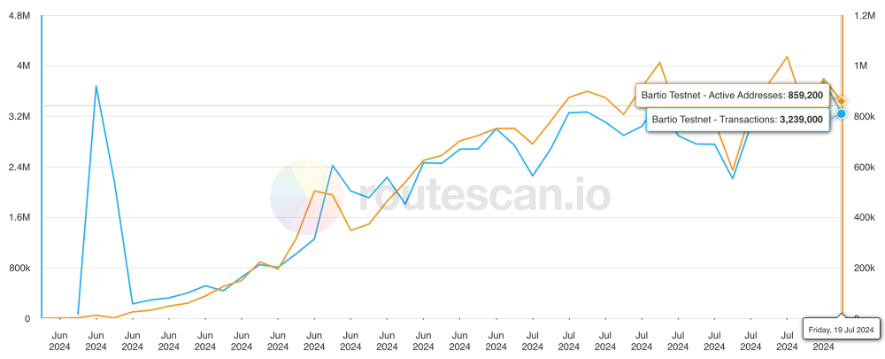
Berachain Daily Active Wallets and Transaction Volume, Source: Beratrails
4. Exploring the Berachain Ecosystem
In typical L1 networks, foundations usually issue tokens and allocate a portion to the ecosystem for development funding, hackathon programs, etc., to help build the ecosystem.
The Berachain team also has an incubation program called "Build-a-Bera," but "Build-a-Bera" only uses funds from the Berachain team to provide seed investments and mentor support for incubated projects, without allocating Berachain's tokens through grants or hackathon distributions.
Smokey The Bera, co-founder of Berachain, once criticized subsidy systems of other networks. The reason the Berachain team can take this stance is because the essence of Berachain's PoL consensus mechanism is to distribute $BGT to users who contribute liquidity to the liquidity pools, thereby supporting ecosystem projects.
Compared to ecosystem incubation schemes of other networks, Berachain does not directly provide assets to protocol development teams. Instead, the "consensus" of network participants guides the liquidity of the protocol, which can be considered a healthier form of ecosystem growth.
Due to the PoL structure of the network participant incentive mechanism, communication and consensus among validators, protocols, and liquidity providers in the Berachain ecosystem are crucial for ecosystem growth. Although Berachain is still in the testing phase, it has already led to many collaborations, with some protocols even attempting to play multiple roles and operate validator nodes themselves.
Next, let's explore some protocols in the Berachain ecosystem.
4.1. Native dApps
Berachain's native dApps are built by the team as infrastructure responsible for the basic functions of the ecosystem. Currently, three types of native dApps are running on the testnet: BEX, Bend, and Berps.
- BEX: A decentralized exchange that allows users to trade or create their own liquidity pools without intermediaries.
- Bend: A decentralized lending protocol that allows users to borrow $HONEY using various assets as collateral or earn interest by providing liquidity with $HONEY.
- Berps: A decentralized perpetual contract exchange that allows users to create leveraged positions using $HONEY as collateral or earn trading profits by providing liquidity with $HONEY and earn trading fees.
Before the launch of other protocols, these native dApps will provide basic DeFi functionality to users in the nascent Berachain ecosystem and also serve as channels for distributing $BGT to liquidity providers participating in the nascent ecosystem. In the current bArtio testnet, it can also be observed that the liquidity pools eligible to receive $BGT are all composed of native dApps.
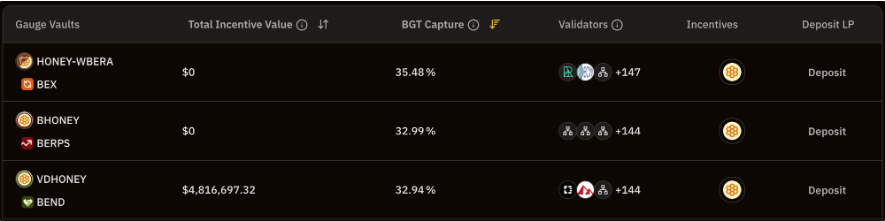
Berachain Treasury Gauge, Source: BGT Station
By using $HONEY as the primary collateral asset, the native dApps further strengthen Berachain's tri-token economic model, expand its utility, and distribute protocol-generated revenue to $BGT holders.
In addition, this economic model has also become a catalyst for ecosystem diversification, encouraging development teams to release protocols on Berachain in various ways to utilize the PoL mechanism and unleash creativity, rather than just providing infrastructure.
4.2. Ways DeFi Protocols Utilize PoL
DeFi protocols on other networks typically pay additional rewards to liquidity providers to attract liquidity and generate protocol revenue.
However, DeFi protocols on Berachain do not incentivize liquidity providers. Instead, they build the following flywheel by incentivizing validators.
The protocol distributes rewards to validators voted for by users, encouraging more users to delegate $BGT to those validators.
To earn more rewards, users continue to delegate $BGT to validators receiving rewards. As the delegated $BGT increases, validators gain more voting power for rewards, helping liquidity pools generate more $BGT rewards.
To earn the $BGT rewards generated by the liquidity pool, users bring in more liquidity from external sources, increasing the protocol's traffic and revenue.
Repeat steps 1-3.
During the establishment of this flywheel, we can also see some protocols negotiating with users based on protocol revenue and future added value, providing more convenience and additional value to users. Some protocols also strengthen their rights by aggregating dispersed liquidity to increase their revenue.
4.2.1. Kodiak
Kodiak is a DEX that provides Concentrated Liquidity AMM (CLAMM) for trading pools like Uniswap v3, allowing users to concentrate their liquidity in specific areas to provide more efficient $BGT mining than BEX.
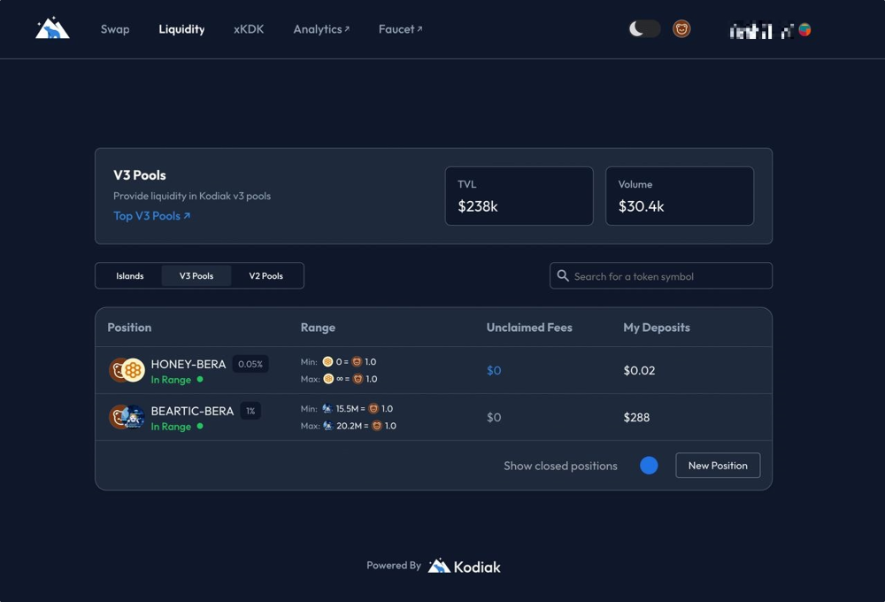
Kodiak V3, Source: Kodiak
Kodiak has two tokens, $KDK and $xKDK, which users can exchange within the protocol, described as follows:
$KDK: Reward token for liquidity providers and traders.
$xKDK: Governance token of Kodiak and non-tradable. Holders can receive income generated by Kodiak, including fees from user transactions and rewards from other protocols.
Concentrated liquidity supply allows users to mine $BGT with higher capital efficiency. However, if price fluctuations exceed the liquidity supply range, the liquidity provided by users will not be available for trading, and they will not receive $BGT and trading fees. Therefore, continuous management of liquidity range is necessary to sustain rewards.
To address this, Kodiak has added the function of Kodiak Islands' insurance pool, which automatically adjusts the liquidity coverage range based on market conditions. This solves the issue of liquidity providers having to constantly manage the liquidity coverage range and addresses the problem of idle liquidity due to deviations in concentrated liquidity coverage range, ensuring ample trading liquidity for Berachain. During the process of automatically adjusting the liquidity coverage range, Kodiak also establishes a complementary relationship with native dApps.
Currently, Kodiak is running a validator node on the bArtio testnet, so it is also likely to be synchronized with the validation mechanism. The future development of this protocol remains to be seen.
4.2.2. Infrared
Infrared is a liquidity staking protocol in the Berachain ecosystem, allowing users to delegate liquidity to the protocol's Vault, which then delegates the liquidity to self-operated validator nodes, generating $BGT liquidity tokens $iBGT and governance tokens $IRED for users.
$iBGT: Token that liquidizes $BGT. Users can use $iBGT in other DeFi protocols to earn additional income.
$IRED: Governance token of Infrared, with the power to decide the $BGT voting rights of Infrared validators and receive income generated by Infrared.
Infrared ensures two functions for providing users with $BGT: exchanging $BERA and voting rights, attracting a large amount of $BGT. As Infrared collects more $BGT in the Berachain ecosystem, the role of $IRED with $BGT voting rights becomes more important. Therefore, it can be expected that many protocols will design models that utilize $IRED as an alternative role to $BGT.
Kodiak is one such protocol and is currently collaborating with Infrared, planning to offer a Kodiak Vault within Infrared, providing an opportunity for Kodiak's liquidity providers to mine $IRED.
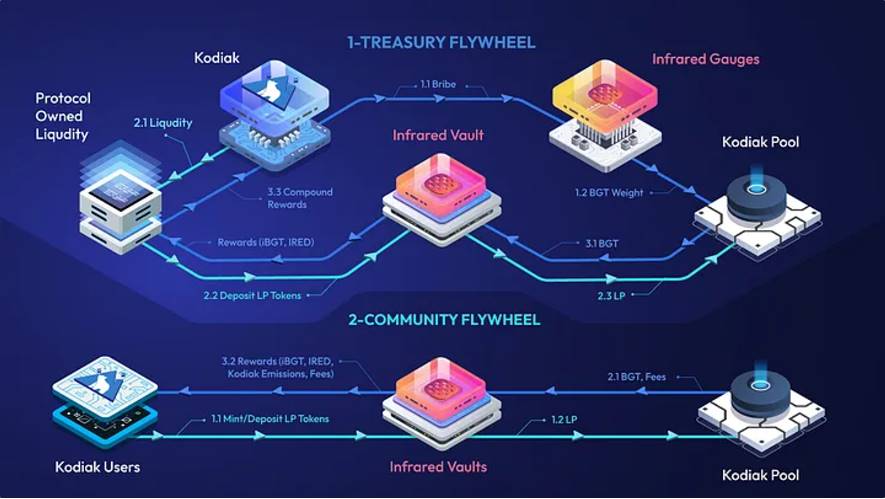
Infrared X Kodiak Flywheel, Source: Kodiak Blog
Other DeFi protocols, such as Gummi and BeraBorrow, will also allow $iBGT as collateral. This indicates that projects have already begun to create a new ecosystem centered around Infrared.
In addition to $BGT liquidity staking, Infrared recently introduced $BERA liquidity staking, aiming to become a comprehensive protocol for liquidity staking in the Berachain ecosystem.
4.3 Community Utilization of PoL
DeFi protocols on Berachain are attempting to solve internal liquidity wars through incentive-based digital quantification and provide convenience and improved capital efficiency for users.
We can also observe that some participants in the PoL ecosystem first establish a community through NFTs and memes, using community activities to build reputation and visibility before turning the established reputation into a window for generating income.
Although this method is more qualitative and may be less efficient in terms of incentives compared to the methods of DeFi protocols, the emergence and combination of derivative protocols in the DeFi ecosystem may hinder new users from entering Berachain. Therefore, the demand for solving liquidity wars through this more qualitative approach is expected to continue to increase in the future.
Furthermore, considering that Berachain originated from an NFT project and has a highly revered community, this approach may also be a more "Berachain" strategy.
4.3.1. The Honey Jar
Honey Jar is a community that developed around the NFT called Honeycomb in 2022, with the core concept of establishing a community-driven flywheel to connect entities and create "Sticky Liquidity."
Similar to the development of Berachain, the Honey Jar community continues to expand by issuing and airdropping a series of derivative NFTs to its holders. As the community grows, Honey Jar begins to collaborate with various projects developed on Berachain, providing various benefits from these projects to NFT holders.
In recent years, Honey Jar has also produced various educational materials about Berachain and provided services for new users in the Berachain ecosystem, such as the testnet Faucet. Additionally, they have incubated the community-based rating service project S&P (Standard & Paws) and Bera Infinity for pricing and rewarding contributions to the Berachain ecosystem, demonstrating that Honey Jar is not just a community but also an entrepreneurial studio for the Berachain ecosystem.
Honey Jar also operates a validator node in the Berachain ecosystem. Due to the strong influence of Honey Jar in the Berachain community through various activities and services, as of July 2023, Honey Jar has become the validator node with the most authorized $BGT.
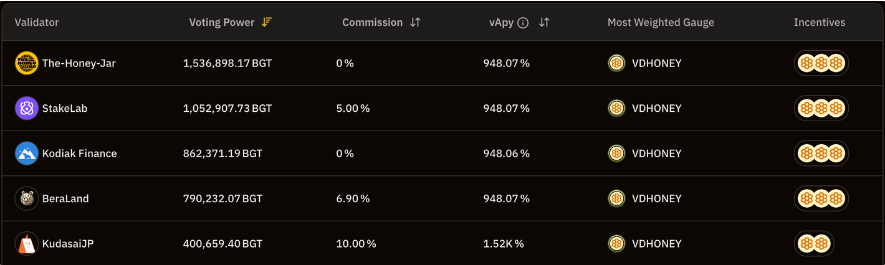
Ranking of authorized $BGT validator nodes, Source: BGT Station
Recently, Honey Jar has been preparing for the liquidity war after the launch of the Berachain mainnet, negotiating rewards and liquidity partnerships with protocols to be launched on Berachain. They have also established a DAO, expected to distribute rewards to Honeycomb NFT holders.
5. Conclusion
Starting from an NFT project, Berachain has built a loyal community and tightly linked the interests of validators, liquidity providers, and protocols through the introduction of the PoL consensus mechanism.
Furthermore, we can see many DeFi protocols building new models through the Berachain consensus mechanism, while community-based projects are striving to establish themselves in the ecosystem in their own way.
Although the goal of the PoL consensus mechanism around Berachain is to establish an ecosystem flywheel, this flywheel may also be a vicious cycle. To ensure the sustainability of Berachain, the following challenges exist:
$BGT inflation: With the continuous inflation of $BGT, the demand for liquidity created for $BGT from external ecosystems is limited. In the long run, the consumption of $BERA must increase, but due to the PoL structure's focus on liquidity, it may be difficult to increase actual network usage.
Possibility of centralization: As the ecosystem matures, it is possible that strong cartels may form around certain validators, protocols, and liquidity whales. If the ecosystem only develops around these cartels, it may be difficult for new protocols to enter the Berachain ecosystem, thereby dampening the enthusiasm of new users.
To address these issues, protocols that can attract new users and drive active trading must emerge, and ecosystem participants must reach a consensus to ensure that protocols that have a positive impact on the ecosystem receive sufficient liquidity support.
Berachain attempts to integrate liquidity and security into the incentive mechanism, and the success of this attempt will have a significant impact on the entire blockchain industry. As it is still in the testnet stage, how to address these challenges in the future will be an interesting topic.
Disclaimer: The content of this report reflects the views of the respective authors and is for reference only. It does not constitute advice to buy or sell tokens or use protocols. Any content in this report does not constitute investment advice and should not be understood as investment advice.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




